Note: This document is for an older version of GRASS GIS that has been discontinued. You should upgrade, and read the current manual page.

NAME
r.contour - Produces a vector map of specified contours from a raster map.KEYWORDS
raster, surface, contours, vectorSYNOPSIS
Flags:
- -t
- Do not create attribute table
- --overwrite
- Allow output files to overwrite existing files
- --help
- Print usage summary
- --verbose
- Verbose module output
- --quiet
- Quiet module output
- --ui
- Force launching GUI dialog
Parameters:
- input=name [required]
- Name of input raster map
- output=name [required]
- Name for output vector map
- step=float
- Increment between contour levels
- levels=float[,float,...]
- List of contour levels
- minlevel=float
- Minimum contour level
- maxlevel=float
- Maximum contour level
- cut=integer
- Minimum number of points for a contour line (0 -> no limit)
- Default: 2
Table of contents
DESCRIPTION
r.contour produces a vector map of specified contours from input raster map. Contours can be produced using a comma-separated list of values in levels, or at some regular increment using the step parameter, using minlevel and maxlevel as minimum and maximum contour values, respectively. If no minlevel or maxlevel is specified, the minimum and maximum cell values in the input raster map will be used.NOTES
r.contour will either step through incremental contours or produce contours from a list of levels, not both. If both a list of levels and a step are specified, the list will be produced and the step will be ignored.Zero is treated as a valid data value by r.contour.
If a contour level exactly matches a category value in the raster map, the contour line may backtrack on itself, causing illegal arcs to be produced in the output vector map.
The optional cut parameter allows the user to specify a minimum number of raster cells eligilble to be included in a contour line written to the output vector map. It acts like a filter, omitting spurs, single points, etc., making the output more generalized.
EXAMPLES
In the Spearfish location, produce a vector contour map from input raster elevation.dem with contour levels from 1000m to 2000m, 100m contour step, and a minimum of 200 input raster points contributing to the contour line:
r.contour input=elevation.dem output=elevation_dem_contours \
minlevel=1000 maxlevel=2000 step=100 cut=200
For an example of using levels with r.contour this example uses the elevation map from the North Carolina database:
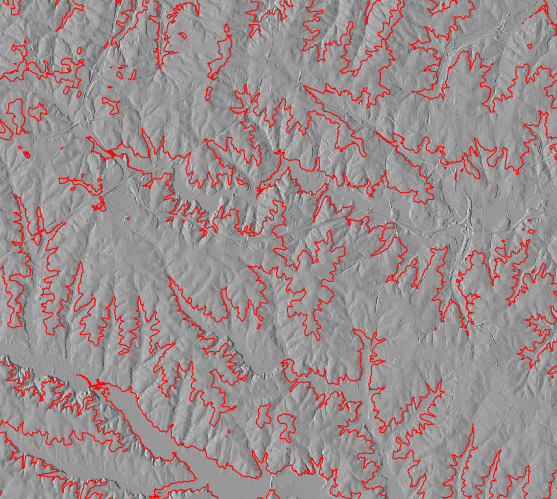
g.region raster=elevation r.contour in=elevation out=contours levels=60,90,120,150 --o d.mon wx0 d.rast elevation_shade d.vect contours color=red
For an example of using steps with r.contour this example uses the LiDAR data derived elevation map from the North Carolina database:
g.region raster=elev_lid792_1m -p
r.contour input=elev_lid792_1m output=elev_lid792_1m_contours \
minlevel=100 maxlevel=150 step=10
AUTHORS
Terry Baker, U.S. Army Construction Engineering Research Laboratory3/2001: cut parameter and fixes by Andrea Aime (aaime@libero.it)
SOURCE CODE
Available at: r.contour source code (history)
Latest change: Saturday Oct 10 16:55:24 2020 in commit: 2cd24d2659e892ff130c310af1079136fadac737
Main index | Raster index | Topics index | Keywords index | Graphical index | Full index
© 2003-2023 GRASS Development Team, GRASS GIS 7.8.9dev Reference Manual