
Note: This document is for an older version of GRASS GIS that will be discontinued soon. You should upgrade, and read the current manual page.
NAME
v.hull - Produces a 2D/3D convex hull for a given vector map.KEYWORDS
vector, geometry, 3DSYNOPSIS
Flags:
- -r
- Limit to current region
- -f
- Create a 'flat' 2D hull even if the input is 3D points
- --overwrite
- Allow output files to overwrite existing files
- --help
- Print usage summary
- --verbose
- Verbose module output
- --quiet
- Quiet module output
- --ui
- Force launching GUI dialog
Parameters:
- input=name [required]
- Name of input vector map
- Or data source for direct OGR access
- layer=string
- Layer number or name ('-1' for all layers)
- A single vector map can be connected to multiple database tables. This number determines which table to use. When used with direct OGR access this is the layer name.
- Default: -1
- output=name [required]
- Name for output vector map
- cats=range
- Category values
- Example: 1,3,7-9,13
- where=sql_query
- WHERE conditions of SQL statement without 'where' keyword
- Example: income < 1000 and population >= 10000
Table of contents
DESCRIPTION
v.hull computes the convex hull of a vector map and outputs the convex hull polygon as a vector area map. The convex hull, or convex envelope, for an object or a set of objects is the minimal convex set containing the given objects. This module creates a vector polygon containing all vector points or lines of the input map.In the case of 3D input points, the hull will be a 3D hull as well, unless the user specifies the -f flag. The 3D hull will be composed of triangular faces.
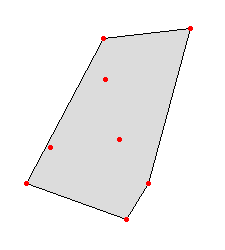
Fig: Convex hull polygon created with v.hull
NOTES
In order to use the where option the layer option must be set to a positive number (the default is '-1' for 'all layers'), otherwise all points from all layers will be used and the cats and where options will be ignored.EXAMPLE
Example of v.hull 3D output (using two random 3D point clouds, North Carolina sample data set):g.region rural_1m -p r.mapcalc "zero = 0" v.random -z output=random3d_a n=10 zmin=0 zmax=200 v.random -z output=random3d_b n=15 zmin=400 zmax=600 v.hull input=random3d_a output=random3d_a_hull v.hull input=random3d_b output=random3d_b_hull d.mon wx0 d.vect random3d_a_hull d.vect random3d_a color=red d.vect random3d_b_hull d.vect random3d_b color=red # 3D view in wxGUI (g.gui)
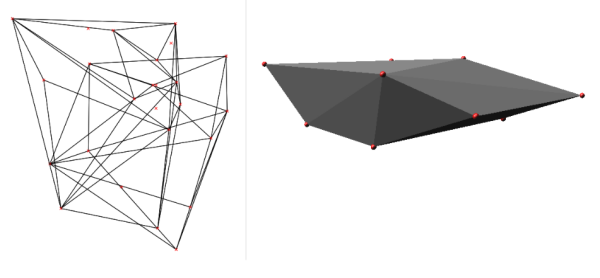
Fig: Convex hull in 3D from 3D points created with v.hull
REFERENCES
- M. de Berg, M. van Kreveld, M. Overmars, O. Schwarzkopf, (2000). Computational geometry, chapter 1.1, 2-8.
- J. O'Rourke, (1998). Computational Geometry in C (Second Edition), chapter 4.
SEE ALSO
v.delaunayAUTHORS
Andrea Aime, Modena, ItalyMarkus Neteler, ITC-irst (update to 5.7)
Benjamin Ducke, CAU Kiel (3D hull support)
Martin Landa, CTU in Prague, Czech Republic (vector lines support)
SOURCE CODE
Available at: v.hull source code (history)
Latest change: Thursday Feb 03 11:10:06 2022 in commit: 547ff44e6aecfb4c9cbf6a4717fc14e521bec0be
Note: This document is for an older version of GRASS GIS that will be discontinued soon. You should upgrade, and read the current manual page.
Main index | Vector index | Topics index | Keywords index | Graphical index | Full index
© 2003-2023 GRASS Development Team, GRASS GIS 8.2.2dev Reference Manual