Note: This document is for an older version of GRASS GIS that has been discontinued. You should upgrade, and read the current manual page.

NAME
r.shade - Drapes a color raster over an shaded relief or aspect map.KEYWORDS
raster, elevation, relief, hillshade, visualizationSYNOPSIS
Flags:
- -c
- Use colors from color tables for NULL values
- --overwrite
- Allow output files to overwrite existing files
- --help
- Print usage summary
- --verbose
- Verbose module output
- --quiet
- Quiet module output
- --ui
- Force launching GUI dialog
Parameters:
- shade=name [required]
- Name of shaded relief or aspect raster map
- color=name [required]
- Name of raster to drape over relief raster map
- Typically, this raster is elevation or other colorful raster
- output=name [required]
- Name of shaded raster map
- brighten=integer
- Percent to brighten
- Options: -99-99
- Default: 0
- bgcolor=name
- Color to use instead of NULL values
- Either a standard color name, R:G:B triplet, or "none"
Table of contents
DESCRIPTION
r.shade will drape a color raster map over a shaded relief map. In place of shaded relief, any raster map can be used including aspect or slope. The color raster map is usually an elevation raster map with colorful color table (as opposed to gray scale color table). However, any raster map can be used including categorical raster maps. The result is a raster map created from elevation and the shade raster.Comparing to creating shaded relief as semi-transparent overlay on the color raster map, this module gives result with more saturated colors.
The input for this module can be created for example using r.slope.aspect or r.relief.
NULL values are propagated by default, so if any of the two input rasters contains NULL cell NULL will be also in the output. If -c flag is used and cell in color raster is NULL, just shade color is used. If cell in shade raster is NULL, shading effect is not applied and original colors are used. If bgcolor option is used, NULL value in any input raster will be in the output replaced by the given color.
NOTES
Refer to the r.his help page for more details; r.shade is a frontend to that module with addition of brightness support similar to one provided by d.shade. However, note that the brightness is not implemenented in the same way as for d.shade and the results might be different. r.shade is using method described in r.his manual page.EXAMPLES
In this example, the aspect map in the North Carolina sample dataset location is used to hillshade the elevation map:g.region raster=aspect -p r.shade shade=aspect color=elevation output=elevation_aspect_shaded d.mon wx0 d.rast elevation_aspect_shaded
g.region raster=elevation
r.relief input=elevation output=elevation_shaded_relief
r.shade shade=elevation_shaded_relief color=elevation \
output=elevation_relief_shaded
d.mon wx1
d.rast elevation_relief_shaded
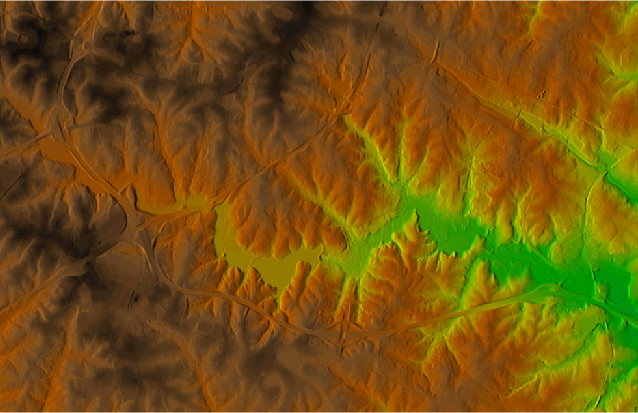
Figure: A detail of raster created by applying shading effect of shaded relief (hillshade) to elevation raster map from North Carolina dataset elevation map
SEE ALSO
r.his, d.his, d.shade, g.pnmcomp, r.slope.aspect, r.reliefAUTHORS
Hamish BowmanVaclav Petras, NCSU OSGeoREL
Inspired by d.shade and manual for r.his.
SOURCE CODE
Available at: r.shade source code (history)
Latest change: Monday Nov 18 20:15:32 2019 in commit: 1a1d107e4f6e1b846f9841c2c6fabf015c5f720d
Main index | Raster index | Topics index | Keywords index | Graphical index | Full index
© 2003-2023 GRASS Development Team, GRASS GIS 7.8.9dev Reference Manual