NAME
r.earthworks - Terrain modeling with cut and fill operationsKEYWORDS
raster, terrain, earthworkSYNOPSIS
r.earthworks
r.earthworks --helpr.earthworks [-pd] elevation=name earthworks=name mode=string operation=string function=string [raster=name] [coordinates=east,north] [points=name] [lines=name] [z=float[,float,...]] [flat=float] [volume=name] [linear=float] [exponential=float] [logistic=float] [gaussian=float] [lorentz=float] [quadratic=float] [cubic=float] [threshold=float] [border=float] [nprocs=integer] [--overwrite] [--help] [--verbose] [--quiet] [--ui]
Flags:
- -p
- Print volume
- -d
- Disable quadtree segmentation
- --overwrite
- Allow output files to overwrite existing files
- --help
- Print usage summary
- --verbose
- Verbose module output
- --quiet
- Quiet module output
- --ui
- Force launching GUI dialog
Parameters:
- elevation=name [required]
- Input elevation raster
- Input elevation raster
- earthworks=name [required]
- Output earthworks
- Output elevation raster
- Default: earthworks
- mode=string [required]
- Earthworking mode
- Options: relative, absolute
- Default: absolute
- relative: Relative to existing topography
- absolute: At given elevation
- operation=string [required]
- Earthworking operation
- Options: cut, fill, cutfill
- Default: cutfill
- cut: Cut into topography
- fill: Fill over topography
- cutfill: Cut and fill
- function=string [required]
- Slope function
- Options: linear, exponential, logistic, gaussian, lorentz, quadratic, cubic
- Default: linear
- linear: linear decay function
- exponential: Exponential decay function
- logistic: Logistic function
- gaussian: Gaussian function
- lorentz: Cauchy-Lorentz distribution
- quadratic: Quadratic function
- cubic: Cubic function
- raster=name
- Input raster spot elevations
- Input raster spot elevations
- coordinates=east,north
- Seed point coordinates
- Seed point coordinates
- points=name
- Input points
- Input points
- lines=name
- Input lines
- Input lines
- z=float[,float,...]
- Elevation value
- Elevation value
- Default: 0.0
- flat=float
- Radius of flats
- Radius of flats
- Default: 0.0
- volume=name
- Output volume
- Output volumetric change raster
- linear=float
- Linear slope
- Linear slope
- Default: 0.1
- exponential=float
- Exponential decay factor
- Exponential decay factor
- Default: 0.04
- logistic=float
- Logistic shape parameter
- Logistic shape parameter
- Default: 0.025
- gaussian=float
- Gaussian standard deviation
- Gaussian standard deviation
- Default: 25
- lorentz=float
- Cauchy-Lorentz scale parameter
- Cauchy-Lorentz scale parameter
- Default: 25
- quadratic=float
- Quadratic coefficient
- Quadratic coefficient
- Default: 0.001
- cubic=float
- Cubic coefficient
- Cubic coefficient
- Default: 0.00001
- threshold=float
- Threshold per quadrant
- Threshold per quadrant
- Default: 500
- border=float
- Border around quadrants
- Border around quadrants
- Default: 250
- nprocs=integer
- Number of threads for parallel computing
- 0: use OpenMP default; >0: use nprocs; <0: use MAX-nprocs
- Default: 0
Table of contents
DESCRIPTION
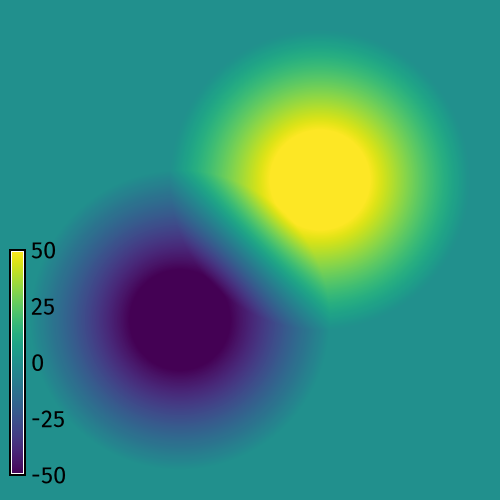
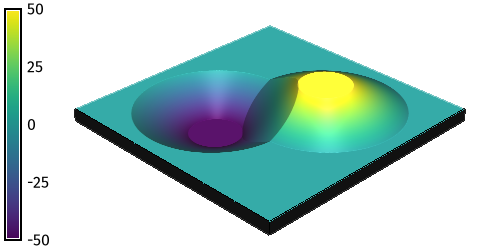
r.earthworks models new landforms using cut and fill operations to add and remove earth from an elevation raster. It can be used to model topographic forms such as hills, pits, ridges, valleys, roads, dams, and levees. In cut operations earth is excavated from the elevation raster, while in fill operations earth is deposited on the elevation raster. In absolute mode earth is added or removed until the specified elevation is reached, while in relative mode earth is added or removed by a height relative to the existing terrain.Inputs
The key inputs for r.earthworks are an existing elevation raster and a set of x-, y-, and z-values for the local minima and maxima of the new landforms. These values can be input as coordinates, points, lines, or a raster. For x- and y-coordinates, 2D points, and 2D lines, an input elevation parameter z must also be specified. This z parameter can be a single constant value or a list of values. Other input parameters for r.earthworks include operation, mode, function, slope, and flats. The operation parameter can be set to cut, fill, or cut-fill mode to excavate, build, or excavate and build terrain. The mode parameter can be set to absolute or relative mode to use either zero or the existing elevation as a datum. In absolute mode, for example, a road would cut through or be built up on embankments over the existing terrain, while in relative mode a road would adapt to the terrain. The function parameter can be set to linear, exponential, logistic, Gaussian, Cauchy-Lorentz, quadratic, or cubic to define the slope from the local minima or maxima to the existing terrain. A slope parameter - either linear, exponential, logistic, gaussian, lorentz, quadratic, or cubic - controls the rate of growth and decay for a given slope function. For example a linear slope function with a rate of 0.1 will generate a constant 10 percent slope. The flats parameter specifies the radius of constant elevation around local minima or maxima. It can be used to model the flat surfaces of topographic features such as plateaus, lakes, roads, and levees.Outputs
In addition to generating an earthworks raster with transformed elevation values, r.earthworks can also calculate the volume of cut and fill. Set the output volume raster to generate a volumetric change raster. Use the-p flag
to print the net volume of cut and fill.
Quadtree Segmentation
To speed computation, r.earthworks uses quadtree segmentation. The computational region is recursively divided into quadrants until each quadrant contains no more a given number of coordinates defined by a threshold parameter. Quadtree segmentation limits earthworking operations to quadrants containing input geometry. Each segmented subregion is grown by a border parameter which has a default value of 250 map units. If this border is not large enough, then the earthworking operations may be incomplete with artifacts along their edges. If artifacts occur, then increase the size of the border. A larger border, however, will increase computation time. When the initial region contains a hundred thousand cells or more and there are more input coordinates than the threshold, quadtree segmentation is used by default, but can be disabled with flag-d.
When segmentation is not used,
it can take a long time to model extensive earthworks
for large regions with a million cells or more.
EXAMPLE
For more detailed instructions and examples, see the earthworks tutorial collection.Cut & Fill Operations
Perform basic cut and fill operations to model peaks and pits from x- and y-coordinates. Setup Set the computational region with g.region and then use map algebra to generate a flat terrain with r.mapcalc.g.region n=500 s=0 e=500 w=0 res=1 r.mapcalc expression="elevation = 0"
r.earthworks elevation=elevation earthworks=peak operation=fill coordinates=250,250 z=50 function=linear linear=0.5 flat=50
r.earthworks elevation=elevation earthworks=pit operation=cut coordinates=250,250 z=-50 function=linear linear=0.5 flat=50
r.earthworks elevation=elevation earthworks=peak_and_pit operation=cutfill coordinates=180,180,320,320 z=-50,50 function=linear linear=0.5 flat=50
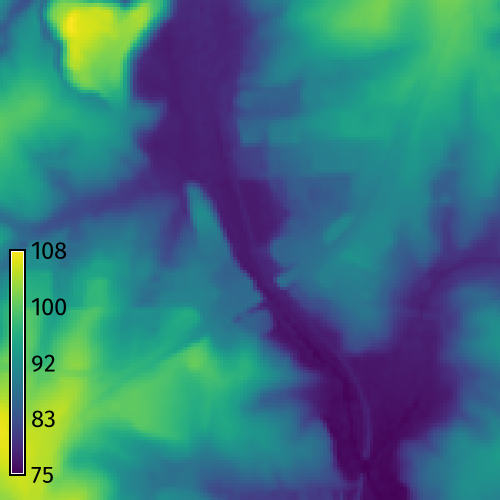
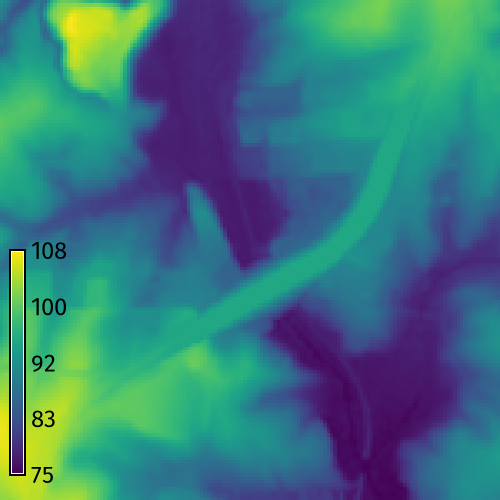
Road Grading
Use a vector map of a road network to grade a road crossing over a valley. Start GRASS in the North Carolina basic dataset. First set the computation region with g.region. Then run r.earthworks with input elevation set toelevation,
input lines set to roadsmajor,
z set to 95,
operation set to fill,
function set to linear,
linear set to 0.25,
and flat set to 25.
Use flag -p to print the volume of fill.
This will grade an embankment through the valley
with a 50 meter wide roadway
at a constant elevation of 95 meters
with side slopes of 25 percent.
Optionally, compute contours with
r.contour.
g.region n=217700 s=216200 w=639200 e=640700 res=10 r.earthworks elevation=elevation earthworks=earthworks lines=roadsmajor z=95 function=linear linear=0.25 operation=fill flat=25 -p r.contour input=earthworks output=contours step=2
Dam Breach Modeling
Model a flood due to a dam breach. Use r.earthworks to breach the dam and then use r.lake to model the maximum possible extent and depth of flooding.g.region n=223740 s=222740 w=634450 e=635450 res=10 r.lake elevation=elevation water_level=104 lake=lake coordinates=635150.7489931877,223203.9595016748 r.earthworks elevation=elevation operation=cut coordinates=635235.4648198467,223210.9879314204 z=103 function=linear linear=0.5 flat=20 r.lake --overwrite elevation=earthworks water_level=104 lake=lake coordinates=635150.7489931877,223203.9595016748
NOTES
In GRASS 8.5 and above, map algebra uses parallel computing for faster raster calculations. The current implementation of parallelization in r.mapcalc can open too many files causing r.earthworks to fail for runs with multiple input coordinates depending on the open file limit of the user's system. This issue can be addressed by enabling quadtree segmentation, setting fewer threads for parallel computing, or raising the open file limit. If this error occurs, try setting smallerthreshold and border parameters
for quadtree segmentation.
Alternatively, try setting
the number of threads for parallel computing
with the nprocs parameter.
Use the shell command ulimit
to temporarily raise the open file limit:
ulimit -S -n 32768
REFERENCES
- Harmon, B., Petrasova, A., & Petras, V., (2026). r.earthworks: a GRASS tool for terrain modeling. Journal of Open Source Software, 11(118), 9270, https://doi.org/10.21105/joss.09270.
- Harmon, B., Petrasova, A., & Petras, V. (2026). r.earthworks: a GRASS tool for terrain modeling (3.0.0). Zenodo. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.15507391
AUTHORS
Brendan HarmonSOURCE CODE
Available at: r.earthworks source code (history)
Latest change: Sunday Feb 15 06:15:45 2026 in commit: 5a948a0a107a607b01ce42171a71af9bbbc992ea
Main index | Raster index | Topics index | Keywords index | Graphical index | Full index
© 2003-2025 GRASS Development Team, GRASS GIS 8.4.3dev Reference Manual