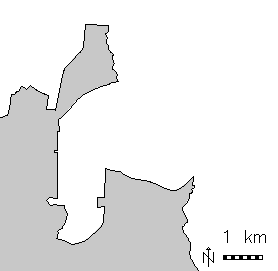
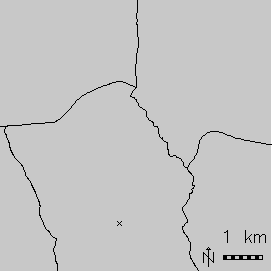
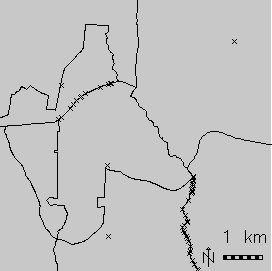
v.overlay: Polygon union (right) of urban area (left) and Census 2000 (middle) areas (North Carolina dataset)
Note: This document is for an older version of GRASS GIS that is outdated. You should upgrade, and read the current manual page.

If areas in ainput are overlaid with areas in binput, it is sometimes necessary to snap areas of binput to those of ainput, otherwise areas can go missing or many sliver areas can be created. Snapping is enabled by default and can be disabled by setting the snap option to a negative value. Recommended values are between 0.00000001 and 0.0001. Using larger values for snapping can have undesired side-effects, but may sometimes be necessary to get a clean output (see example below). In general, it is recommended to start with a small snapping threshold, gradually increasing the threshold until the result is reasonably clean. Snapping modifies only boundaries in binput, which are snapped to boundaries in ainput. Boundaries in ainput are not modified.
If the first number of the olayer option is > 0, then the resulting output map has a merged attribute table in the given layer number. The original column names have a prefix (a_ and b_) corresponding to ainput and binput map.
If the second number of the olayer option is > 0, then the categories of ainput in layer alayer are transferred to the output layer with the second number.
If the third number of the olayer option is > 0, then the categories of binput in layer blayer are transferred to the output layer with the third number.
If the first number of the olayer option is > 0, then attributes of the tables from ainput and binput are joined into a new table linked to the output map with a new cat column.
If the second number of the olayer option is > 0, then the attribute table of ainput is copied to the output map.
If the third number of the olayer option is > 0, then the attribute table of binput is copied to the output map.
v.overlay ainput=lake binput=province output=lakeXprovince operator=or
# input maps d.vect urbanarea d.vect census_wake2000 # union v.overlay ain=census_wake2000 bin=urbanarea out=urban_census2000 operator=or # show result, graphically zooming a subset g.region n=230400 s=223800 w=655800 e=662400 d.erase d.vect urban_census2000 # show merged attribute table v.db.select urban_census2000 where="cat=108" -v cat|108 a_cat|98 a_AREA|231001264 a_PERIMETE|67804.305 a_TRACT_|98 a_TRACT_ID|98 a_RINGS_OK|1 a_RINGS_NO|0 a_ID|98 a_FIPSSTCO|37183 a_TRT2000|054108 a_STFID|37183054108 a_TRACTID|541.08 a_TRACT|541.08 b_cat|55 b_OBJECTID|55 b_UA|73261 b_NAME|Raleigh b_UA_TYPE|UA



As can be seen by the resulting large number of centroids on boundaries, the urban areas do not match exactly the Census 2000 areas. In this case a clean result can be obtained by snapping with a threshold of 0.1 m.
g.region vect=zipcodes_wake
# extract Raleigh city:
v.extract in=zipcodes_wake out=raleigh \
where="ZIPNAME = 'RALEIGH'"
# clip road network to city polygon:
v.overlay ainput=roadsmajor atype=line binput=raleigh \
out=roadsmajor_raleigh operator=and \
olayer=0,1,0
Last changed: $Date: 2014-03-16 09:58:34 -0700 (Sun, 16 Mar 2014) $
Main index - vector index - Full index
© 2003-2014 GRASS Development Team