Note: This document is for an older version of GRASS GIS that has been discontinued. You should upgrade, and read the current manual page.

NAME
r.learn.predict - Apply a fitted scikit-learn estimator to rasters in a GRASS GIS imagery group.KEYWORDS
raster, classification, regression, machine learning, scikit-learn, predictionSYNOPSIS
Flags:
- -p
- Output class membership probabilities
- A raster layer is created for each class. For the case of a binary classification, only the positive (maximum) class is output
- -z
- Only predict class probabilities
- --overwrite
- Allow output files to overwrite existing files
- --help
- Print usage summary
- --verbose
- Verbose module output
- --quiet
- Quiet module output
- --ui
- Force launching GUI dialog
Parameters:
- group=name [required]
- Group of raster layers used for prediction
- GRASS imagery group of raster maps representing feature variables to be used in the machine learning model
- load_model=name [required]
- Load model from file
- File representing pickled scikit-learn estimator model
- output=name [required]
- Output Map
- Raster layer name to store result from classification or regression model. The name will also used as a perfix if class probabilities or intermediate of cross-validation results are ordered as maps.
- chunksize=integer
- Number of pixels to pass to the prediction method
- Number of pixels to pass to the prediction method. GRASS GIS reads raster by-row so chunksize is rounded down based on the number of columns
- Default: 100000
Table of contents
DESCRIPTION
r.learn.predict performs the prediction phase of a machine learning workflow. The user is required to load a prefitted scikit-learn estimator using the load_model parameter, which can be developed using the r.learn.train module, or can represent any fitted scikit-learn compatible estimator that is pickled to a file. The GRASS GIS imagery group to apply the model is set using the group parameter.
NOTES
r.learn.predict is designed to keep system memory requirements relatively low. For this purpose, the rasters are read from the disk row-by-row, using the RasterRow method in PyGRASS. This however does not represent an efficient volume of data to pass to the classifiers, which are mostly multithreaded. Instead, groups of rows as passed to the estimator. The chunksize parameter represents the maximum memory size (in MB) for each of these blocks of data. Note that the module will consume more memory than this, especially if the estimator model was trained using multiple cores.
EXAMPLE
Here we are going to use the GRASS GIS sample North Carolina data set as a basis to perform a landsat classification. We are going to classify a Landsat 7 scene from 2000, using training information from an older (1996) land cover dataset.
Landsat 7 (2000) bands 7,4,2 color composite example:
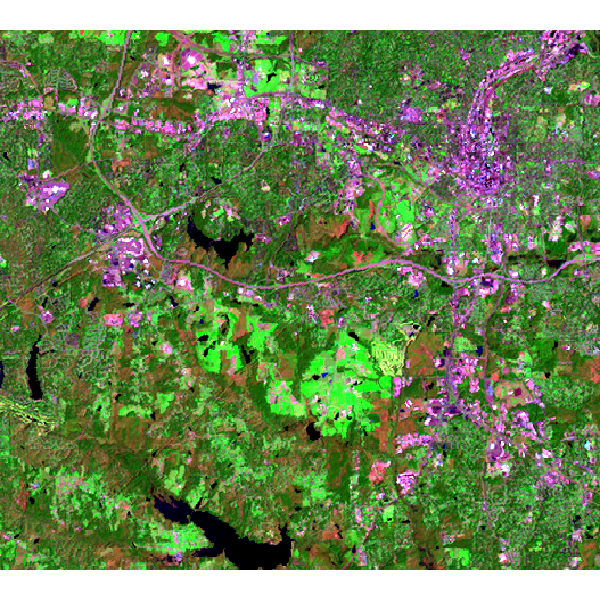
Note that this example must be run in the "landsat" mapset of the North Carolina sample data set location.
First, we are going to generate some training pixels from an older (1996) land cover classification:
g.region raster=landclass96 -p r.random input=landclass96 npoints=1000 raster=training_pixels
Then we can use these training pixels to perform a classification on the more recently obtained landsat 7 image:
# train a random forest classification model using r.learn.train r.learn.train group=lsat7_2000 training_map=training_pixels \ model_name=RandomForestClassifier n_estimators=500 save_model=rf_model.gz # perform prediction using r.learn.predict r.learn.predict group=lsat7_2000 load_model=rf_model.gz output=rf_classification # check raster categories - they are automatically applied to the classification output r.category rf_classification # copy color scheme from landclass training map to result r.colors rf_classification raster=training_pixels
Random forest classification result:
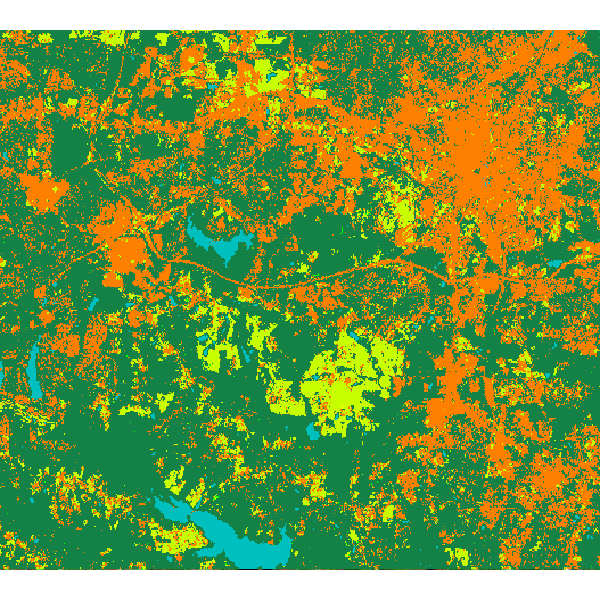
SEE ALSO
r.learn.ml2 (overview), r.learn.trainREFERENCES
Scikit-learn: Machine Learning in Python, Pedregosa et al., JMLR 12, pp. 2825-2830, 2011.
AUTHOR
Steven PawleySOURCE CODE
Available at: r.learn.predict source code (history)
Accessed: Tuesday May 06 05:57:38 2025
Main index | Raster index | Topics index | Keywords index | Graphical index | Full index
© 2003-2024 GRASS Development Team, GRASS GIS 8.3.3dev Reference Manual