
NAME
r.in.pdal - Creates a raster map from LAS LiDAR points using univariate statistics and r.in.xyz.KEYWORDS
raster, import, LIDAR, statistics, conversionSYNOPSIS
Flags:
- -s
- Scan data file for extent then exit
- -g
- In scan mode, print using shell script style
- --overwrite
- Allow output files to overwrite existing files
- --help
- Print usage summary
- --verbose
- Verbose module output
- --quiet
- Quiet module output
- --ui
- Force launching GUI dialog
Parameters:
- input=name [required]
- LAS input file
- output=name [required]
- Name for output raster map
- resolution=float
- 2D grid resolution (north-south and east-west)
- Default: 1.0
- raster_reference=string
- Raster map to be used as pixel geometry reference
- Raster map to align to, e.g. an orthophoto of the same region
- raster_file=string
- External raster map to be used as pixel geometry reference
- External raster map to align to, e.g. an orthophoto of the same region
- method=string
- Statistic to use for raster values
- Options: n, min, max, range, sum, mean, stddev, variance, coeff_var, median, percentile, skewness, trimmean
- Default: mean
- n: Number of points in cell
- min: Minimum value of point values in cell
- max: Maximum value of point values in cell
- range: Range of point values in cell
- sum: Sum of point values in cell
- mean: Mean (average) value of point values in cell
- stddev: Standard deviation of point values in cell
- variance: Variance of point values in cell
- coeff_var: Coefficient of variance of point values in cell
- median: Median value of point values in cell
- percentile: Pth (nth) percentile of point values in cell
- skewness: Skewness of point values in cell
- zrange=min,max
- Filter range for z data (min,max)
- zscale=float
- Scale to apply to z data
- Default: 1.0
- type=string
- Type of raster map to be created / Storage type for resultant raster map
- Options: CELL, FCELL, DCELL
- Default: FCELL
- CELL: Integer
- FCELL: Single precision floating point
- DCELL: Double precision floating point
- percent=integer
- Percent of map to keep in memory
- Options: 1-100
- Default: 100
- pth=integer
- Pth percentile of the values
- Options: 1-100
- trim=float
- Discard <trim> percent of the smallest and <trim> percent of the largest observations
- Options: 1-50
- footprint=string
- Footprint of the data as vector map
Table of contents
DESCRIPTION
r.in.pdal creates a raster map from LAS LiDAR points using the Point Data Abstraction Library (PDAL) by binning the points into a raster map using univariate statistics. The user may choose from a variety of statistical methods which will be used for binning when creating the new raster map.The computational region of a LiDAR point file can be determined by scanning the file using the -s flag.
Optionally r.in.pdal creates an estimated vector footprint area map of the LAS file when using the footprint parameter (the footprint is generated by PDAL).
Since a new raster map is created during the binning, the binning of points depends on the computational region settings (extent and resolution) which is by default set to the extent of the LiDAR input file (see more about binning below). The resulting raster resolution can be specified with the parameter resolution.
r.in.pdal is designed for processing massive point cloud datasets, for example raw LiDAR or sidescan sonar swath data. It has been tested with large datasets.
For details concerning raster binning see the manual page of r.in.lidar.
NOTES
r.in.pdal uses g.region to set the extent and resolution of the resulting raster and internally r.in.xyz to import the LiDAR points.EXAMPLES
Import of a LAS file using PDAL into a mapset in the sample NC SPM location. The sample LAS file is available here.
# check metadata
pdal info --summary lidar_raleigh_nc_spm_height_feet.las
# scan extent and exit
r.in.pdal input=lidar_raleigh_nc_spm_height_feet.las output=lidar_raleigh -s
# scan extent (g.region style) and exit
r.in.pdal input=lidar_raleigh_nc_spm_height_feet.las output=lidar_raleigh -s -g
# import while aligning pixel geometry to existing "elevation" 10m res. raster map
# specifying EPSG manually because SRS information is missing in this LAS file
r.in.pdal input=lidar_raleigh_nc_spm_height_feet.las raster_reference=elevation \
resolution=10 output=lidar_raleigh method=mean proj_in=EPSG:3358
# optionally: footprint=lidar_raleigh_footprint
# visualize
d.mon wx0
g.list vector
d.rast lidar_raleigh
d.vect streets_wake
# analyse differences between DEM and rasterized point cloud
# LAS files come with height in US feet units
r.mapcalc "diff = elevation - lidar_raleigh * 0.3048006096012192"
r.univar -e diff
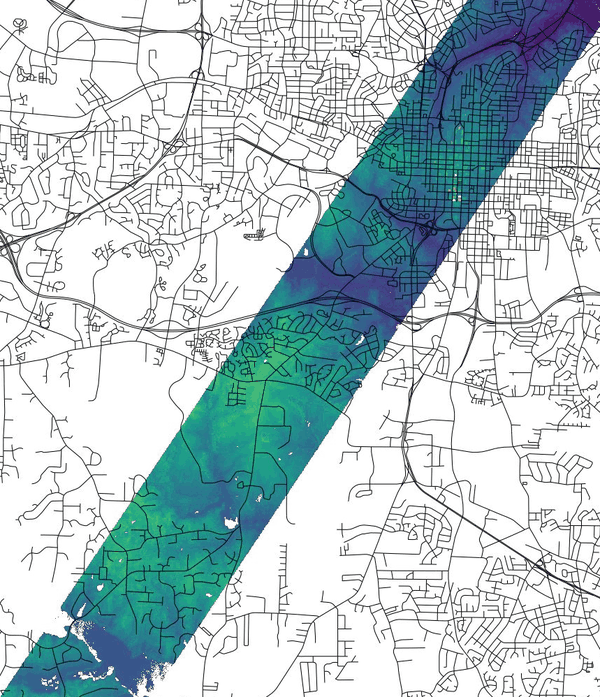
Figure: View showing the difference of the elevation map and LiDAR point data binned to raster map with r.in.pdal
SEE ALSO
r.in.xyz, r.in.lidar, v.in.lidarAUTHORS
Anika Bettge, mundialis GmbH & Co. KGVaclav Petras, NCSU GeoForAll Lab (projection, computational region)
Documentation: Markus Neteler, mundialis GmbH & Co. KG
Last changed: $Date: 2018-08-09 04:48:49 +0200 (Thu, 09 Aug 2018) $
SOURCE CODE
Available at: r.in.pdal source code (history)
Main index | Raster index | Topics index | Keywords index | Graphical index | Full index
© 2003-2019 GRASS Development Team, GRASS GIS 7.4.5svn Reference Manual
