
NAME
v.hull - Uses a GRASS vector points map to produce a convex hull vector map.
KEYWORDS
vector, geometry
SYNOPSIS
v.hull
v.hull help
v.hull [-af] input=name output=name [--overwrite] [--verbose] [--quiet]
Flags:
- -a
- Use all vector points (do not limit to current region)
- -f
- Create a 'flat' 2D hull even if the input is 3D points
- --overwrite
- Allow output files to overwrite existing files
- --verbose
- Verbose module output
- --quiet
- Quiet module output
Parameters:
- input=name
- Name of input vector points map
- output=name
- Name of output vector area map
DESCRIPTION
v.hull computes the convex hull of a vector points map and outputs the
convex hull polygon as a vector area map. The convex hull, or convex envelope,
for an object or a set of objects is the minimal convex set containing the
given objects. This module creates a vector polygon containing all vector
points of the input map.
In the case of 3D input points, the hull will be a 3D hull as well, unless the
user specifies the -f flag. The 3D hull will be composed of triangular
faces.
Example of v.hull output:
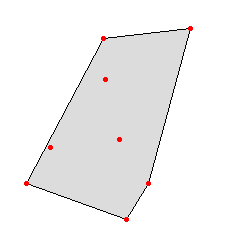
|
Convex hull polygon created with v.hull
|
EXAMPLE
Example of v.hull 3D output (using two random 3D point clouds):
g.region rural_1m -p
r.mapcalc zero=0
v.random -z out=random3d_a n=10 zmin=0 zmax=200
v.random -z out=random3d_b n=15 zmin=400 zmax=600
v.hull random3d_a out=random3d_a_hull
v.hull random3d_b out=random3d_b_hull
nviz zero vect=random3d_a_hull,random3d_b_hull
REFERENCES
M. de Berg, M. van Kreveld, M. Overmars, O. Schwarzkopf, (2000).
Computational geometry, chapter 1.1, 2-8.
J. O'Rourke, (1998).
Computational Geometry in C (Second Edition), chapter 4.
SEE ALSO
v.delaunay
AUTHOR
Andrea Aime, Modena, Italy
Markus Neteler, ITC-irst (update to 5.7)
Benjamin Ducke, CAU Kiel (3D hull support)
Last changed: $Date: 2008-01-28 05:40:03 -0800 (Mon, 28 Jan 2008) $
Main index - vector index - Full index
© 2003-2008 GRASS Development Team


