
Note: This document is for an older version of GRASS GIS that will be discontinued soon. You should upgrade, and read the current manual page.
NAME
r.grow.distance - Generates a raster map containing distances to nearest raster features and/or the value of the nearest non-null cell.KEYWORDS
raster, distance, proximitySYNOPSIS
Flags:
- -m
- Output distances in meters instead of map units
- -n
- Calculate distance to nearest NULL cell
- --overwrite
- Allow output files to overwrite existing files
- --help
- Print usage summary
- --verbose
- Verbose module output
- --quiet
- Quiet module output
- --ui
- Force launching GUI dialog
Parameters:
- input=name [required]
- Name of input raster map
- distance=name
- Name for distance output raster map
- value=name
- Name for value output raster map
- metric=string
- Metric
- Options: euclidean, squared, maximum, manhattan, geodesic
- Default: euclidean
- minimum_distance=float
- Minimum distance threshold
- maximum_distance=float
- Maximum distance threshold
Table of contents
DESCRIPTION
r.grow.distance generates raster maps representing the distance to the nearest non-null cell in the input map and/or the value of the nearest non-null cell.NOTES
The flag -n calculates the respective pixel distances to the nearest NULL cell.The user has the option of specifying five different metrics which control the geometry in which grown cells are created, (controlled by the metric parameter): Euclidean, Squared, Manhattan, Maximum, and Geodesic.
The Euclidean distance or Euclidean metric is the "ordinary" distance between two points that one would measure with a ruler, which can be proven by repeated application of the Pythagorean theorem. The formula is given by:
d(dx,dy) = sqrt(dx^2 + dy^2)
The Squared metric is the Euclidean distance squared, i.e. it simply omits the square-root calculation. This may be faster, and is sufficient if only relative values are required.
The Manhattan metric, or Taxicab geometry, is a form of geometry in which the usual metric of Euclidean geometry is replaced by a new metric in which the distance between two points is the sum of the (absolute) differences of their coordinates. The name alludes to the grid layout of most streets on the island of Manhattan, which causes the shortest path a car could take between two points in the city to have length equal to the points' distance in taxicab geometry. The formula is given by:
d(dx,dy) = abs(dx) + abs(dy)
The Maximum metric is given by the formula
d(dx,dy) = max(abs(dx),abs(dy))
The Geodesic metric is calculated as geodesic distance, to be used only in latitude-longitude locations. It is recommended to use it along with the -m flag in order to output distances in meters instead of map units.
If minimum_distance is given, all cells with a distance smaller than minimum_distance will be set to NULL.
If maximum_distance is given, all cells with a distance larger than maximum_distance will be set to NULL. The resultant output is equivalent to a buffer.
If both minimum_distance and maximum_distance are given, the result will be similar to a doughnut, a restricted belt for a given distance range. All cells outside this distance range will be set to NULL.
EXAMPLES
Distance from the streams network
North Carolina sample dataset:g.region raster=streams_derived -p r.grow.distance input=streams_derived distance=dist_from_streams r.colors map=dist_from_streams color=rainbow
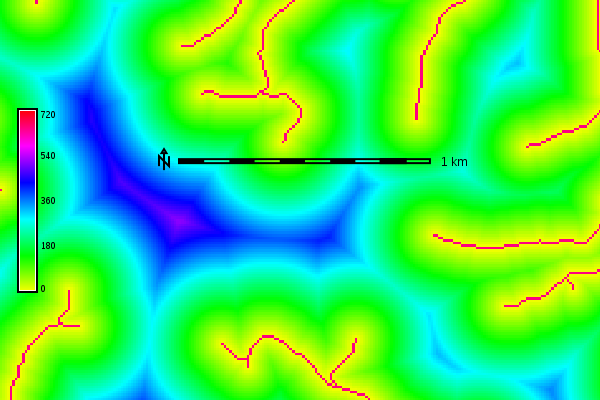
Euclidean distance from the streams network in meters (map subset)
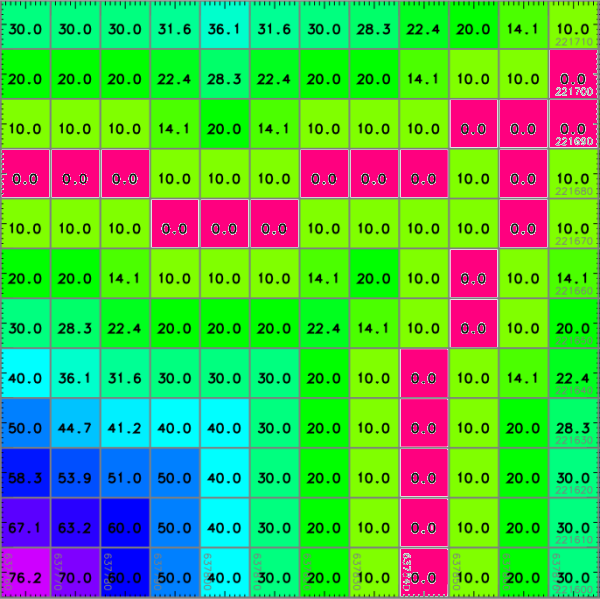
Euclidean distance from the streams network in meters (detail, numbers shown with d.rast.num)
Distance from sea in meters in latitude-longitude location
g.region raster=sea -p r.grow.distance -m input=sea distance=dist_from_sea_geodetic metric=geodesic r.colors map=dist_from_sea_geodetic color=rainbow
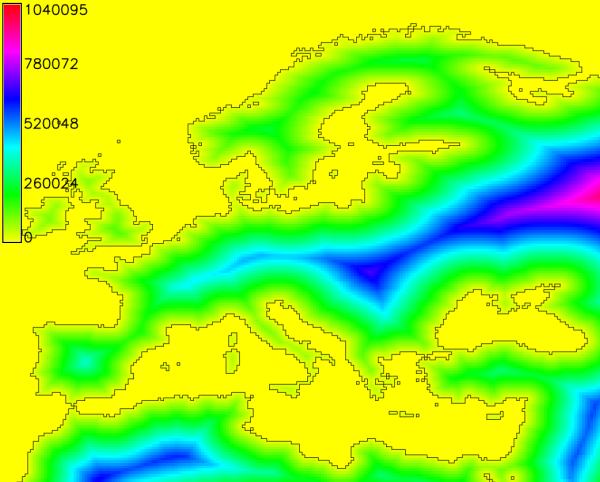
Geodesic distances to sea in meters
SEE ALSO
r.grow, r.distance, r.buffer, r.cost, r.patch
Wikipedia Entry:
Euclidean Metric
Wikipedia Entry:
Manhattan Metric
AUTHOR
Glynn ClementsSOURCE CODE
Available at: r.grow.distance source code (history)
Latest change: Thursday Feb 03 11:10:06 2022 in commit: 547ff44e6aecfb4c9cbf6a4717fc14e521bec0be
Note: This document is for an older version of GRASS GIS that will be discontinued soon. You should upgrade, and read the current manual page.
Main index | Raster index | Topics index | Keywords index | Graphical index | Full index
© 2003-2023 GRASS Development Team, GRASS GIS 8.2.2dev Reference Manual