Note: This document is for an older version of GRASS GIS that has been discontinued. You should upgrade, and read the current manual page.

wxGUI
Table of contents
DESCRIPTION
wxGUI is a native Graphical User Interface (GUI) for GRASS GIS. Its main features include displaying geographical data in 2D and 3D, calling GRASS GIS modules, and interacting with data.Overview
The GUI is composed of three main components:- The Layer Manager includes map layer management, integrated command-line prompt, and command output window tab.
- The Map Display Window integrates basic tools for zooming, panning, data querying, and map elements (north arrows, barscale, etc.). Each display window is associated with its own set of map layers in the layer manager. The user may start multiple map displays during a session. The map layers for each display are grouped under different tabs in the Layer Manager.
- Module dialogs enable running GRASS modules that can be searched and launched via Tools tab.
Layer Manager
The Layer Manager provides an interactive graphical interface for creating and managing GRASS displays. There is a toolbar to manage displayed map layers, a layer tree frame in which map layers for display are organized, a command output window tab, and interactive command line prompt. On Linux and Windows platforms, the layer manager also has a menu bar with a set of pull-down menus for all GRASS GIS functions (analysis, file I/O, GIS configuration and management); on a Mac, the GRASS functions menu is at the top of the screen.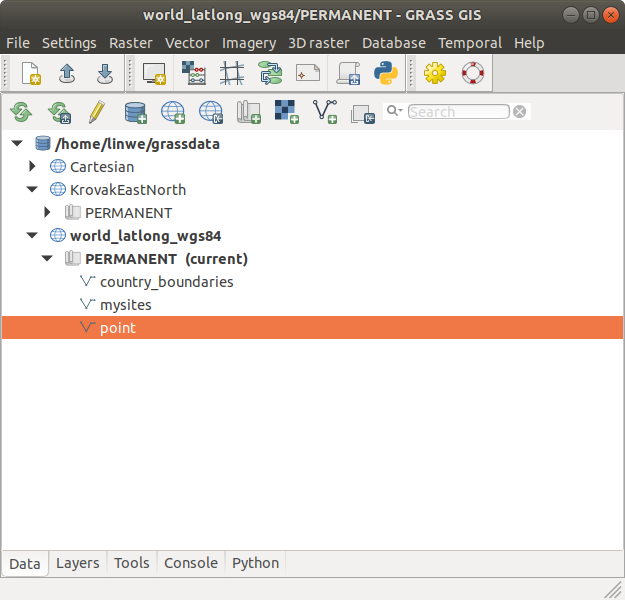
Figure: Layer Manager screenshot on Ubuntu
The top left button of the toolbar opens a new Map Display Window. Each map display has a unique set of layers to display and region settings. Other toolbar buttons add layers of different types for display in the selected map display window. There are additional buttons for saving or opening workspace file, and others.
Map layers are listed in the window frame below the toolbar. Layers can include raster and vector maps, vector labels, and commands (where any GRASS command can be written). Layers are displayed as arranged in the layer tree: the bottom layer is displayed first and the top layer is displayed last, as if the layers were a series of stacked overlays.
The check box to the left of each layer makes it active or inactive for display. Only active layers are displayed/redisplayed when the display button is pressed. Layers can be organized into groups; entire groups can be activated or deactivated for display. Layer tree composition can be saved to a workspace file and opened in subsequent sessions, restoring all layers and their display options.
A right mouse click on a layer or left clicking the button to the right of the layer opens a dropdown menu with options to remove or rename the layer (not the actual map), change its display properties (d.rast and d.vect options such as color, symbol, etc.), show its metadata (r.info, v.info) or attributes, if applicable.
A left mouse double click on a layer opens GUI for its display options These options are those for the d.* command for each layer type (d.rast, d.vect, or d.grid, for example).
Layer Manager Toolbar
 Start new map display
Start new map display- Opens a new map display and creates empty layer tree tab in Layer Manager.
 Create new workspace
Create new workspace- Removes all layers from the layer tree and creates a new, empty tree where new layers can be added.
 Open existing workspace file
Open existing workspace file- Opens an previously saved workspace file, containing a set of display layers and their option settings.
 Save current workspace to file
Save current workspace to file- Saves current set of layers and their options to a workspace file.
 Load map layers into workspace
Load map layers into workspace- Loads selected raster or vector maps into current layer tree.
 Add raster map layer
Add raster map layer- Adds raster map to layer tree, see d.rast.
 Add various raster map layers (RGB, HIS, shaded relief...)
Add various raster map layers (RGB, HIS, shaded relief...)- Opens a dropdown menu that allows user to select to:
 Add 3D raster map layer
Add 3D raster map layer- Adds 3D raster map to layer tree.
 Add RGB raster layer
Add RGB raster layer- Combines and displays three raster maps defined as red, green, and blue channels to create an RGB color map, see d.rgb.
 Add HIS raster layer
Add HIS raster layer- Combines and displays two or three raster maps defined as hue, intensity, and (optionally) saturation channels to create a color map, see d.his.
 Add shaded relief raster map layer
Add shaded relief raster map layer - Adds shaded relief raster map layer, see r.relief and d.shade.
 Add raster arrows layer
Add raster arrows layer- Adds map of raster cells with directional arrows drawn. Arrow direction and length are determined by separate aspect/directional map and (optional) slope/intensity map, see d.rast.arrow.
 Add raster numbers layer
Add raster numbers layer- Adds map of raster cells with numbers representing the cell values, see d.rast.num.
 Add vector map layer
Add vector map layer- Adds a vector map layer, see d.vect.
 Add various vector map layers (thematic, chart...)
Add various vector map layers (thematic, chart...)- Opens a dropdown menu that allows user to select to:
 Add thematic area (choropleth) map layer
(for all vector types)
Add thematic area (choropleth) map layer
(for all vector types)- Adds layer for thematic display values from a numeric attribute column associated with a vector map. Options include: thematic display type (graduated colors or point sizes), methods for creating display intervals, SQL query of attribute column to limit vector objects to display, control of point icon types and sizes, control of thematic color schemes, creation of legend for thematic map, and saving the results of thematic mapping to a ps.map instructions file for later printing, see d.vect.thematic.
 Add thematic chart layer (for vector points)
Add thematic chart layer (for vector points)- Adds layer in which pie or bar charts can be automatically created at vector point locations. Charts display values from selected columns in the associated attribute table. Options include: chart type, layer and attributes to chart, chart colors, and chart size (fixed or based on attribute column), see d.vect.chart.
 Add group
Add group- Adds an empty group. Layers can then be added to the group.
 Add grid or vector labels overlay
Add grid or vector labels overlay- Opens a dropdown menu that allows user to select to:
 Add overlay grids and lines
Add overlay grids and lines- Adds layer to display regular grid (for all locations) see d.grid
 Add labels layer for vector objects (from existing labels file)
Add labels layer for vector objects (from existing labels file)- Add a layer of text from a labels file for vector objects created with the v.label module. A labels file can also be created with a text editor, see d.labels.
 Add geodesic line layer
Add geodesic line layer- Add layer to display geodesic line for latitude/longitude locations only, see d.geodesic
 Add rhumbline layer
Add rhumbline layer
- Add layer to display rhumblines (for latitude/longitude locations only), see d.rhumbline.
 Add command layer
Add command layer- Adds a layer in which a GRASS GIS command or command list can be entered.
For a command list use the semi-colon (";") symbol as a separator.
For example:
Note that when an option of the command contains spaces, you need to "escape" them with the backslash ('\') character, for example:
d.rast soils;d.rast -o roads;d.vect streams col=blue
d.text text=Population\ density
 Delete selected layer
Delete selected layer- Removes selected map layer or map layer group from layer tree.
 Edit vector maps
Edit vector maps- Opens vector digitizer to allow editing selected vector map.
 Show attribute table
Show attribute table- Opens attribute table manager for selected vector map.
 Import raster or vector data
Import raster or vector data-
 Import raster data
Import raster data- Import selected raster data into GRASS using r.in.gdal and load them into current layer tree.
 Link external raster data
Link external raster data- Link selected external raster data as GRASS raster maps (using r.external) and load them into current layer tree.
 Set raster output format
Set raster output format- Define external format for newly created raster maps (see r.external.out for details)
 Import vector data
Import vector data- Import selected vector data into GRASS using v.in.ogr and load them into current layer tree.
 Link external vector data
Link external vector data- Link selected external vector data as GRASS vector maps (using v.external) and load them into current layer tree.
 Set vector output format
Set vector output format- Define external format for newly created vector maps (see v.external.out for details)
 Raster Map Calculator
Raster Map Calculator- Launches Raster Calculator GUI front-end for r.mapcalc.
 Graphical Modeler
Graphical Modeler- Launches graphical modeler to create models and run them.
 Georectifier Tool
Georectifier Tool- Launches GCP Manager to create, edit, and manage Ground Control Points.
 Cartographic Composer
Cartographic Composer- Launches Cartographic Composer to create interactively hardcopy map outputs.
 Show GUI settings
Show GUI settings- Opens dialog to change GUI settings.
 Show help
Show help- Opens GRASS manual.
Map Display Window
The map display window includes toolbar that can be docked and undocked from the window, a map canvas where a map composition of one or more layers is displayed, and a statusbar with information about the geographic region of the maps displayed.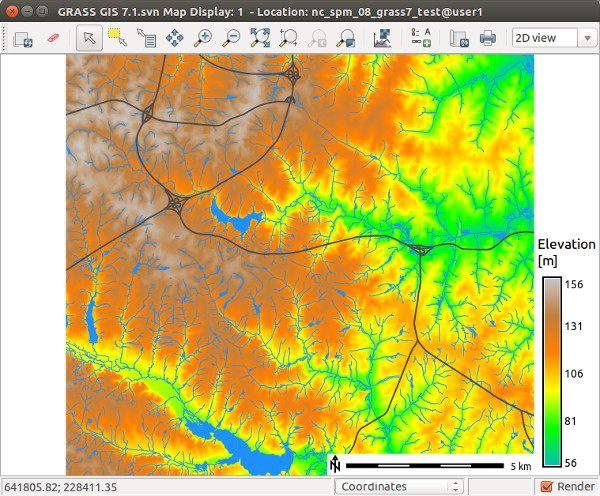
Figure: Map Display screenshot on Ubuntu
Each Map Display Window has a unique layer tree (in the layer manager) and geographic region setting. At the top of the window is a toolbar with buttons to manage the map in the display (render, erase, zoom and pan), for query and and analysis (distance measurement, profile, and histogram creation), to overlay map elements onto the display (scale, north arrow, legend, and custom text), and to export or print the display.
In the statusbar, the user can choose to display the geographic coordinates under the cursor, current geographical region extent, computational region (including graphical visualization in map display), map display geometry (number of rows, columns, resolution) and map scale. Checking the render button in the statusbar will cause the map display to update automatically any time a map is added to, removed from, or changed in its layer tree.
It is important to note that zooming in any display will have no effect on the 'computational region' setting (set with g.region). Only by selecting the 'Set current region to match display' item in the zoom menu (in the map display toolbar) will the current display extents be copied to the computational region extents.
Map Display Toolbar
 Re-render display
Re-render display- Re-renders all active map layers regardless of whether they have changed or not, see d.redraw.
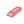 Erase display
Erase display- Erases the currently selected map display to a white background, see d.erase.
 Pointer
Pointer- Select arrow cursor for map display.
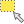 Select features from vector map
Select features from vector map- Interactively select features from given vector map. Selection can be stored to a new vector map, see v.what and v.extract.
 Query raster/vector maps
Query raster/vector maps- Query selected raster, RGB raster (all three map channels will be queried), or vector map(s) using the mouse. Map(s) must be selected before query. Vector charts and thematic vector maps cannot be queried. The results of the query will be displayed in a dialog. See r.what, v.what.
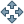 Pan
Pan- Interactive selection of a new center of view in the active display monitor. Drag the pan cursor while pressing the left mouse button to pan. Panning changes the location of the region displayed but not the size of the area displayed or the resolution. Panning does not affect the computational region for other GIS processes, see g.region.
 Zoom in
Zoom in- Interactive zooming with the mouse in the active display monitor. Drawing a box or just click with the mouse (left button) and zoom-in cursor causes the display to zoom in so that the area defined by the box fills the display. The map resolution is not changed. Clicking with the zoom-in cursor causes the display to zoom in by 30%, centered on the point where the mouse is clicked. Zooming resets the display region extents (both size and location of area displayed). It does not affect the computational region for other GIS processes, see g.region.
 Zoom out
Zoom out- Interactive zooming with the mouse in the active display monitor. Drawing a box or just click with the mouse (left button) and zoom-out cursor causes the display to zoom in so that the area displayed shrinks to fill the area defined by the box. The map resolution is not changed. Clicking with the zoom-out cursor causes the display to zoom out by 30%, centered on the point where the mouse is clicked. Zooming resets the display region extents (both size and location of area displayed). It does not affect the computational region for other GIS processes, see g.region.
 Zoom to selected map(s)
Zoom to selected map(s)- Set zoom extent based on selected raster or vector maps. Zooming resets the display region extents (both size and location of area displayed). It does not affect the computational region for other GIS processes, see g.region.
 Zoom to computational region extent
Zoom to computational region extent- Set zoom extent based on the current computational region extent, see g.region.
 Return to previous zoom
Return to previous zoom- Returns to the previous zoom extent. Up to 10 levels of zoom back are maintained, see g.region.
 Various zoom options
Various zoom options- Opens a dropdown menu that allows user to:
- Zoom to default region
- Zoom to saved region. Zooms to previously saved named region.
- Set computational region extent from display. The computational region (the mapset's WIND file) is set to match the current display extent (does not change the resolution), see g.region.
- Set computational region extent interactively. The computational region is set simply by drawing a box with the left mouse button on Map Display.
- Set computational region from named region. This option doesn't affect display zoom.
- Save display geometry to named region
- Save computational region to named region
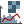 Analyze menu
Analyze menu- Opens a dropdown menu with:
 Measure distance
Measure distance- Interactive measurement of lengths defined with the mouse. The length of each segment and the cumulative length of all segments measuered is displayed in the command output window frame. Lengths are measured in the current measurement unit. Double-click to switch off measuring.
 Measure area
Measure area- Interactive measurement of area defined with the mouse. Area is measured in the current measurement unit. Double-click to switch off measuring.
 Profile surface map
Profile surface map- Interactively create profile of a raster map. Profile transect is drawn with the mouse in map display. The profile may be of the displayed map or a different map. Up to three maps can be profiled simultaneously.
 Create bivariate scatterplot of raster maps
Create bivariate scatterplot of raster maps- Interactively create bivariate scatterplot of raster maps.
 Create histogram of raster map
Create histogram of raster map- Displays histogram of selected raster map or image in new window.
 Create histogram with d.histogram
Create histogram with d.histogram- Displays histogram of selected raster map or image in new window, see d.histogram.
 Vector network analysis tool
Vector network analysis tool- See tool's manual page.
 Add overlay
Add overlay- opens a dropdown menu that allows user to
 Add raster map legend
Add raster map legend- Adds layer to display with legend of selected raster map, see d.legend.
 Add scalebar
Add scalebar- Adds layer to display a scalebar. Options include scalebar placement (using screen coordinates or a mouse), scalebar format, and scalebar colors, see d.barscale.
 Add north arrow
Add north arrow- Adds layer to display a north arrow. Options include north arrow placement (using screen coordinates or a mouse), north arrow style and color, see d.northarrow.
 Add text layer
Add text layer- Adds layer to display a line of text using default GRASS font (selected with d.font). Options include: text placement (screen coordinates); and text size, bolding, and color, see d.text.
 Save display to graphic file
Save display to graphic file- Save the visible image in map display to different raster graphic formats.
 Print map
Print map- Prints map on system native printer or PostScript device; saves visible map display (including PostScript text and labels) to PDF or EPS file.
- Map display mode
- Opens a dropdown menu for selecting different display mode
- 2D view
- Normal GIS display. All active layers are composited and displayed in 2D mode.
- 3D view
- Experimental replacement for NVIZ. Displays all active layers in 3D perspective using OpenGL. A new control panel opens to manage the 3D view. 3D view can be zoomed, panned, rotated, and tilted. The vertical exaggeration of rasters and 3D vectors can be set. Various color and lighten settings are possible. Not yet functional for Windows platforms
- Vector digitizer
- Puts display into vector digitizing mode and opens a new digitizing toolbar. The user can digitize a new vector map or edit an existing map.
- Raster digitizer
- Puts display into raster digitizing mode and opens a new digitizing toolbar. The user can digitize a new raster map or edit an existing map.
Keyboard short-cuts
Layer Manager
- Ctrl+Tab
- Switch 'Layers' and 'Console' tab
- Ctrl+Q
- Quit
- Ctrl+R
- Render map in all map displays
- Ctrl+N
- Create new workspace
- Ctrl+O
- Load workspace from file
- Ctrl+S
- Close workspace
- Ctrl+Shift+L
- Add multiple raster or vector map layers to current map display
- Ctrl+Shift+R
- Add raster map layer to current map display
- Ctrl+Shift+V
- Add vector map layer to current map display
- Ctrl+W
- Close current map display
- Tab
- Show command tooltips
- Esc
- Hide command tooltips
- Ctrl+Space
- Show auto-complete suggestions
- Up/Down
- List command history
- Enter
- Run command
- Ctrl++
- Increase font size (numerical keyboard plus key)
- Ctrl+-
- Decrease font size (numerical keyboard minus key)
- Ctrl+mouse wheel
- Increase or decrease font size
Map Display
- F11
- Fullscreen mode (toggle on/off)
- Ctrl+W
- Close map display
- Ctrl+R
- Render map (re-renders map)
- F5
- Render map (re-renders map)
Starting the GUI from command line
By default, the GUI is always started, but if only the command line (shell) is running, the GUI can be also started manually using:g.gui
g.gui -d wxpython
g.gui workspace=file.gxw
The user can also start GRASS from the shell command line with the wxGUI specifying the --gui switch:
grass --gui
The GUI can be quit by selecting the 'File > Quit GRASS GIS' menu item which gives options to close only GUI or to quit GRASS GIS entirely if GRASS GIS is running with a command line (a shell in a terminal application). Exiting the shell (typically by the exit command) ends the GRASS session including any running GUIs.
Background information
wxGUI is a native Graphical User Interface (GUI) for GRASS GIS written in Python using wxPython library.SEE ALSO
wxGUI componentswxGUI module dialogs wxGUI toolboxes (menu customization)
See also wxGUI wiki page (especially various video tutorials), and Quick wxGUI Tutorial.
AUTHORS
Martin Landa, FBK-irst (2007-2008), Trento, Italy, and Czech Technical University in Prague, Czech RepublicMichael Barton, Arizona State University, USA
Daniel Calvelo Aros
Jachym Cepicky
Markus Metz, Germany
Anna Kratochvilova, OSGeoREL, Czech Technical University in Prague, Czech Republic
Vaclav Petras, OSGeoREL, Czech Technical University in Prague, Czech Republic
Stepan Turek, OSGeoREL, Czech Technical University in Prague, Czech Republic
Tereza Fiedlerova, OSGeoREL, Czech Technical University in Prague, Czech Republic
Matej Krejci, OSGeoREL, Czech Technical University in Prague, Czech Republic
Icons created by Robert Szczepanek, Poland (Git repository)
SOURCE CODE
Available at: wxGUI source code (history)
Latest change: Thursday May 18 09:47:05 2023 in commit: 6f654dd68b2ea4f07c1dcdeb96f94ae6534ea8c0
Main index | Topics index | Keywords index | Graphical index | Full index
© 2003-2024 GRASS Development Team, GRASS GIS 8.3.3dev Reference Manual