
NAME
i.cva - Performs Change Vector Analysis (CVA) in two dimensions.KEYWORDS
imagery, transformation, CVA, change vector analysisSYNOPSIS
Flags:
- --overwrite
- Allow output files to overwrite existing files
- --help
- Print usage summary
- --verbose
- Verbose module output
- --quiet
- Quiet module output
- --ui
- Force launching GUI dialog
Parameters:
- xaraster=name [required]
- Name of the first raster for X axis
- xbraster=name [required]
- Name of the the second raster for X axis
- yaraster=name [required]
- Name of the first raster for Y axis
- ybraster=name [required]
- Name of the second raster for Y axis
- output=basename [required]
- Name for output basename raster maps (angle and magnitude)
- Name for output basename raster map(s)
- custom_threshold=float
- Use a custom threshold
- stat_threshold=float
- Use a statystical parameter for the threshold (mean + N * standard deviation)
Table of contents
DESCRIPTION
i.cva calculates Change Vector Analysis (CVA) for two input variables. CVA is a remote sensing technique used for change detection analysis. As input for CVA, two maps for each date must be given: in general, on X axis an indicator of overall reflectance and on Y axis an indicator of vegetation conditions. A common choice for the indicators is Albedo and NDVI (Normalized Difference Vegetation Index) or the Brightness and Greenness features features of the Tasselled Cap (TC) transform.For each pixel of the original image, CVA gives in output a map of the angle and a map of the magnitude of the vector of the change between two dates.
Read Malila et al. for a complete explanation of the technique. This module might require a first transformation of the data to Top Of Atmosphere Reflectance (TOAR); if the TC transform are chosen as indicators, the TC transform should be then performed as well before running CVA.
Four parameters are required in input:
- xaraster: first date map for X axis,
- xbraster: second date map for X axis,
- yaraster: first date map for Y axis,
- ybraster: second date map for Y axis.
The following maps can be generated in output:
- basename_angle: map of the angles of the change vector between the two dates;
- basename_angle_class: map of the angles, classified by the four quadrants (0-90, 90-180, ...);
- basename_magnitude: map of the magnitudes of the change vector between the two dates;
- basename_change: final map of the change
The change detection map is created using the classified angle map and applying
a threshold to the magnitude: the change is given by the pixels that have
values higher than the threshold, divided in four categories depending on
the quadrant they belong to.
The threshold can be chosen manually (custom value, given by personal
criteria) or using statistical criteria. In this case the mean of the magnitude
values is used and the user can choose the multiples of N standard
deviation to sum to the mean (threshold = mean + N * standard deviation).
One could consider of running the module at first without assigning a
threshold, in order to have an idea of the range of the magnitude and to
choose an appropriate custom threshold (for univariate statistical parameters
run r.univar). In this case i.cva gives
in output only three maps: the angle, angle classified and magnitude maps.
EXAMPLE
Calculation of CVA maps from North Carolina Landsat 5 TM and 7 ETM scenes, using lsat5_1987 and lsat7_2002.The Tasselled cap maps are calculated for TOAR data.
# compute tasscap of 1987 scene
g.region raster=lsat5_1987_10 -p
i.tasscap sensor=landsat5_tm \
input=lsat5_1987_10,lsat5_1987_20,lsat5_1987_30,lsat5_1987_40,lsat5_1987_50,lsat5_1987_70 \
output=lsat5_1987_tasscap
# compute tasscap of 2002 scene
g.region raster=lsat7_2002_10 -p
i.tasscap sensor=landsat7_etm \
input=lsat7_2002_10,lsat7_2002_20,lsat7_2002_30,lsat7_2002_40,lsat7_2002_50,lsat7_2002_70 \
output=lsat7_2002_tasscap
# compute CVA
i.cva xaraster=lsat5_1987_tasscap.1 xbraster=lsat7_2002_tasscap.1 \
yaraster=lsat5_1987_tasscap.2 ybraster=lsat7_2002_tasscap.2 \
output=CVA_87_02 stat_threshold=1
Calculating DeltaX and DeltaY
Writing angle map CVA_87_02_angle
Writing magnitude map CVA_87_02_magnitude
Mean of magnitude values is: 0.091335330260002
Standard deviation of magnitude values is: 0.0671211630131731
Writing change detection map CVA_87_02_change
Threshold is 0.158456493273
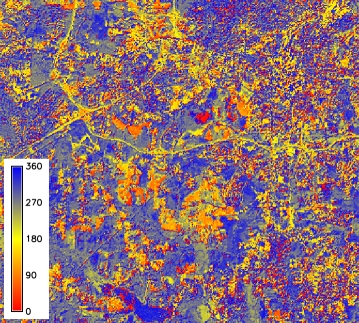
CVA angle map 1 |
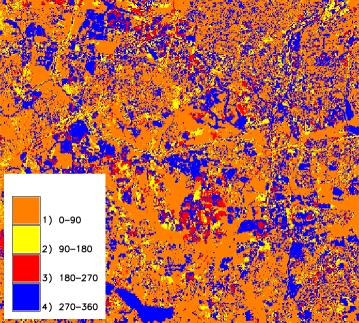
CVA classified angle map |
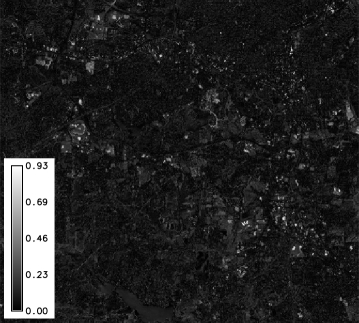
CVA magnitude map |
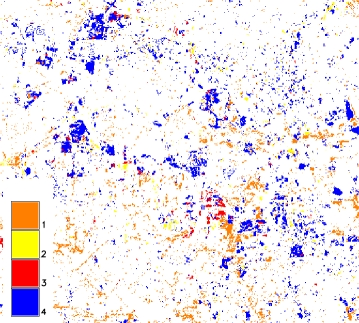
CVA change map |
Optionally, labels can be added to the four quadrants of the change map (after Zanchetta et al., 2016):
# assign legend cat i_cva_legend_rules.csv 1:moisture reduction 2:chlorophyll increase 3:moisture increase 4:bare soil increase r.category map=CVA_87_02_change separator=":" rules=i_cva_legend_rules.csv # assign colors cat i_cva_color_rules.csv 1 217:255:0 2 10:214:10 3 75:173:255 4 139:105:20 r.colors map=CVA_87_02_change rules=i_cva_color_rules.csv
REFERENCES
- Malila W A, Lafayette W. Change Vector Analysis (1980): An Approach for Detecting Forest Changes with Landsat. LARS Symp., pp. 326-335 (PDF)
- Zanchetta, A., Bitelli, G. & Karnieli, A. (2016): Monitoring desertification by remote sensing using the Tasselled Cap transform for long-term change detection. Nat Hazards, 83(Suppl 1):223-237. (DOI)
SEE ALSO
i.albedo, i.vi, i.aster.toar, i.landsat.toar, r.univarAUTHOR
Anna ZanchettaSOURCE CODE
Available at: i.cva source code (history)
Main index | Imagery index | Topics index | Keywords index | Graphical index | Full index
© 2003-2020 GRASS Development Team, GRASS GIS 7.8.3dev Reference Manual