
NAME
r.colors.cubehelix - Create or apply a cubehelix color table to a GRASS raster mapKEYWORDS
raster, color table, cubehelix, seabornSYNOPSIS
r.colors.cubehelix
r.colors.cubehelix --helpr.colors.cubehelix [-dngae] [map=name[,name,...]] [output=name] [start=float] [nrotations=float] [gamma=float] [hue=float] [light=float] [dark=float] [ncolors=integer] [--overwrite] [--help] [--verbose] [--quiet] [--ui]
Flags:
- -d
- Generate discrete color table
- Generate discrete (interval) color table instead of a continuous one
- -n
- Reverse the order of colors (invert colors)
- If set, the color table will go from dark to light
- -g
- Logarithmic scaling
- -a
- Logarithmic-absolute scaling
- -e
- Histogram equalization
- --overwrite
- Allow output files to overwrite existing files
- --help
- Print usage summary
- --verbose
- Verbose module output
- --quiet
- Quiet module output
- --ui
- Force launching GUI dialog
Parameters:
- map=name[,name,...]
- Raster map(s) to apply color table to
- output=name
- Name for the new color table rules file
- start=float
- The hue at the start of the helix
- Options: 0-3
- Default: 0
- nrotations=float
- Rotations around the hue wheel
- Rotations around the hue wheel over the range of the color table
- Options: 0-3
- Default: 0.4
- gamma=float
- Gamma factor to emphasize darker (<1) or lighter (>1) colors
- Options: 0-
- Default: 1.0
- hue=float
- Saturation of the colors
- Options: 0-1
- Default: 0.8
- light=float
- Intensity of the lightest color in the color table
- Options: 0-1
- Default: 0.85
- dark=float
- Intensity of the darkest color in the color table
- Options: 0-1
- Default: 0.15
- ncolors=integer
- Number of colors in the color table
- Number of color intervals in a discrete color table with -d
- Options: 2-
- Default: 6
Table of contents
DESCRIPTION
The r.colors.cubehelix module generates a cubehelix color table and assigns it to given raster map if requested. The color table is generated using seaborn Python package. Several pararameters are available to control the cubehelix. When option map is specified r.colors.cubehelix assigns the color rules to the given raster map. The color tables is always stratched based on the range of values of the mapDepending on the use case, it may be advantageous to use the -d to discretize the color table into intervals.
NOTES
This module depends on seaborn which needs to be installed on your computer. Use your Python package manager (e.g. pip) or distribution package manager to install it.EXAMPLES
Creating a color table as GRASS color rules
We do 0.6 rotation around the axis and use discrete (interval) color table rather than the standard continuous. If we don't specify output file, it is printed to standard output:r.colors.cubehelix -d ncolors=5 nrotations=0.6
0.000% 218:222:192 20.000% 218:222:192 20.000% 198:166:136 40.000% 198:166:136 40.000% 173:108:112 60.000% 173:108:112 60.000% 119:61:98 80.000% 119:61:98 80.000% 48:28:59 100.000% 48:28:59
Setting color table for a raster map
Now we set several different color tables for the elevation raster map from the North Carolina sample dataset. We use continuous and discrete color tables (gradients). The color tables ae stretched to fit the raster map range.r.colors.cubehelix -d ncolors=8 nrotations=0.6 map=elevation
d.legend raster=elevation labelnum=10 at=5,50,7,10
r.colors.cubehelix nrotations=1.4 start=4 map=elevation
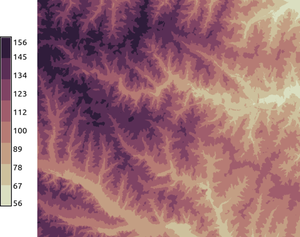
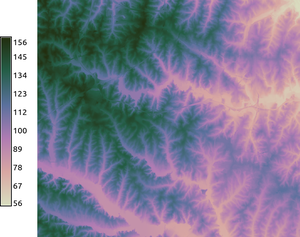
Setting color table for a vector map
First we create a text file with color rules:r.colors.cubehelix -i rot=0.6 output=cubehelix.txt
v.colors map=points rules=cubehelix.txt
REFERENCES
- Green, D. A., 2011, A colour scheme for the display of astronomical intensity images, Bulletin of the Astronomical Society of India, 39, 289.
SEE ALSO
r.colors, v.colors, r3.colors, r.cpt2grass, r.colors.matplotlib
seaborn
cubehelix_palette
function documentation and an
example
AUTHOR
Vaclav Petras, NCSU OSGeoREL
SOURCE CODE
Available at: r.colors.cubehelix source code (history)
Main index | Raster index | Topics index | Keywords index | Graphical index | Full index
© 2003-2020 GRASS Development Team, GRASS GIS 7.8.3dev Reference Manual