
NAME
r.convergence - Calculate convergence index.KEYWORDS
raster, terrainSYNOPSIS
Flags:
- -c
- Use circular window (default: square)
- -s
- Add slope convergence (radically slow down calculation time)
- --overwrite
- Allow output files to overwrite existing files
- --help
- Print usage summary
- --verbose
- Verbose module output
- --quiet
- Quiet module output
- --ui
- Force launching GUI dialog
Parameters:
- input=name [required]
- Digital elevation model map
- output=name [required]
- Output convergence index map
- window=integer [required]
- Window size
- Default: 3
- weights=string [required]
- Method for reducing the impact of the cell due to distance
- Options: standard, inverse, power, square, gentle
- Default: standard
Table of contents
OPTIONS
- -s
- Increase convergence if slope value is high. Slope parameter radically slow down computation time, especially if window parameter is high. If slope is used addational modifier is used according to formula: sin(current)*sin(target) + cos(current)*cos(target). if slope of current and target cells are equal. The modifier is 1. If not, the modifier is applied with formula: acos(cos(convergence) * modifier)
- -c
- use circular window instead of suqare (default)
- input
- Digital elevation model. Data can be of any type and any projection. To calculate relief convergnece, r.convergence uses real distance which is recalculated into cell distance, according formula:
distance_between_current_cell_and_traget_cell/distance_between_current_cell_and_nearest_neighbour_cell.It is important if convergence is calculated for large areas in LatLong projecton. - weights
- Parameter describing the reduction of the impact of the cell due to its distance, where distance in cells:
- standard:no decay
- inverse:distance modifier is calculated as 1/x
- power:distance modifier is calculated as 1/(x*x)
- power:distance modifier is calculated as 1/(x*x)
- gentle:distance modifier is calculated as 1/((1-x)/(1+x))
- window
- window size. Must be odd. For now there is no limits in window size. r.convergence uses window size instead of classical radius for compatibility with other GRASS programs.
- output
- Map of convergence index. The values ranges from -100 (max divergent, real peaks and ridges) by 0 (planar areas) to 100 (max convergent, real pits and channels). Classical convergence index presented with degrees (-90 to 90)
DESCRIPTION
How convergence index is calculated (3 x 3 window):
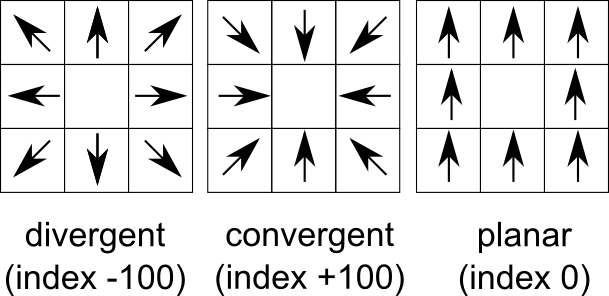
SEE ALSO
r.slope.aspect, r.param.scale, r.neighbour,REFERENCES
Claps, P., Fiorentino, M., Oliveto, G., (1994), Informational entropy of fractal river networks, Journal of Hydrology, 187(1-2), 145-156 .
Bauer J., Rohdenburg H., Bork H.-R., (1985), Ein Digitales Reliefmodell als Vorraussetzung fuer ein deterministisches Modell der Wasser- und Stoff-Fluesse, IN: Bork, H.-R., Rohdenburg, H., Landschaftsgenese und Landschaftsoekologie, Parameteraufbereitung fuer deterministische Gebiets-Wassermodelle, Grundlagenarbeiten zu Analyse von Agrar-Oekosystemen, 1-15.
Böhner J., Blaschke T., Montanarella, L. (eds.) (2008). SAGA Seconds Out. Hamburger Beiträge zur Physischen Geographie und Landschaftsökologie, 19: 113 s.
AUTHOR
Jarek JasiewiczSOURCE CODE
Available at: r.convergence source code (history)
Main index | Raster index | Topics index | Keywords index | Graphical index | Full index
© 2003-2020 GRASS Development Team, GRASS GIS 7.8.3dev Reference Manual