
NAME
r.sim.terrain - Dynamic landscape evolution modelKEYWORDS
raster, terrain, landscape, evolutionSYNOPSIS
Flags:
- -f
- Fill depressions
- --overwrite
- Allow output files to overwrite existing files
- --help
- Print usage summary
- --verbose
- Verbose module output
- --quiet
- Quiet module output
- --ui
- Force launching GUI dialog
Parameters:
- elevation=name [required]
- Name of input elevation raster map
- runs=string [required]
- Run for a single rainfall event or a series of events
- Options: event, series
- Default: event
- event: single rainfall event
- series: series of rainfall events
- mode=string [required]
- SIMWE erosion deposition, USPED transport limited, or RUSLE 3D detachment limited mode
- Options: simwe_mode, usped_mode, rusle_mode
- Default: simwe_mode
- simwe_mode: SIMWE erosion deposition mode
- usped_mode: USPED transport limited mode
- rusle_mode: RUSLE 3D detachment limited mode
- rain_intensity=integer
- Rainfall intensity in mm/hr
- Default: 50
- rain_duration=integer
- Total duration of storm event in minutes
- Default: 60
- precipitation=name
- Precipitation file
- Name of input precipitation file
- k_factor=name
- K factor
- Soil erodibility factor
- k_factor_value=float
- K factor constant
- Soil erodibility constant
- Default: 0.25
- c_factor=name
- C factor
- Land cover factor
- c_factor_value=float
- C factor constant
- Land cover constant
- Default: 0.1
- m=float
- Water flow exponent
- Default: 1.5
- n=float
- Slope exponent
- Default: 1.2
- walkers=integer
- Number of walkers (max = 7000000)
- Default: 1000000
- runoff=name
- Runoff coefficient
- Runoff coefficient (0.6 for bare earth, 0.35 for grass or crops, 0.5 for shrubs and trees, 0.25 for forest, 0.95 for roads)
- runoff_value=float
- Runoff coefficient
- Runoff coefficient (0.6 for bare earth, 0.35 for grass or crops, 0.5 for shrubs and trees, 0.25 for forest, 0.95 for roads)
- Default: 0.35
- mannings=name
- Manning's roughness coefficient
- mannings_value=float
- Manning's roughness coefficient
- Default: 0.04
- detachment=name
- Detachment coefficient
- detachment_value=float
- Detachment coefficient
- Default: 0.01
- transport=name
- Transport coefficient
- transport_value=float
- Transport coefficient
- Default: 0.01
- shearstress=name
- Shear stress coefficient
- shearstress_value=float
- Shear stress coefficient
- Default: 0.0
- density=name
- Sediment mass density
- Sediment mass density in g/cm^3
- density_value=float
- Sediment mass density
- Sediment mass density in g/cm^3
- Default: 1.4
- mass=name
- Mass of sediment per unit area
- Mass of sediment per unit area in kg/m^2
- mass_value=float
- Mass of sediment per unit area
- Mass of sediment per unit area in kg/m^2
- Default: 116.
- grav_diffusion=float
- Gravitational diffusion coefficient
- Gravitational diffusion coefficient in m^2/s
- Default: 0.1
- erdepmin=float
- Minimum values for erosion-deposition
- Minimum values for erosion-deposition in kg/m^2s
- Default: -0.5
- erdepmax=float
- Maximum values for erosion-deposition
- Maximum values for erosion-deposition in kg/m^2s
- Default: 0.5
- start=string [required]
- Start time in year-month-day hour:minute:second format
- Default: 2016-01-01 00:00:00
- rain_interval=integer [required]
- Time interval between evolution events in minutes
- Default: 1
- temporaltype=name [required]
- The temporal type of the space time dataset
- Options: absolute, relative
- Default: absolute
- threads=integer
- Number of threads for multiprocessing
- Default: 1
- elevation_timeseries=name [required]
- Name of the output space time raster dataset
- Default: elevation_timeseries
- depth_timeseries=name
- Name of the output space time raster dataset
- Default: depth_timeseries
- erdep_timeseries=name
- Name of the output space time raster dataset
- Default: erdep_timeseries
- flux_timeseries=name
- Name of the output space time raster dataset
- Default: flux_timeseries
- difference_timeseries=name
- Name of the output space time raster dataset
- Default: difference_timeseries
Table of contents
DESCRIPTION
r.sim.terrain is a short-term landscape evolution model that simulates topographic change for both steady state and dynamic flow regimes across a range of spatial scales. It uses empirical models (RUSLE3D & USPED) for soil erosion at watershed to regional scales and a physics-based model (SIMWE) for shallow overland water flow and soil erosion at subwatershed scales to compute short-term topographic change. This either steady state or dynamic model simulates how overland sediment mass flows reshape topography for a range of hydrologic soil erosion regimes based on topographic, land cover, soil, and rainfall parameters.
EXAMPLES
Basic instructions
A basic example for the North Carolina sample dataset. Install the add-on module r.sim.terrain. Copy the raster elevation map elev_lid792_1m from the PERMANENT mapset to the current mapset. Set the region to this elevation map at 1 meter resolution. Run r.sim.terrain with the RUSLE model for a 120 min event with a rainfall intensity of 50 mm/hr at a 3 minute interval. Set the empirical coefficients m and n to 0.4 and 1.3 respectively. Use the `-f` flag to fill depressions in order to reduce the effect of positive feedback loops.g.extension extension=r.sim.terrain g.copy raster=elev_lid792_1m@PERMANENT,elevation g.region raster=elev_lid792_1m res=1 r.sim.terrain -f elevation=elevation runs=event mode=rusle_mode rain_intensity=50.0 rain_duration=120 rain_interval=3 m=0.4 n=1.3
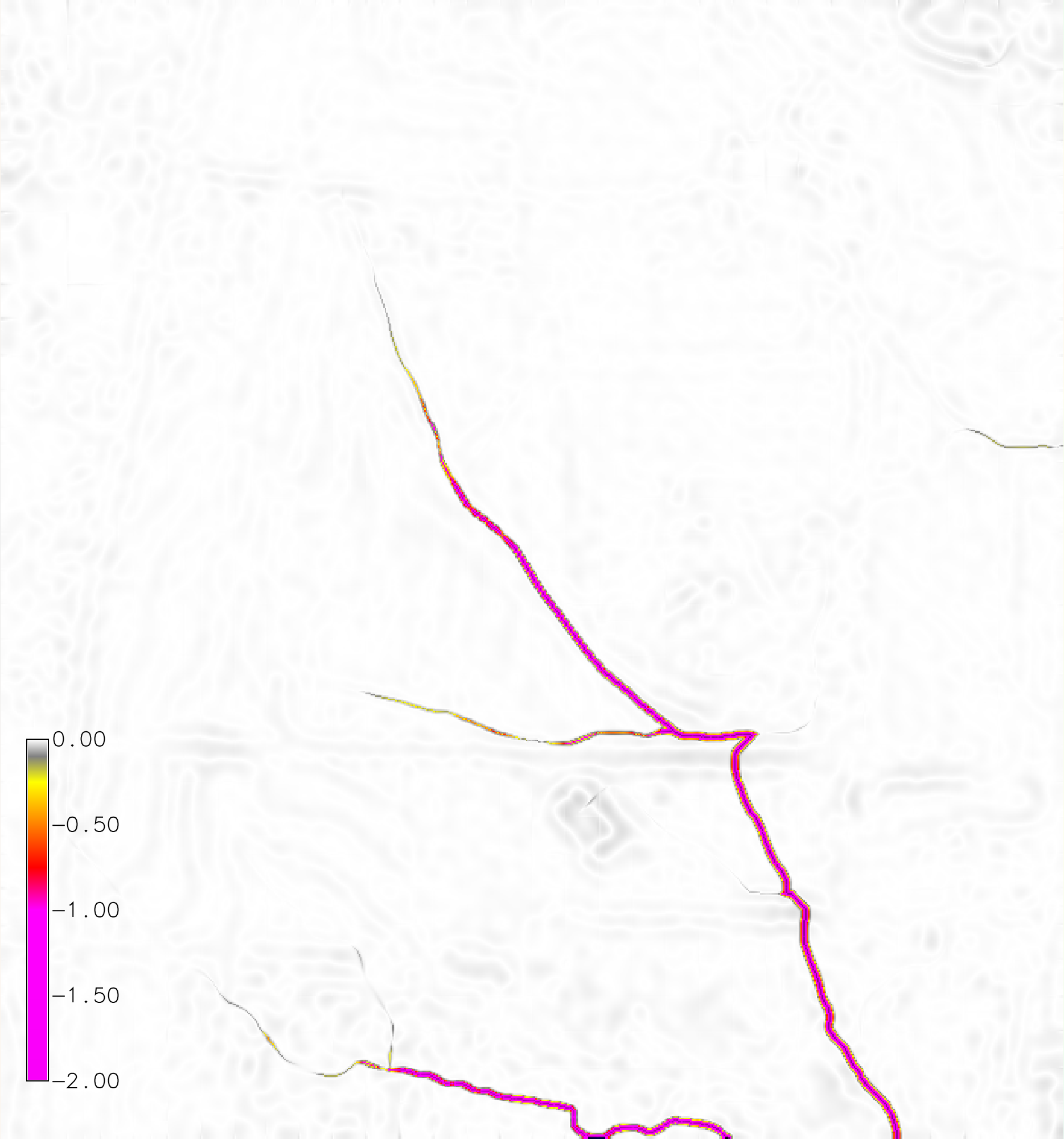
Figure: Net difference (m) for a dynamic RUSLE simulation of a 120 min event with a rainfall intensity of 50 mm/hr with a 3 minute interval.
Spatially variable soil and landcover
Clone or download the landscape evolution sample dataset with a time series of lidar-based digital elevation models and orthoimagery for a highly eroded subwatershed of Patterson Branch Creek, Fort Bragg, NC, USA.
Run r.sim.terrain with the simwe model for a 120 min event with a rainfall intensity of 50 mm/hr. Use a transport value lower than the detachment value to trigger a transport limited erosion regime. Use the -f flag to fill depressions in order to reduce the effect of positive feedback loops.
g.mapset -c mapset=transport location=nc_spm_evolution g.region region=region res=1 r.mask vector=watershed g.copy raster=elevation_2016@PERMANENT,elevation_2016 r.sim.terrain -f elevation=elevation_2016 runs=event mode=simwe_mode \ rain_intensity=50.0 rain_interval=120 rain_duration=10 walkers=1000000 \ detachment_value=0.01 transport_value=0.0001 manning=mannings runoff=runoff
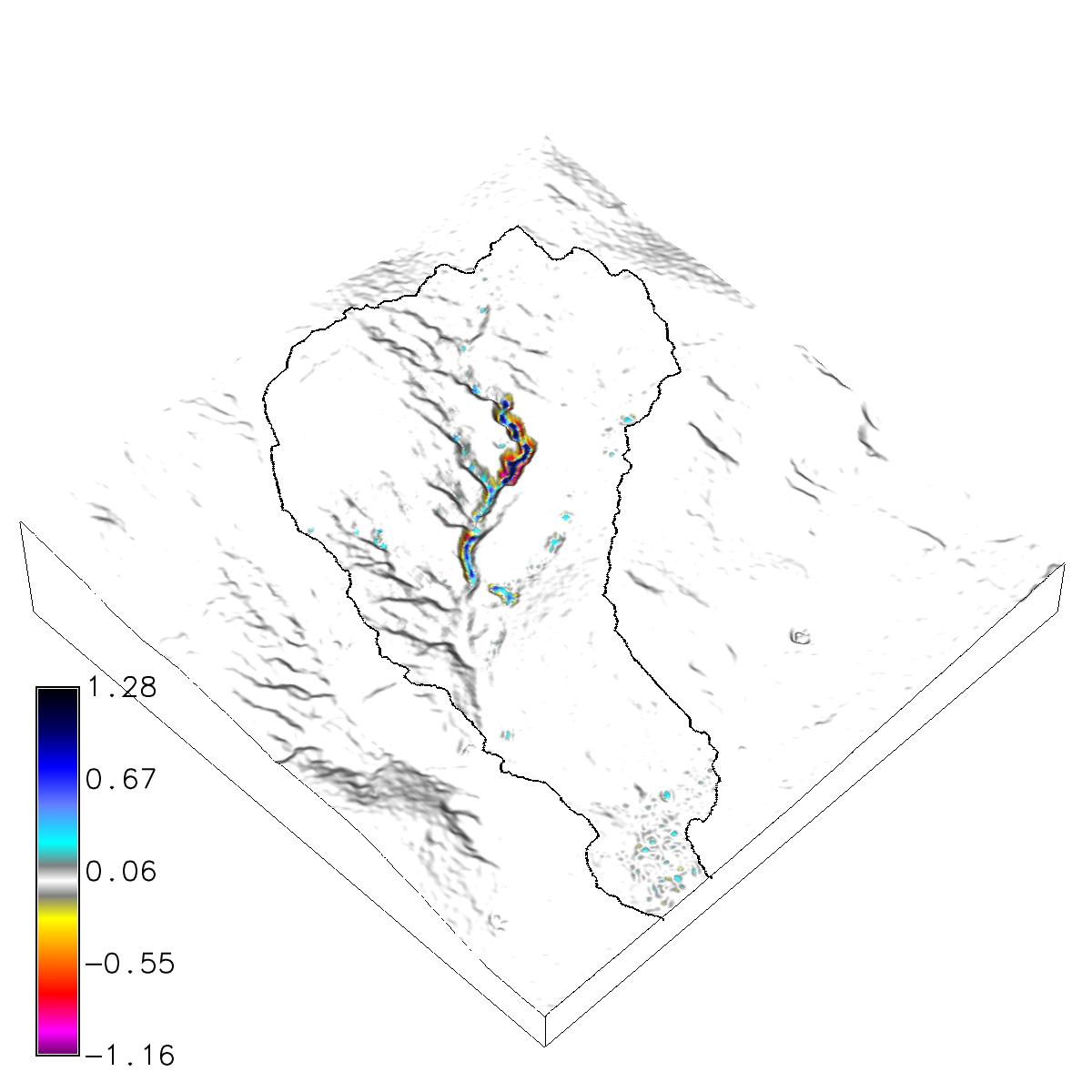
Figure: Net difference (m) for a steady state, transport limited SIMWE simulation of a 120 min event with a rainfall intensity of 50 mm/hr.
ERROR MESSAGES
If the module fails withERROR: Unable to insert dataset of type raster in the temporal database. The mapset of the dataset does not match the current mapset.
REFERENCES
- Harmon, B. A., Mitasova, H., Petrasova, A., and Petras, V.: r.sim.terrain 1.0: a landscape evolution model with dynamic hydrology, Geosci. Model Dev., 12, 2837–2854, https://doi.org/10.5194/gmd-12-2837-2019, 2019.
- Mitasova H., Barton M., Ullah I., Hofierka J., Harmon R.S., 2013. 3.9 GIS-Based Soil Erosion Modeling. In J. F. Shroder, ed. Treatise on Geomorphology. San Diego: Academic Press, pp. 228-258. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-374739-6.00052-X.
SEE ALSO
r.sim.water, r.sim.sedimentAUTHOR
Brendan A. Harmon
Louisiana State University
brendan.harmon@gmail.com
SOURCE CODE
Available at: r.sim.terrain source code (history)
Latest change: Thu Feb 3 09:32:35 2022 in commit: f17c792f5de56c64ecfbe63ec315307872cf9d5c
Main index | Raster index | Topics index | Keywords index | Graphical index | Full index
© 2003-2022 GRASS Development Team, GRASS GIS 8.0.3dev Reference Manual