Note: This document is for an older version of GRASS GIS that has been discontinued. You should upgrade, and read the current manual page.

NAME
r.boxplot - Draws the boxplot of raster values. Optionally, this is done per category of a zonal raster layerKEYWORDS
display, raster, plot, boxplotSYNOPSIS
Flags:
- -o
- Include outliers
- Draw boxplot(s) with outliers
- -n
- Draw notches
- Draw boxplot(s) with notch
- -h
- Horizontal boxplot(s)
- Draw the boxplot horizontal
- -s
- Show category numbers
- Show the category numbers of the zonal map
- -c
- Zonal colors
- Color boxploxs using the colors of the categories of the zonal raster
- --overwrite
- Allow output files to overwrite existing files
- --help
- Print usage summary
- --verbose
- Verbose module output
- --quiet
- Quiet module output
- --ui
- Force launching GUI dialog
Parameters:
- map=name [required]
- Name of raster map
- zones=name
- Zonal raster
- categorical map with zones
- output=name
- Name of output image file
- Name for output file
- plot_dimensions=string
- Plot dimensions (width,height)
- Dimensions (width,height) of the figure in inches
- fontsize=integer
- Font size
- Default font size
- Default: 10
- dpi=integer
- DPI
- resolution of plot
- map_outliers=string
- Name of outlier map
- Create a vector point layer of outliers
- range=float
- Range (value > 0)
- this determines how far the plot whiskers extend out from the box. If range is positive, the whiskers extend to the most extreme data point which is no more than range times the interquartile range from the box. A value of zero causes the whiskers to extend to the data extremes.
- Default: 1.5
- raster_statistics=string[,string,...]
- Plot the raster median and IQR
- Options: median, IQR
- order=string
- Sort boxplots
- Sort boxplots based on their median values
- Options: descending, ascending
- rotate_labels=float
- Rotate labels
- Rotate labels (degrees)
- Options: -90-90
- raster_stat_color=name
- Color of the raster IQR and median
- Color of raster IQR and median
- Default: grey
- raster_stat_alpha=float
- Transparency of the raster IQR band
- Options: 0-1
- Default: 0.2
- bx_color=name
- Color of the boxplots
- Color of boxplots
- Default: white
- bx_width=float
- Boxplot width
- The width of the boxplots (0,1])
- Options: 0-1
- Default: 0.75
- bx_lw=float
- boxplot linewidth
- The linewidth of the boxplots
- Default: 1
- median_lw=float
- width of the boxplot median line
- Default: 1.1
- median_color=name
- Color of the boxlot median line
- Color of median
- Default: orange
- whisker_linewidth=float
- Whisker and cap linewidth
- The linewidth of the whiskers and caps
- Default: 1
- flier_marker=string
- Flier marker
- Set flier marker (see https://matplotlib.org/stable/api/markers_api.html for options)
- Default: o
- flier_size=string
- Flier size
- Set the flier size
- Default: 2
- flier_color=name
- Flier color
- Set the flier color
- Default: black
Table of contents
DESCRIPTION
r.boxplot draws boxplots of the raster values of an input raster map. The user has the option to define a zonal (categorical) map. In that case, a boxplot will be drawn for each zone, using the values of the input raster that fall within that zone.
If there is a zonal map, the user can add a line and band to represent the median and interquartile range (IQR) of the input layer. Note that all values of the input raster (within the region's extent) are used to compute the median and IQR. If the zones of the zonal map cover only part of the region, the user can mask out the non-covered parts of the input map first by means of r.mask. That will result in an IQR and median representing the values that fall within the zones of the zonal map only. Otherwise, the computational region can be changed to fit the extent of the zonal map with g.region.
By default, the resulting plot is displayed on screen. However, the user can also save the plot to file using the output option. The format is determined by the extension given by the user. So, if output = outputfile.png, the plot will be saved as a PNG file.
The whiskers extend to the most extreme data point, which is no more than range ✕ the IQR from the box. By default, a range of 1.5 is used, but the user can change this. Note that range values need to be larger than 0.
By default, outliers are not included in the plot. Set the -o flag to include them in the plot. To also create a point vector map with the locations of the outliers, the user needs to provide the name of the output map using map_outliers.
There are a few layout options, including the option to rotate the plot and the x-axis labels, print the boxplot(s) with notches, sort the boxplot from low to high (ascending) or from high to low (descending) median, color the boxplots according to the corresponding categories of the zonal raster, set the type and color of the outliers, set the color and width of the median line(s), set the color and transparency of the raster's median line and IQR band, and set the width of the boxplots.
NOTE
The r.boxplot module operates on the raster array defined by the current region settings, not the original extent and resolution of the input map. See g.region to understand the impact of the region settings on the calculations. To include outliers, the function converts the raster cell with outlier values to a point vector layer. This may take some time if there are a lot of outliers. So, if users are working with very large raster layers, they should be cautious to not set the range value too low as that may result in a huge number of outliers.The zonal map needs to be an integer map. If it is not, the function will exit with the error message, 'The zonal raster must be of type CELL (integer)'.
If the -c flag is used, the bxp_color and median_color are ignored, even if set by the user. The option to color boxploxs using the colors of the zonal raster categories (c flag) only works if the zonal map contains a color table. If it does not, the function exits with the error message that 'The zonal map does not have a color table'. If the user thinks there is a color table, run r.colors.out and check if the categories are integers. If not, that is the problem. If they are all integers, you probably have caught a bug.
The module respects the mask (if set), and the region settings. This means you can quickly change the area for which to create a boxplot by simply changing the region and/or setting a (different) mask.
EXAMPLE
Example 1
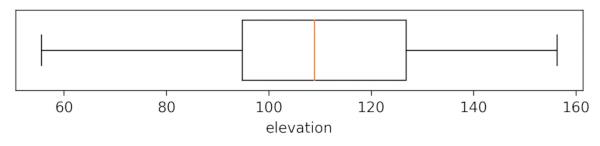
Draw a boxplot of the values of the elevation layer from the NC sample dataset. Set the -h flag to print the boxplot horizontally. Set the plot dimensions to 7 inch wide, 1 inch high.g.region raster=elevation r.boxplot -h input=elevation plot_dimensions="7,1" output="r_boxplot_01.png"
Example 2
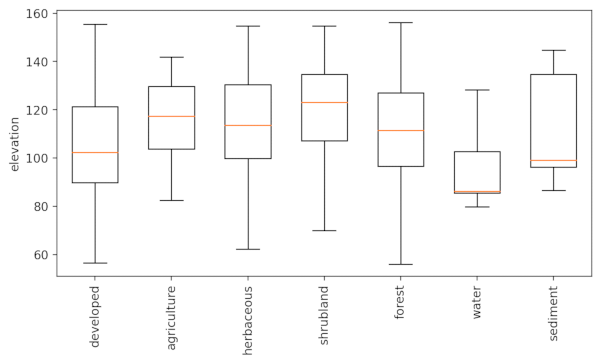
elevation layer per category from the landclass96 layer from the same NC sample dataset. Use the -r flag to rotate the x-asis labels.r.boxplot -r input=elevation zone=landclass96 output="r_boxplot_02.png"
Example 3
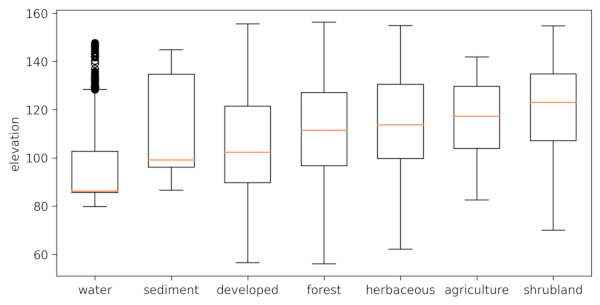
Draw boxplots of the values of the elevation layer per category from the landclass96 layer from the same NC sample dataset. Set the -o flag to include outliers. Use bx_sort=ascending to order the boxplots from low to high median. Provide a name for the outlier map to save the outlier locations as a point vector map.r.boxplot -o bx_sort=ascending input=elevation zones=landclass96 output="r_boxplot_03.png" map_outliers="outliers"
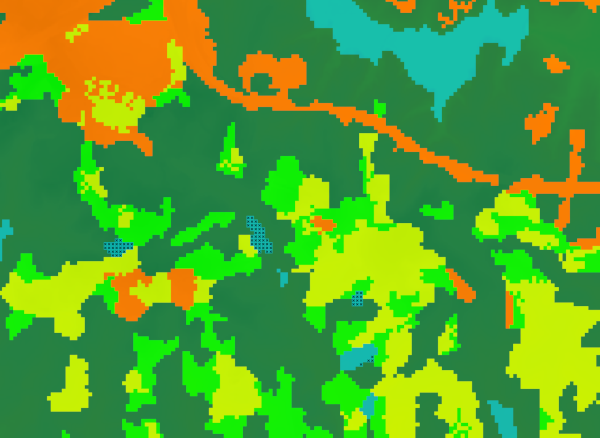
Below, part of the landclass96 raster map is shown, with the vector point layer with location of outliers on top. Curiously, for some lakes, only part of the raster cells are outliers.
Example 4
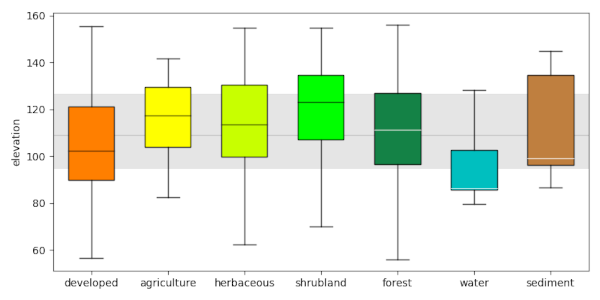
Draw boxplots of the values of the elevation layer per category from the landclass96 layer from the same NC sample dataset. Set the -c flag to color the boxplots, use bx_sort=ascending to order the boxplots from low to high median, and set the font size to 11.r.boxplot -c bx_sort=ascending fontsize=11 input=elevation zones=landclass96 output="r_boxplot_04.png"
Example 5
To make it easier to compare the elevation distribution across the different land classes, you can plot a line and band representing the median and interquartile range of the whole raster layer.r.boxplot -c input=elevation zones=landclass96 raster_statistics=median,IQR
Note, if the zones of your zonal map do not cover the entire area, you may want to use r.mask to mask out the non-covered parts of the input map, or alternatively, create a new input raster with only values within the zones of the zonal layer.
Acknowledgements
This work was carried in the framework of the Save the tiger, save the grassland, save the water project by the Innovative Bio-Monitoring research group.SEE ALSO
r.scatterplot, r.stats.zonal, v.boxplotAUTHOR
Paulo van Breugel, HAS green academy, Innovative Biomonitoring research group, Climate-robust Landscapes research groupSOURCE CODE
Available at: r.boxplot source code (history)
Latest change: Friday Feb 21 10:10:05 2025 in commit: 7d78fe34868674c3b6050ba1924e1c5675d155c9
Main index | Raster index | Topics index | Keywords index | Graphical index | Full index
© 2003-2024 GRASS Development Team, GRASS GIS 8.3.3dev Reference Manual