NAME
v.random - Generates random 2D/3D vector points.KEYWORDS
vector, sampling, statistics, random, point pattern, stratified random sampling, level1SYNOPSIS
Flags:
- -z
- Create 3D output
- -a
- Generate n points for each individual area (requires restrict parameter)
- -b
- Do not build topology
- Advantageous when handling a large number of points
- --overwrite
- Allow output files to overwrite existing files
- --help
- Print usage summary
- --verbose
- Verbose module output
- --quiet
- Quiet module output
- --ui
- Force launching GUI dialog
Parameters:
- output=name [required]
- Name for output vector map
- npoints=integer [required]
- Number of points to be created
- restrict=name
- Name of input vector map
- Restrict points to areas in input vector
- layer=string
- Layer number or name ('-1' for all layers)
- A single vector map can be connected to multiple database tables. This number determines which table to use. When used with direct OGR access this is the layer name.
- Default: -1
- cats=range
- Category values
- Example: 1,3,7-9,13
- where=sql_query
- WHERE conditions of SQL statement without 'where' keyword
- Example: income < 1000 and population >= 10000
- zmin=float
- Minimum z height (needs -z flag or column name)
- Default: 0.0
- zmax=float
- Maximum z height (needs -z flag or column name)
- Default: 0.0
- seed=integer
- The seed to initialize the random generator. If not set the process ID is used
- column=name
- Name of column for z values
- Writes z values to column
- column_type=string
- Type of column for z values
- Options: integer, double precision
- Default: double precision
Table of contents
- DESCRIPTION
- NOTES
- EXAMPLES
- Generating random points in 2D
- Generating random points in 2D with binary attributes
- Generating random points in 3D
- Generating random points in selected areas
- Generating random adjacent areas
- Random sampling from raster map
- Random sampling from vector map
- Stratified random sampling: Random sampling from vector map by attribute
- Stratified random sampling: Random sampling from vector map with spatial constraints
- SEE ALSO
- AUTHOR
DESCRIPTION
v.random randomly generates vector points within the current region using the selected random number generator.v.random can generate also 3D vector points or write random value to the attribute table. Point height range or attribute value range is controlled by specifying zmin and zmax options. Both z values are included in range (zmin <= z <= zmax). Generated random attribute value type can be controlled by column_type. Use integer column type for integers and double precision for floating point numbers. Integer values are calculated by rounding random floating point number.
To produce repeatable results a random seed can be set using the option seed.
Restriction to vector areas
If an restrict vector map with areas is specified, the location of random points is restricted to the selected areas. By default, the requested number of points are distributed across all areas.If the -a flag is given, the requested number of points is generated for each individual area. For example, if 20 points should be generated and the input map has 100 individual areas, 2000 points will be generated in total.
Attributes attached to restrict vector map are also transferred if the layer parameter is defined > 0, see example below.
NOTES
Importantly, attributes will only be transferred if layer > 0 (e.g.,layer=1).
EXAMPLES
All examples are based on the North Carolina sample dataset.Generating random points in 2D
Generate 20 random points with binary attributes (only 0 or 1):v.random output=binary_random npoints=20 zmin=0 zmax=1 column='binary' v.db.select binary_random cat|binary 1|0.63495 2|0.233421 3|0.489302 4|0.748264 5|0.505556 6|0.32975 [...] v.univar -d binary_random Calculating geometric distances between 20 primitives... [...] minimum: 148.515 maximum: 16572.8 [...]
Generating random points in 2D with binary attributes
Generate 20 random points with binary attributes (only 0 or 1):v.random output=binary_random npoints=20 zmin=0 zmax=1 column='binary' column_type=integer v.db.select binary_random cat|binary 1|0 2|0 3|0 4|0 5|1 6|0 [...]
Generating random points in 3D
Generate 20 random 3D points using a specific random seed:v.random seed=52 output=height_random npoints=40 zmin=110 zmax=170 -z v.univar -d height_random Calculating geometric distances between 40 primitives... [...] minimum: 334.889 maximum: 18351.9 range: 18017 sum: 5.38425e+06 mean: 7266.2 mean of absolute values: 7266.2 population standard deviation: 3563.95 [...] skewness: 0.34703
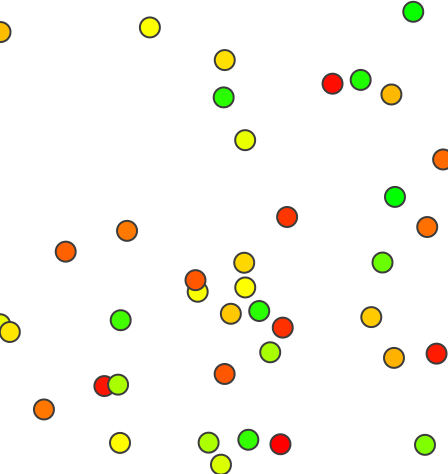
Random points with different X, Y, and Z coordinates
Generating random points in selected areas
Generate 3 random points only in selected areas ("RALEIGH" related ZIP code areas):v.random restrict=zipcodes_wake output=zipcodes_local_random_n3 npoints=3 where="ZIPNAME = 'RALEIGH'" -a # visualization d.mon wx0 d.vect zipcodes_wake d.vect zipcodes_wake fcolor=yellow where="ZIPNAME = 'RALEIGH'" d.vect zipcodes_local_random_n3 color=red icon=basic/circle
Generating random adjacent areas
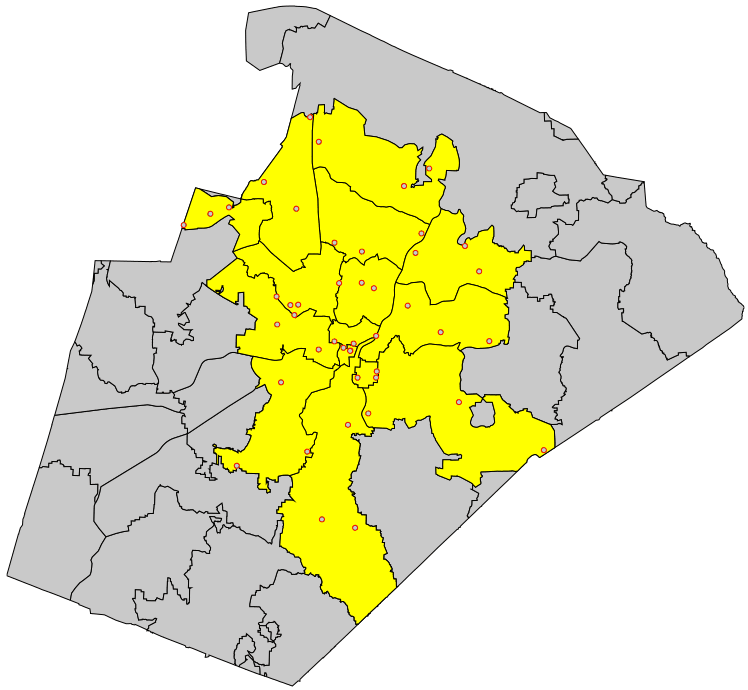
To generate random adjacent areas, first the centroids are generated as points, then a triangulation is run (North Carolina sample dataset:g.region vector=nc_state v.random output=randpoints6k npoints=6000 v.voronoi input=randpoints6k output=randareas6k v.info -t randareas6k v.category randareas6k option=print # plot vector areas d.mon wx0 d.vect randareas6k -c
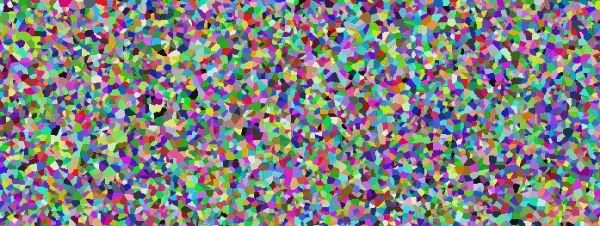
Random adjacent areas from random points (here: used as centroids)
To eventually obtain isolated areas, selected areas can be extracted with v.extract.
These vector areas can also be rasterized:
# rasterize areas # note: rastermaps must result in at least 6k pixel in this example g.region vector=nc_state res=500 -p -a v.to.rast randareas6k out=randareas6k use=cat r.colors randareas6k color=random d.rast randareas6k
Random sampling from raster map
Generate 20 random samples from a raster map:g.region -p raster=elevation v.random output=random_samples npoints=20 v.db.addtable map=random_samples columns='cat INTEGER, sample DOUBLE PRECISION' v.what.rast map=random_samples raster=elevation column=sample v.db.select random_samples cat|sample 1|103.9935 2|129.1266 3|96.01388 [...]
Random sampling from vector map
Generate 20 random points and sample attribute data from geology (vector) map:g.region -p vector=geology v.random output=random_samples npoints=20 v.db.addtable map=random_samples columns='cat integer, geology varchar(100)' v.what.vect map=random_samples column=geology query_map=geology query_layer=1 query_column=GEO_NAME v.db.select random_samples cat|geology 1|PzZm 2| 3|Zatm [...]
Stratified random sampling: Random sampling from vector map by attribute
Generate 20 random points restricted to forested areas:g.region -p raster=landclass96 r.to.vect -v input=landclass96 output=landclass96 type=area v.random restrict=landclass96 output=random_samples npoints=20 where="label = 'forest'" layer=1 v.db.select map=random_samples cat|landclass96_cat|landclass96_label 1|5|forest 2|5|forest 3|5|forest ...
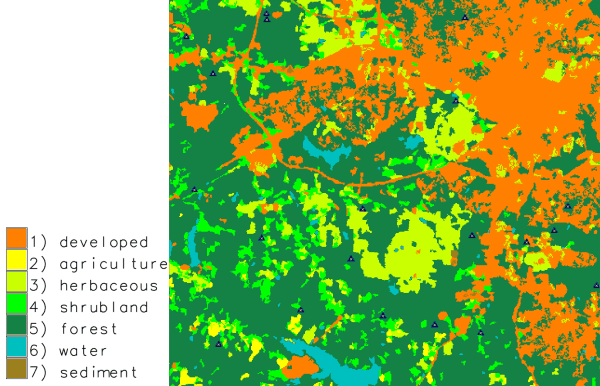
Random points only sampled in forested areas (stratified random sampling)
Stratified random sampling: Random sampling from vector map with spatial constraints
Generating n points for each individual area: in this example two random points in each water body:g.region -p raster=landclass96 r.to.vect -v input=landclass96 output=landclass96 type=area v.random restrict=landclass96 output=random_samples npoints=2 where="label = 'water'" layer=1 -a
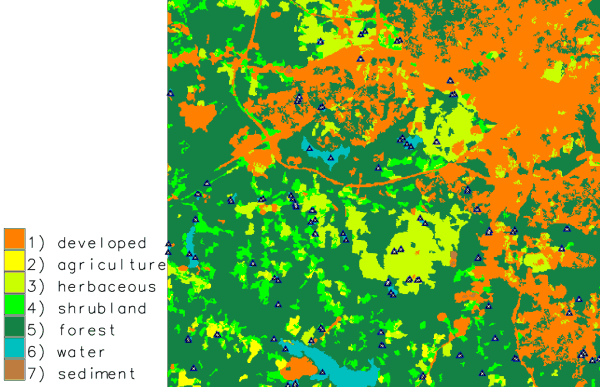
Two random points sampled in each individual water body (stratified random sampling)
SEE ALSO
g.region, r.random, v.db.addtable, v.perturb, v.sample, v.univar, v.what.rast, v.what.vectAUTHOR
James Darrell McCauley <darrell@mccauley-usa.com>,when he was at: Agricultural Engineering Purdue University
SOURCE CODE
Available at: v.random source code (history)
Latest change: Tuesday Dec 17 20:17:20 2024 in commit: d962e90c026708a4815ea2b9f46c0e84c17de22d
Main index | Vector index | Topics index | Keywords index | Graphical index | Full index
© 2003-2025 GRASS Development Team, GRASS GIS 8.4.3dev Reference Manual