
NAME
v.fill.holes - Fill holes in areas by keeping only outer boundariesKEYWORDS
vector, geometry, fill, exterior, ring, perimeterSYNOPSIS
v.fill.holes
v.fill.holes --helpv.fill.holes input=name [layer=string] [cats=range] [where=sql_query] output=name [--overwrite] [--help] [--verbose] [--quiet] [--ui]
Flags:
- --overwrite
- Allow output files to overwrite existing files
- --help
- Print usage summary
- --verbose
- Verbose module output
- --quiet
- Quiet module output
- --ui
- Force launching GUI dialog
Parameters:
- input=name [required]
- Name of input vector map
- Or data source for direct OGR access
- layer=string
- Layer number or name
- Vector features can have category values in different layers. This number determines which layer to use. When used with direct OGR access this is the layer name.
- Default: 1
- cats=range
- Category values
- Example: 1,3,7-9,13
- where=sql_query
- WHERE conditions of SQL statement without 'where' keyword
- Example: income < 1000 and population >= 10000
- output=name [required]
- Name for output vector map
Table of contents
DESCRIPTION
v.fill.holes fills empty spaces inside areas, specifically it preserves areas with centroids while areas without centroids, which typically represent holes, are removed. v.fill.holes goes over all areas in a vector map and it preserves only outer boundaries of each area while removing inner boundaries which are considered holes. The holes become part of the area which contained them. No boundaries of these holes are preserved.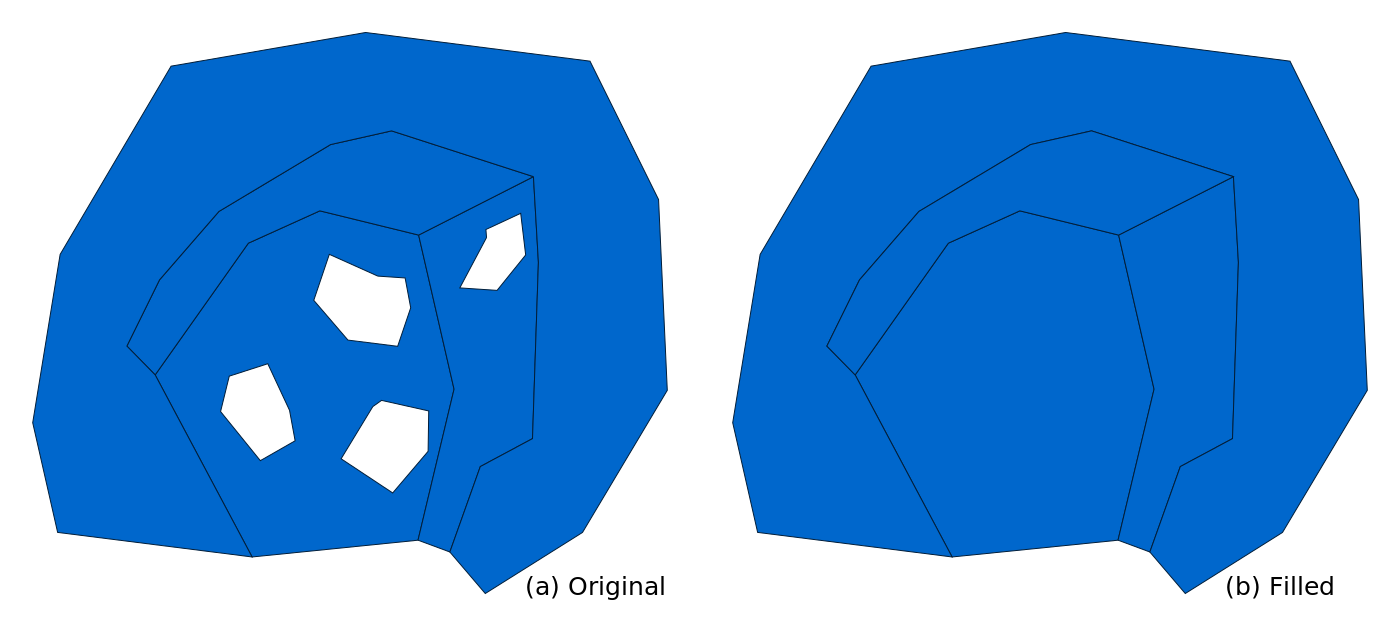
Figure: Holes inside areas are removed. (a) Original areas with holes and (b) the same areas but with holes filled.

Figure: Empty space in between two areas does not belong to either area, so it is filled only after the boundaries between areas are dissolved, i.e., areas merged into one. (a) Original areas with space in between, (b) one area with a hole after dissolving the common boundary, and (c) hole filled.
Topology
Strictly speaking, in the GRASS topological model, an area is a closed boundary (or a series of connected closed boundaries) which may have a centroid. If it has a centroid, it is rendered as a filled area in displays and this is what is usually considered an area from the user perspective. These are the areas where v.fill.holes preserves the associated outer boundary (or boundaries). Other closed boundaries, i.e., those without a centroid, are not carried over to the output. All other features are removed including points and lines.Attributes
If a specific layer is selected, attributes for that layer are preserved for the areas based on the category or categories associated with each area. By default, layer number 1 is selected. In case there are attribute tables associated with other layers or attributes associated with categories of other features than areas with centroids, this attribute data is not carried over to the output just like the corresponding geometries.EXAMPLE
The lakes vector map in the North Carolina sample dataset represents islands inside lakes as areas distinguished by attributes. To demonstrate v.fill.holes, we will first extract only the lakes which will create holes where the islands were located. Then, we will fill the holes created in the lakes to get the whole perimeter of the lakes including islands. Remove the islands by extracting everything else (results in holes):v.extract input=lakes where="FTYPE != 'ROCK/ISLAND'" output=lakes_only
v.fill.holes input=lakes_only output=lakes_filled

Figure: The filled lake (blue) and borders of the original lakes with islands removed (light blue). Figure shows a smaller area in the north of the data extent.
SEE ALSO
- v.dissolve for removing common boundaries based on attributes,
- v.clean for removing topological issues,
- r.fillnulls for filling empty spaces in raster maps using interpolation,
- r.fill.stats for filling empty spaces in raster maps using statistics.
AUTHOR
Vaclav Petras, NCSU Center for Geospatial Analytics, GeoForAll LabSOURCE CODE
Available at: v.fill.holes source code (history)
Latest change: Tuesday May 06 23:45:42 2025 in commit: 59db85624e4fd204e389e27e1ddc28028dd3edfc
Main index | Vector index | Topics index | Keywords index | Graphical index | Full index
© 2003-2025 GRASS Development Team, GRASS GIS 8.4.3dev Reference Manual