
NAME
d.vect.thematic2 - Displays thematic map created from vector features and numeric attributes.KEYWORDS
display, cartography, vector, thematic, legendSYNOPSIS
Flags:
- -g
- Save thematic map commands to group file for GIS Manager
- -l
- Create graphic legend in x11 display monitor
- -f
- Only draw fills (no outlines) for areas and points
- -s
- Output legend for GIS Manager (for scripting use only)
- -m
- Use math notation brackets in legend
- --help
- Print usage summary
- --verbose
- Verbose module output
- --quiet
- Quiet module output
- --ui
- Force launching GUI dialog
Parameters:
- map=name [required]
- Name of vector map
- Or data source for direct OGR access
- layer=string
- Layer number or name
- Vector features can have category values in different layers. This number determines which layer to use. When used with direct OGR access this is the layer name.
- Default: 1
- column=name [required]
- Name of attribute column to use for thematic display (must be numeric)
- type=string[,string,...]
- Input feature type
- Options: point, line, boundary, centroid, area
- Default: point,line,area
- where=sql_query
- WHERE conditions of SQL statement without 'where' keyword
- Example: income < 1000 and population >= 10000
- themetype=string [required]
- Type of thematic display
- Options: graduated_colors, graduated_points, graduated_lines
- Default: graduated_colors
- themecalc=string [required]
- Thematic divisions of data for display
- Options: interval, std_deviation, quartiles, custom_breaks
- Default: interval
- breakpoints=string
- Break points for custom breaks option
- Separate values by spaces (0 10 20 30 ...)
- icon=string
- Vector point icon for point data
- Options: basic/box, basic/circle, basic/cross2, basic/diamond, basic/star, basic/cross1, basic/x
- Default: basic/circle
- size=float
- Icon size for point data
- Minimum icon size/line width for graduated points/lines)
- Default: 5
- maxsize=float
- Maximum icon size/line width for graduated points and lines
- Default: 20
- nint=integer
- Number of classes for interval theme (integer)
- Default: 4
- colorscheme=string [required]
- Color scheme for graduated color mapping
- Select 'single_color' for graduated point/line display
- Options: blue-red, red-blue, green-red, red-green, blue-green, green-blue, cyan-yellow, yellow-cyan, custom_gradient, single_color
- Default: blue-red
- point_color=string
- Color for graduated points map
- GRASS named color or R:G:B triplet. Set color scheme to single color
- Default: 255:0:0
- line_color=string
- Color for graduated lines or point/area outlines
- GRASS named color or R:G:B triplet. Set color scheme to single color.
- Default: 0:0:0
- start_color=string
- Beginning color for custom color gradient
- Must be expressed as R:G:B triplet
- Default: 255:0:0
- end_color=string
- Ending color for custom color gradient
- Must be expressed as R:G:B triplet
- Default: 0:0:255
- monitor=string
- Select WXGUI display monitor for legend
- Options: wx0, wx1, wx2, wx3, wx4, wx5, wx6, none
- Default: wx1
- psmap=string
- Root for the name of psmap instruction files to be in current directory
- If not set, no psmap instruction files will be created)
- group=name
- Name of group file where thematic map commands will be saved
- rgb_column=name
- Name of color column to populate RGB values
Table of contents
DESCRIPTION
d.vect.thematic2 creates thematic maps from vector features of all types and numeric attributes stored in the attribute table connected to a vector map.Thematic maps can be displayed by either a graduated color scheme (for all vector types), as graduated icon sizes (for point and centroid types), or graduated line widths (for lines and boundaries with associated attributes), see themetype option for details. The user selects the vector map to be mapped and attribute column from which to derive mapping intervals, and (optionally) the layer for attribute data.
In thematic maps, the color or point size changes for each range of attribute values. Value ranges for thematic mapping can be set at regular intervals, standard deviation units on either side of the mean, quartiles, or delimited by user-defined breakpoints, see themecalc option. User-defined breakpoints (themecalc=custom_breaks) can be entered via breakpoints option.
NOTES
There is option colorscheme to define the color scheme (graduated colors) and range of point sizes (graduated points) for thematic maps.
Optionally, a simple text legend is printed when -l flag is given. A graphic legend can be drawn in the selected display monitor.
Thematic colors can be uploaded by rgb_column option to a specified attribute column (which is created automatically if doesn't exist in the table) for later display via d.vect and rgb_column option.
When the psmap option is set to 'name', two psmap instruction files are created (in the current directory if no path is given), one for the map ('name.psmap') and one for the legend ('name_legend.psmap'). The map file also contains 'label' commands which allow to create a legend directly in the map by adding a 'vlegend' command. See the ps.map manual page for more details.
The algorithm currently uses the v.univar to calculate basic descriptive statistics needed for thematic mapping (minimum, maximum, mean, standard deviation, and quartiles).
EXAMPLES
Earthquake points with color gradient:d.vect.thematic2 -l recent_earthquakes column=magnitude type=point
Earthquake points with different sizes:
d.vect.thematic2 -l recent_earthquakes column=magnitude type=point \
themetype=graduated_points maxsize=15
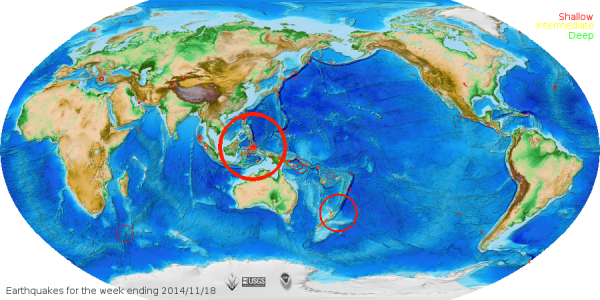
Example for earthquake map rendering (script code)
North Carolina: differences between 'elevation' (10m) and 'elev_state_500m':
# random sampling of elevation points: g.region raster=elevation -p v.random random npoints=200 v.db.addtable random column="el10 double precision" # transfer elevations to attribute table of random points map: v.what.rast random rast=elevation column=el10 v.db.select random # comparative sampling of second map, incl. differences: v.sample input=random column=el10 raster=elev_state_500m output=elev_sample v.db.select elev_sample # univariate statistics: v.univar -e elev_sample column=diff type=point # thematic map: d.mon wx0 d.vect.thematic2 -l elev_sample column=diff type=point
North Carolina sample dataset example:
g.region vector=nc_state d.vect.thematic2 -l precip_30ynormals column=annual type=point
SEE ALSO
d.vect, d.vect.chart, v.univarAUTHORS
Michael Barton, Arizona State University
Various updates by:
Daniel Cavelo Aros,
Martin Landa,
Jachym Cepicky.
Last changed: $Date: 2008-08-15 08:16:42 +0200 (Fri, 15 Aug 2008)$
SOURCE CODE
Available at: d.vect.thematic2 source code (history)
Main index | Display index | Topics index | Keywords index | Graphical index | Full index
© 2003-2019 GRASS Development Team, GRASS GIS 7.4.5svn Reference Manual