
NAME
v.stream.order - Compute the stream order of stream networks stored in a vector map at specific outlet vector pointsKEYWORDS
vector, hydrology, stream network, stream orderSYNOPSIS
Flags:
- --overwrite
- Allow output files to overwrite existing files
- --help
- Print usage summary
- --verbose
- Verbose module output
- --quiet
- Quiet module output
- --ui
- Force launching GUI dialog
Parameters:
- input=name [required]
- Name of input vector map
- Name of the stream networks vector map
- points=name [required]
- Name of the input vector point map
- Name of the points vector map that defines the water outlets of the stream networks
- output=name [required]
- Name of the vector output map
- The name for the stream order vector output map
- threshold=float
- threshold in projection units used to search for outflow points at the stream network
- Default: 25
- order=string[,string,...]
- The stream order to compute
- Options: strahler, shreve, scheidegger, drwal
- Default: strahler,shreve
- columns=string[,string,...]
- The columns that should be copied from the input stream vector map. By default all will be copied.
- Default: all
- recursionlimit=integer
- The Python recursion limit that should be used (Python default is 1000)
- Default: 10000
Table of contents
DESCRIPTION
The module v.stream.order is designed to compute different stream order approaches based on a stream network vector map and a water outlet vector point map. It requires two inputs:- A vector line map with one or several independent stream networks
- A vector point map that defines the water outlet points in the stream network
The direction of the stream flow will be adjusted in outlet direction and stored in the
output vector map.
To determine the outlet stream network segment, a nearest neighbor search is performed.
The threshold of the search can be adjusted with the threshold option.
It is required to specify the threshold as floating point value
that is interpreted using the locations projection unit.
It is required that the vector line direction of the network segment that was found
at the outlet point, is directed to the outlet point. Since, the depth-first search
network traversing will be performed in upstream direction. Stream networks in
downstream direction will be detected. However, the stream order will not be computed.
The stream order table entries will be empty.
The output vector map contains a column for each specified order algorithm,
the network id, the outlet category of the vector point input map
and the column reversed. The column reversed indicates if the
stream network segment was reversed in direction to point to
the water outlet point (0 - not reversed, 1 - reversed).
In addition all columns from the stream network input map
are copied to the output vector map. The input vector map columns that
should be copied will be automagically renamed in the output vector map,
if the column names are conflicting with each other. Use the columns
parameter to specifiy a subset of columns that should be copied.
The keyword all is used to copy all columns to the output vector map
that are found in the input vector map (default).
Note
Be aware that the stream network map must be topological correct.
Each independent stream network must be properly connected.
The implemented stream order algorithms rely on topological relations between lines and nodes
and are not designed to handle loops and channels in the stream networks correctly.
The network traversing method, that is used to compute the stream order numbers,
is recursively implemented. In case of large stream networks, or networks
with many loops, the maximum recursion depth of Python may be reached.
The module will stop then with an maximum recursion depth exceeded exception.
This parameter can be adjusted with the recursionlimit option. The default in Python is 1000.
The default in v.stream.order is 10000.
Supported stream order algorithms
The following algorithm examples are based on this stream network. Be aware of the wrong stream directions that will be adjusted by v.stream.order.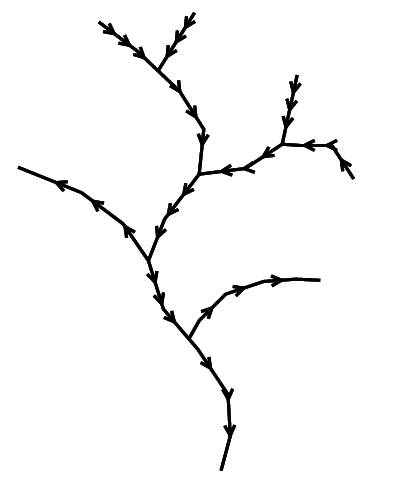
Strahler's stream order
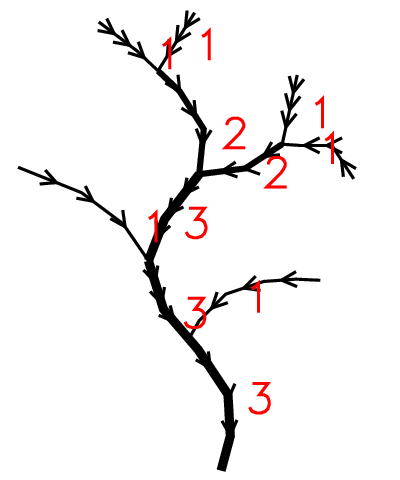
Strahler's stream order is a modification of Horton's streams order which fixes the ambiguity of Horton's ordering. In Strahler's ordering the main channel is not determined; instead the ordering is based on the hierarchy of tributaries. The ordering follows these rules:
- if the node has no children, its Strahler order is 1.
- if the node has one and only one tributuary with Strahler greatest order i, and all other tributaries have order less than i, then the order remains i.
- if the node has two or more tributaries with greatest order i, then the Strahler order of the node is i + 1.
Advantages and disadvantages of Strahler's ordering: Strahler's stream order has a good mathematical background. All catchments with streams in this context are directed graphs, oriented from the root towards the leaves. Equivalent definition of the Strahler number of a tree is that it is the height of the largest complete binary tree that can be homeomorphically embedded into the given tree; the Strahler number of a node in a tree is equivalent to the height of the largest complete binary tree that can be embedded below that node.
The disadvantage of that methods is the lack of distinguishing a main channel which may interfere with the analytical process in highly elongated catchments. It is not able to handle loops in the ordered graph correctly.
Shreve's stream magnitude
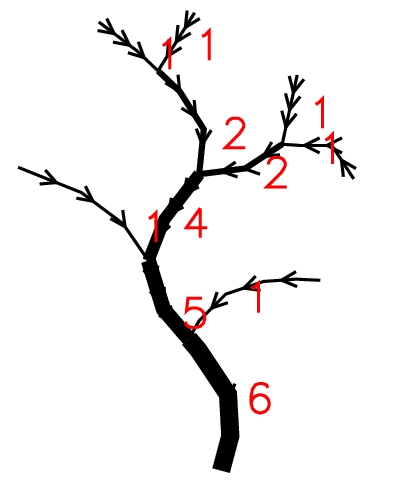
That ordering method is similar to Consisted Associated Integers proposed by Scheidegger. It assigns magnitude of 1 for every initial channel. The magnitude of the following channel is the sum of magnitudes of its tributaries. The number of a particular link is the number of initials which contribute to it.
Scheidegger's stream magnitude
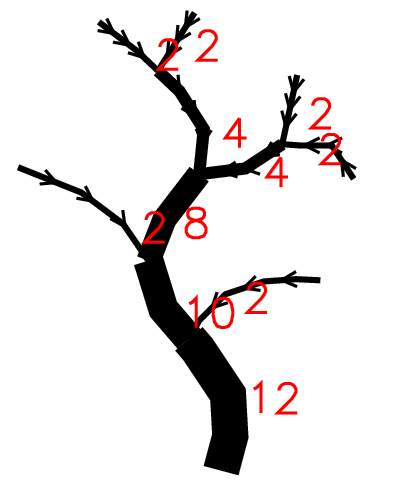
That ordering method is similar to Shreve's stream magnitude. It assigns magnitude of 2 for every initial channel. The magnitude of the following channel is the sum of magnitudes of its tributaries. The number of a particular link is the number of streams -1 contributing to it.
Drwal's stream hierarchy
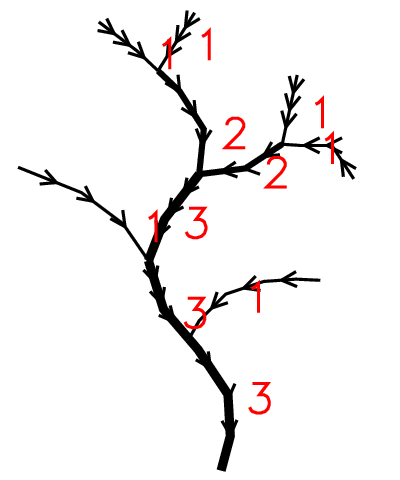
That ordering method is a compromise between Strahler ordering and Shreve magnitude. It assigns order of 1 for every initial channel. The order of the following channel is calculated according Strahler formula, except, that streams which do not increase order of next channel are not lost. To increase next channel to the higher order R+1 are require two channels of order R, or one R and two R-1 or one R, and four R-2 or one R, one R-1 and two R-2 etc. The the order of particular link show the possible value of Strahler'order if the network was close to idealized binary tree. Drwal's order is computed based on Shreve's magnitude with the formula: floor(log(shreve,2))+1.
Advantages and disadvantages of Drwal's hierarhy: The main advantages of Drwal's hierarchy is that it produces natural stream ordering with whcich takes into advantage both ordering and magnitude. It shows the real impact of particular links of the network run-off. The main disadvantage is that it minimize bifurcation ratio of the network.
Examples
Stream order computation based on North Carolina location
# We need to generate 4 outlet points that will lead to
# 4 stream networks and therefore 4 output vector maps
cat > points.csv << EOF
640781.56098|214897.033189
642228.347134|214979.370612
638470.926725|214984.99142
645247.580918|223346.644849
EOF
v.in.ascii output=streams_outlets input=points.csv x=1 y=2
v.stream.order input=streams@PERMANENT points=streams_outlets \
output=streams_order threshold=25 order=strahler,shreve
v.info streams_order
v.db.select streams_order | less
Stream order computation based on v.stream.order testsuite data
v.stream.order input=stream_network points=stream_network_outlets \
output=stream_network_order threshold=25 \
order=strahler,shreve,drwal,scheidegger
v.info stream_network_order
v.db.select stream_network_order | less
SEE ALSO
r.stream.orderREFERENCES
r.stream.orderDepth first search at Wikipedia
Strahler number at Wikipedia
AUTHOR
IGB-Berlin,Johannes Radinger; Implementation: Geoinformatikbüro Dassau GmbH , Soeren Gebbert
This tool was developed as part of the BiodivERsA-net project 'FISHCON' and has been funded by the German Federal Ministry for Education and Research (grant number 01LC1205).
Documentation of the implemented algorithms are in most parts copied from r.stream.order implemented by: Jarek Jasiewicz and Markus Metz
Last changed: $Date: 2016-05-06 17:04:06 +0200 (Fri, 06 May 2016) $
SOURCE CODE
Available at: v.stream.order source code (history)
Main index | Vector index | Topics index | Keywords index | Graphical index | Full index
© 2003-2018 GRASS Development Team, GRASS GIS 7.4.1svn Reference Manual