
Note: A new GRASS GIS stable version has been released: GRASS GIS 7.8, available here.
Updated manual page: here
NAME
g.parser - Provides full parser support for GRASS scripts.Table of contents
KEYWORDS
general, support, scriptsSYNOPSIS
g.parser --helpg.parser [-s] [-t] [-n] filename [argument,...]
Flags:
- -t
- Print strings for translation
- -s
- Write option values to standard output instead of reinvoking script
- -n
- Write option values to standard output separated by null character
DESCRIPTION
The g.parser module provides full parser support for GRASS scripts, including an auto-generated GUI interface, help page template, and command line option checking. In this way a simple script can very quickly be made into a full-fledged GRASS module.OPTIONS
Unless the -s or -n switch is used, the arguments are stored in environment variables for use in your scripts. These variables are named "GIS_FLAG_<NAME>" for flags and "GIS_OPT_<NAME>" for options. The names of variables are converted to upper case. For example if an option with key input was defined in the script header, the value will be available in variable GIS_OPT_INPUT and the value of flag with key f will be available in variable GIS_FLAG_F.For flags, the value will be "1" if the flag was given, and "0" otherwise.
If the -s or -n switch is used, the options and flags are written to standard output in the form opt_<name>=<value> and flag_<name>=<value>, preceded by the string @ARGS_PARSED@. If this string doesn't appear as the first line of standard output, it indicates that the script was invoked with a switch such as --html-description. In this case, the data written by g.parser to standard output should be copied to the script's standard output verbatim. If the -s switch is used, the options and flags are separated by newlines. If the -n switch is used, the options and flags are separated by null characters.
Typical header definitions are as follows:
#%module #% description: g.parser test script #%end #%flag #% key: f #% description: A flag #%end #%option #% key: raster #% type: string #% gisprompt: old,cell,raster #% description: Raster input map #% required: yes #%end
The parsers allows using predefined standardized options and flags, see the list of options and flags in the programmer manual. Eg. the option
#%option #% key: raster #% type: string #% gisprompt: old,cell,raster #% description: Raster input map #% required: yes #%end
#%option G_OPT_R_MAP #% key: raster #%end
#%rules #% exclusive: capfile_output, capfile #%end
#%rules #% required: raster, vector #%end
#%rules #% required: -i,-d,-c #%end
NOTES
An option can be instructed to allow multiple inputs by adding the following line:#% multiple: yes
IFS=,
for opt in $GIS_OPT_INPUT ; do
... "$opt"
done
A "guisection" field may be added to each option and flag to specify that the options should appear in multiple tabs in the auto-generated GUI. Any options without a guisection field go into the "Required" or "Options" tab. For example:
#% guisection: tabname
A "key_desc" field may be added to each option to specify the text that appears in the module's usage help section. For example:
#% key_desc: filename
If a script is run with --o, the parser will set GRASS_OVERWRITE=1, which has the same effect as passing --o to every module which is run from the script. Similarly, passing --q or --v will set GRASS_VERBOSE to 0 or 3 respectively, which has the same effect as passing --q or --v to every module which is run from the script. Rather than checking whether --o, --q or --v were used, you should be checking GRASS_OVERWRITE and/or GRASS_VERBOSE instead. If those variables are set, the script should behave the same way regardless of whether they were set by --o, --q or --v being passed to the script or set by other means.
Conditional parameters
Marking an option as "required" will result in the parser raising a fatal error if the option is not given, with one exception: if a flag has the suppress_required option, and that flag is given, all requirements are ignored. This feature is intended for flags which abandon "normal operation" for the module; e.g. r.in.gdal's -f flag (list supported formats) uses it.But in general, an option cannot be marked as required if it is optional except for the special case of a suppress_required flag. The parser has the ability to specify option relationships.
For C, the relevant functions are those in lib/gis/parser_dependencies.c.
For scripts, relationships are specified using a "rules" section, e.g.
#%rules #% required: altitude,elevation #%end
- exclusive: at most one of the options may be given
- required: at least one of the options must be given
- requires: if the first option is given, at least one of the subsequent options must also be given
- requires_all: if the first option is given, all of the subsequent options must also be given
- excludes: if the first option is given, none of the subsequent options may be given
- collective: all or nothing; if any option is given, all must be given
AUTOMATED SCRIPT CREATION
The flag --script added to a GRASS command, generates shell output. To write out a g.parser boilerplate for easy prototyping of Python scripts, the flag --script can be added to any GRASS command. Example:v.in.db --script
Help page template (HTML)
The flag --html-description added to a GRASS command generates a related help page template in HTML. Example:v.in.db --html-description
GUI window parser (XML)
The flag --interface-description added to a GRASS command generates a related help page template in XML. Example:v.in.db --interface-description
Web Processing Service (WPS)
The flag --wps-process-description added to a GRASS command generates a Web Processing Service process description. Example:v.in.db --wps-process-description
reStructuredText
The flag --rst-description added to a GRASS command generates module interface description in reStructuredText, a lightweight markup language. Example:v.in.db --rst-description
TRANSLATION
g.parser provides some support for translating the options of scripts. If called with the -t switch before the script filename like thisg.parser -t somescriptfile
EXAMPLES
All examples below autogenerate the graphical user interface when invoked without parameters of flags:
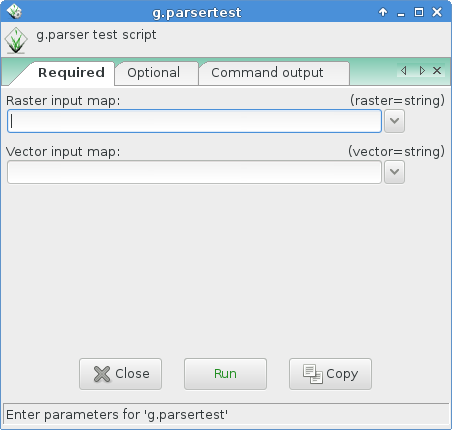
To run properly, the script needs to be copied into a directory listed in $GRASS_ADDON_PATH environmental variable with the executable flag being set.
The script will provide a GUI (as above) and the following usage help text:
test.py|sh|pl --help Description: g.parser test script (python) Usage: test.sh [-f] raster=string vector=string [option1=string] [--verbose] [--quiet] Flags: -f A flag --v Verbose module output --q Quiet module output Parameters: raster Raster input map vector Vector input map option1 An option
Example code for Python
#!/usr/bin/env python
# g.parser demo script for python programming
#%module
#% description: g.parser test script (python)
#% keyword: keyword1
#% keyword: keyword2
#%end
#%flag
#% key: f
#% description: A flag
#%end
#%option G_OPT_R_MAP
#% key: raster
#% required: yes
#%end
#%option G_OPT_V_MAP
#% key: vector
#%end
#%option
#% key: option1
#% type: string
#% description: An option
#% required: no
#%end
import os
import sys
import grass.script as grass
def main():
flag_f = flags['f']
option1 = options['option1']
raster = options['raster']
vector = options['vector']
#### add your code here ####
if flag_f:
print "Flag -f set"
else:
print "Flag -f not set"
# test if parameter present:
if option1:
print "Value of option1 option: '%s'" % option1
print "Value of raster option: '%s'" % raster
print "Value of vector option: '%s'" % vector
#### end of your code ####
return 0
if __name__ == "__main__":
options, flags = grass.parser()
sys.exit(main())
Example code for SHELL
#!/bin/sh
# g.parser demo script for shell programming
#%module
#% description: g.parser test script (shell)
#%end
#%flag
#% key: f
#% description: A flag
#%end
#%option G_OPT_R_MAP
#% key: raster
#% required: yes
#%end
#%option G_OPT_V_MAP
#% key: vector
#%end
#%option
#% key: option1
#% type: string
#% description: An option
#% required: no
#%end
if [ -z "$GISBASE" ] ; then
echo "You must be in GRASS GIS to run this program." 1>&2
exit 1
fi
if [ "$1" != "@ARGS_PARSED@" ] ; then
exec g.parser "$0" "$@"
fi
#### add your code below ####
echo ""
if [ $GIS_FLAG_F -eq 1 ] ; then
g.message message="Flag -f set"
else
g.message message="Flag -f not set"
fi
# test if parameter present:
if [ -n "$GIS_OPT_OPTION1" ] ; then
echo "Value of GIS_OPT_OPTION1: '$GIS_OPT_OPTION1'"
fi
g.message message="Value of GIS_OPT_option1: '$GIS_OPT_option1'"
g.message message="Value of GIS_OPT_raster: '$GIS_OPT_raster'"
g.message message="Value of GIS_OPT_vect: '$GIS_OPT_vector'"
#### end of your code ####
Example code for Perl
#!/usr/bin/perl -w
use strict;
# g.parser demo script
#%module
#% description: g.parser test script (perl)
#% keyword: keyword1
#% keyword: keyword2
#%end
#%flag
#% key: f
#% description: A flag
#%end
#%option G_OPT_R_MAP
#% key: raster
#% required: yes
#%end
#%option G_OPT_V_MAP
#% key: vector
#%end
#%option
#% key: option1
#% type: string
#% description: An option
#% required: no
#%end
if ( !$ENV{'GISBASE'} ) {
printf(STDERR "You must be in GRASS GIS to run this program.\n");
exit 1;
}
if( $ARGV[0] ne '@ARGS_PARSED@' ){
my $arg = "";
for (my $i=0; $i < @ARGV;$i++) {
$arg .= " $ARGV[$i] ";
}
system("$ENV{GISBASE}/bin/g.parser $0 $arg");
exit;
}
#### add your code here ####
print "\n";
if ( $ENV{'GIS_FLAG_F'} eq "1" ){
print "Flag -f set\n"
}
else {
print "Flag -f not set\n"
}
printf ("Value of GIS_OPT_option1: '%s'\n", $ENV{'GIS_OPT_OPTION1'});
printf ("Value of GIS_OPT_raster: '%s'\n", $ENV{'GIS_OPT_RASTER'});
printf ("Value of GIS_OPT_vect: '%s'\n", $ENV{'GIS_OPT_VECTOR'});
#### end of your code ####
Easy creation of a script
By using the --script flag with any GRASS GIS module (must be run in a GRASS GIS session) header, description, keywords, parameters, flags and a template main Python script section will be printed in the terminal which can be saved to a file and used for further script programming.In this example, the module v.what.rast is used as an example. The output is shown below:
v.what.rast --script
#!/usr/bin/env python
############################################################################
#
# MODULE: v.what.rast_wrapper
# AUTHOR(S): username
# PURPOSE: Wrapper for v.what.rast
# COPYRIGHT: (C) 2017 by username, and the GRASS Development Team
#
# This program is free software; you can redistribute it and/or modify
# it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by
# the Free Software Foundation; either version 2 of the License, or
# (at your option) any later version.
#
# This program is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
# but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
# MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the
# GNU General Public License for more details.
#
############################################################################
#%module
#% description: Uploads raster values at positions of vector points to the table.
#% keyword: vector, sampling, raster, position, querying, attribute table, surface information
#%end
#%flag
#% key: i
#% description: Interpolate values from the nearest four cells
#%end
#%flag
#% key: p
#% description: Print categories and values instead of updating the database
#%end
#%option
#% key: map
#% type: string
#% required: yes
#% multiple: no
#% key_desc: name
#% label: Name of vector points map for which to edit attributes
#% description: Or data source for direct OGR access
#% gisprompt: old,vector,vector
#%end
#%option
#% key: layer
#% type: string
#% required: no
#% multiple: no
#% label: Layer number or name
#% description: Vector features can have category values in different layers. This number determines which layer to use. When used with direct OGR access this is the layer name.
#% answer: 1
#% gisprompt: old,layer,layer
#%end
#%option
#% key: type
#% type: string
#% required: no
#% multiple: yes
#% options: point,centroid
#% description: Input feature type
#% answer: point
#%end
#%option
#% key: raster
#% type: string
#% required: yes
#% multiple: no
#% key_desc: name
#% description: Name of existing raster map to be queried
#% gisprompt: old,cell,raster
#%end
#%option
#% key: column
#% type: string
#% required: no
#% multiple: no
#% key_desc: name
#% description: Name of attribute column to be updated with the query result
#% gisprompt: old,dbcolumn,dbcolumn
#%end
#%option
#% key: where
#% type: string
#% required: no
#% multiple: no
#% key_desc: sql_query
#% label: WHERE conditions of SQL statement without 'where' keyword
#% description: Example: income < 1000 and population >= 10000
#%end
import sys
import grass.script as grass
def main():
# put code here
return 0
if __name__ == "__main__":
options, flags = grass.parser()
sys.exit(main())
SEE ALSO
g.filename, g.findfile, g.tempfileOverview table: Parser standard options
Related Wiki pages: Using GRASS GIS with other programming languages
AUTHOR
Glynn ClementsLast changed: $Date$
SOURCE CODE
Available at: g.parser source code (history)
Note: A new GRASS GIS stable version has been released: GRASS GIS 7.8, available here.
Updated manual page: here
Main index | General index | Topics index | Keywords index | Graphical index | Full index
© 2003-2020 GRASS Development Team, GRASS GIS 7.6.2dev Reference Manual