
NAME
r.fuzzy.set - Calculate membership value of any raster map according to a user's rules.KEYWORDS
raster, fuzzy logicSYNOPSIS
r.fuzzy.set
r.fuzzy.set --helpr.fuzzy.set input=name output=name points=string[,string,...] [side=string] [boundary=string] [shape=float] [height=float] [--overwrite] [--help] [--verbose] [--quiet] [--ui]
Flags:
- --overwrite
- Allow output files to overwrite existing files
- --help
- Print usage summary
- --verbose
- Verbose module output
- --quiet
- Quiet module output
- --ui
- Force launching GUI dialog
Parameters:
- input=name [required]
- Raster map to be fuzzified
- output=name [required]
- Membership map
- points=string[,string,...] [required]
- Inflection points: a,b[,c,d]
- Default: a,b[,c,d]
- side=string
- Fuzzy range
- Options: both, left, right
- Default: both
- boundary=string
- Type of fuzzy boundaries
- Options: Linear, S-shaped, J-shaped, G-shaped
- Default: S-shaped
- shape=float
- Shape modifier: -1 to 1
- Options: -1-1
- Default: 0.
- height=float
- Membership height: 0 to 1
- Options: 0-1
- Default: 1.
Table of contents
OPTIONS
- input
- Name of input raster map to be fuzzified. This map may be of any type and may require null values.
- points
- A list containing 4 (A,B,C,D) or 2 (A,B) points defining set boundaries as defined in Figure 1.
Points do not have to be in map range, but this may lead to only 0 or 1 membership for
the whole map. For side parameter "both", range between A and D defines base,
and the range between B and C defines the core of the fuzzy set. Between A and B and between C and D are the
set's boundaries. If side is "both", points requires 4 points, or else 2 points.
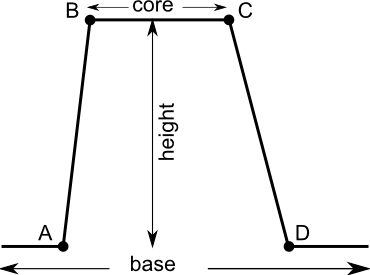
Figure 1: Fuzzy set definition - side
- This option indicates if set is fuzzified of both sides (both), left or right side. See description for details.
OUTPUTS
- output
- Map containing membership value of original map. Map is always of type FCELLS and contains values from 0 (no membership) to 1 (full membership). Values between 0 and 1 indicate partial membership
FUZZY SET PARAMETERS
- boundary
- Defines the shape of the fuzzy boundary. The default and most
popular is S-shaped. Linear, J-shaped and G-shaped boundaries are also
available. The same boundaries are applied to the both sides.
The available options are illustrated in Figure 2.
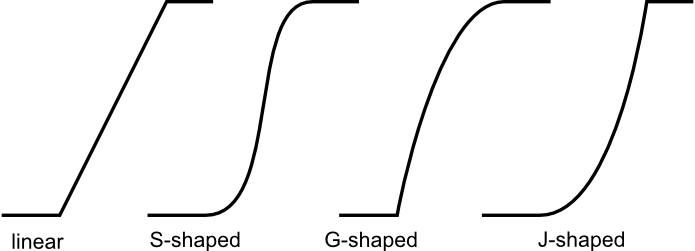
Figure 2: Boundary definition for boundary parameter values "Linear", "S-shaped", "G-shaped", and "J-shaped". - shape
- Optional shape modifier. Range from -1 to 1. The default value is 0 and
should not be changed in most of the time. The negative values indicate more
dilatant set, the positive values more concentrate set. See NOTES for
details.
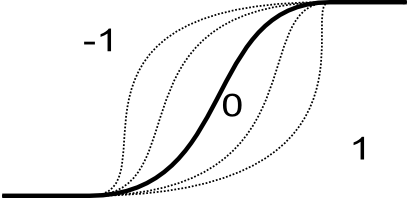
Figure 3: Impact of shape parameter on shape boundary - height
- Optional height modifier. Range from 0 to 1. The default value is 1 and indicates full membership. If height is less than one, the maximum membership is equal to height. See Figure 1: Fuzzy set definition.
DESCRIPTION
Definition of fuzzy set
Fuzzy sets are sets whose elements have degrees of membership. Zadeh (1965) introduced fuzzy sets as an extension of the classical notion of sets. Classical membership of elements in a set are binary terms: an element either belongs or does not belong to the set. Fuzzy set theory use the gradual assessment of the membership of elements in a set. A membership function is valued in the real unit interval [0, 1]. Classical sets are special cases of the membership functions of fuzzy sets, if the latter only takes values 0 or 1. Classical sets are in fuzzy set theory usually called crisp sets. Fuzzy set theory can be used in a wide range of domains in which information is imprecise, including many GIS operations.NOTES
Calculation of boundary shape
Depending on type of the boundary, different equations are used to determine its shape:Linear: the membership is calculated according following equation:
value <= A -> x = 0
A < value > B -> x = (value-A)/(B-A)
B <= value >= C -> x = 1
C < value > D -> x = (D-value)/(D-C)
value >= D -> x = 0
where x: membership
S-shaped: the membership is calculated according following equation:
sin(x * Pi/2)^m (for positive shape parameter)
1-cos(x * Pi/2)^m (for negative shape parameter)
where x: membership, and
m = 2^exp(2 * |shape|)
For default shape=0, m = 2 (most common parameter for that equation).
G-shaped: the membership is calculated according following equation:
tan(x * Pi/4)^1/m
where x: membership, and
m = 2^exp(-2 * shape) (for negative shape parameter)
m = 2^(1-shape) (for positive shape parameter)
For default shape=0, m = 2 (most common parameter for that equation).
J shaped: it uses following equations:
tan(x * Pi/4)^m
where x: membership, and
m = 2^exp(2 * shape) (for positive shape parameter)
m = 2^(1+shape) (for negative shape parameter)
For default shape=0, m = 2 (most common parameter for that equation).
SEE ALSO
r.fuzzy.logic, r.fuzzy.system, r.mapcalcREFERENCES
- Jasiewicz, J. (2011). A new GRASS GIS fuzzy inference system for massive data analysis. Computers & Geosciences (37) 1525-1531. DOI https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cageo.2010.09.008
- Zadeh, L.A. (1965). "Fuzzy sets". Information and Control 8 (3): 338–353. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0019-9958(65)90241-X.
- Novák, Vilém (1989). Fuzzy Sets and Their Applications. Bristol: Adam Hilger. ISBN 0-85274-583-4.
- Klir, George J.; Yuan, Bo (1995). Fuzzy sets and fuzzy logic: theory and applications. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice Hall PTR. ISBN 0-13-101171-5.
- Klir, George J.; St Clair, Ute H.; Yuan, Bo (1997). Fuzzy set theory: foundations and applications. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice Hall. ISBN 0133410587.
- Meyer D, Hornik K (2009a). Generalized and Customizable Sets in R. Journal of Statistical Software, 31(2), 1-27. DOI https://doi.org/10.18637/jss.v031.i02
- Meyer D, Hornik K (2009b). sets: Sets, Generalized Sets, and Customizable Sets. R~package version~1.0, URL https://cran.r-project.org/package=sets.
AUTHOR
Jarek JasiewiczSOURCE CODE
Available at: r.fuzzy.set source code (history)
Latest change: Sunday Aug 17 09:42:07 2025 in commit: aaa98676c0950081a9d07c628b519a4300fedd44
Main index | Raster index | Topics index | Keywords index | Graphical index | Full index
© 2003-2025 GRASS Development Team, GRASS GIS 8.4.3dev Reference Manual