
Note: This document is for an older version of GRASS GIS that will be discontinued soon. You should upgrade, and read the current manual page.
NAME
r3.cross.rast - Creates cross section 2D raster map from 3D raster map based on 2D elevation mapKEYWORDS
raster3d, profile, raster, voxelSYNOPSIS
r3.cross.rast
r3.cross.rast --helpr3.cross.rast [-m] input=string elevation=string output=string [--overwrite] [--help] [--verbose] [--quiet] [--ui]
Flags:
- -m
- Use 3D raster mask (if exists) with input map
- --overwrite
- Allow output files to overwrite existing files
- --help
- Print usage summary
- --verbose
- Verbose module output
- --quiet
- Quiet module output
- --ui
- Force launching GUI dialog
Parameters:
- input=string [required]
- Input 3D raster map for cross section
- elevation=string [required]
- 2D elevation map used to create the cross section map
- output=string [required]
- Resulting cross section 2D raster map
Table of contents
DESCRIPTION
This module creates a cross section 2D map from one 3D raster volume map based on a 2D elevation map. It checks if the value of the elevation map is located in the z-coordinate space of the 3D map. If so, the 3D voxel value for this position is transferred to the related cross section output map cell, otherwise the NULL value is set.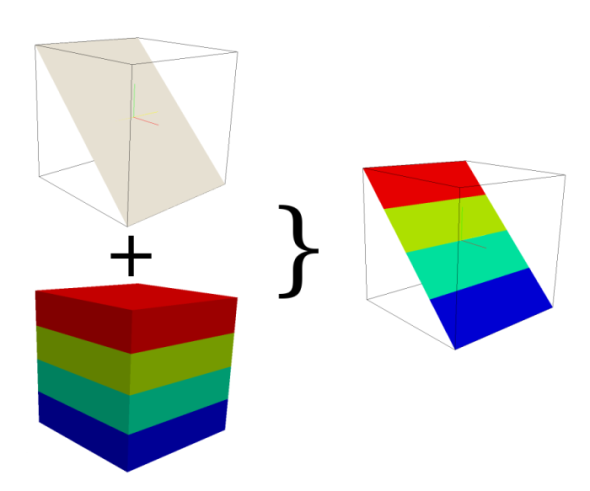
If the 2D and 3D region settings are different, the 2D resolution will be adjust to the 3D resolution.
NOTES
To create a cut plane elevation map use r.mapcalc. Some examples:- To create a cut plane elevation map in x direction type
r.mapcalc "cutplane = col()*x",
x be the value for the elevation. If the range of col() is 1 ... 10, the elevation map has the range 1 ... 10 if x == 1 and if x == 10 the range 10 ... 100 - To create a cut plane elevation map in y direction type
r.mapcalc "cutplane = row()*x",
x be the value for the elevation. If the range of col() is 1 ... 10, the elevation map has the range 1 ... 10 if x == 1 and if x == 10 the range 10 ... 100 - The user can also make a cut in y and x direction with r.mapcalc by
using
r.mapcalc "cutplane = (row()+col())*x"
EXAMPLES
Simple Spearfish example
g.region -d g.region res=150 res3=150 t=1000 b=0 tbres=100 # synthetic data, could be geological structures: r3.mapcalc "map3d = sin(row())+sin(col())+sin(depth()*depth())" #create a cutplane map r.mapcalc "cutplane = col()*10" #create the cross section map r3.cross.rast input=map3d elevation=cutplane output=crosssection
SEE ALSO
g.region, r.mapcalc, r3.mapcalc, r3.to.rastAUTHOR
Sören GebbertSOURCE CODE
Available at: r3.cross.rast source code (history)
Latest change: Thursday Feb 03 11:10:06 2022 in commit: 547ff44e6aecfb4c9cbf6a4717fc14e521bec0be
Note: This document is for an older version of GRASS GIS that will be discontinued soon. You should upgrade, and read the current manual page.
Main index | 3D raster index | Topics index | Keywords index | Graphical index | Full index
© 2003-2023 GRASS Development Team, GRASS GIS 8.2.2dev Reference Manual