Note: This document is for an older version of GRASS GIS that has been discontinued. You should upgrade, and read the current manual page.

NAME
r.patch.smooth - Module for patching rasters with smoothing along edgesKEYWORDS
raster, patchSYNOPSIS
Flags:
- -s
- Use spatially variable overlap
- --overwrite
- Allow output files to overwrite existing files
- --help
- Print usage summary
- --verbose
- Verbose module output
- --quiet
- Quiet module output
- --ui
- Force launching GUI dialog
Parameters:
- input_a=name [required]
- Name for input raster map A
- Name of input raster map
- input_b=name [required]
- Name for input raster map B
- Name of input raster map
- output=name [required]
- Name for output raster map
- overlap=name
- Name for raster map of spatially variable overlap
- Name for output raster map
- blend_mask=string
- Raster containing edge of raster A which is not to be blended
- Useful when raster A has common edge with raster B
- smooth_dist=float
- Smoothing distance in map units
- transition_angle=float
- Angle of transition for spatially variable overlap
- Recommended values between 1 and 5 degrees
- parallel_smoothing=integer
- Size of smoothing window for smoothing edges of spatially variable overlap zone
- Small value results in more rugged shape of the overlap zone, large values result in spatially non-variable overlap zone. Requires odd values.
- Options: 3-99
- Default: 9
- difference_reach=integer
- Look for maximum difference between surfaces in surrounding n cells from the edge
- Recommended values between 3 and 9
- Options: 2-100
- Default: 3
Table of contents
DESCRIPTION
Module fuses rasters representing elevation together by patching them and smoothing values along edges using either fixed or spatially variable overlap width. Spatially variable overlap width is given by the difference along the edge between the two rasters. Higher difference results in larger overlap width to smooth the transition.r.patch.smooth can be used, for example, for updating older, lower resolution DEM (input_b) with newer, higher resolution DEM (input_a). Note that both DEMs must be aligned and have the same resolution. Smoothing uses weighted averaging on the overlap of the rasters. r.patch.smooth supports 2 types of smoothing. The default one is simpler and uses fixed overlap width defined in smooth_dist. Since the differences along the seam line can vary, the second option uses spatially variable overlap width and can be activated with flag -s. The width is then computed based on the elevation differences along the edge and transition angle transition_angle controlling the steepness of the transition. If option overlap is specified, a map representing the spatially variable overlap is created and can be used for inspecting the fusion results.
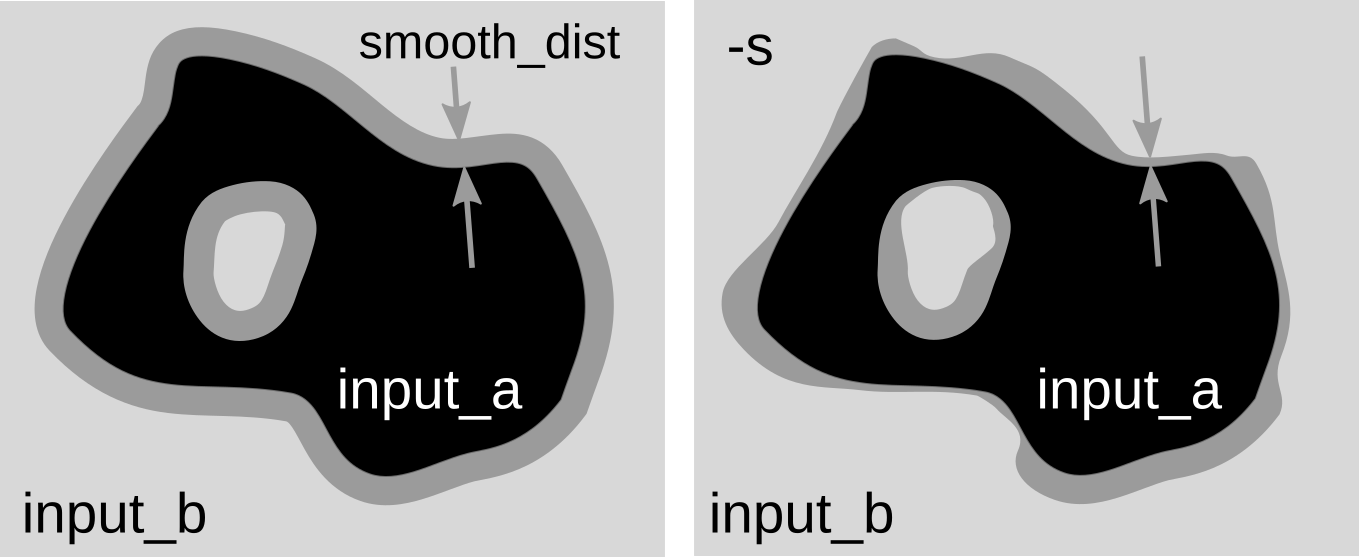
Difference between fixed overlap width and spatially variable overlap.
For spatially variable overlap, options parallel_smoothing and difference_reach can be specified. Option parallel_smoothing smoothes the overlap zone in direction parallel to the edge. Option difference_reach enables to increase the sensitivity to higher differences on the edges by taking maximum difference values in the cells close to edges.
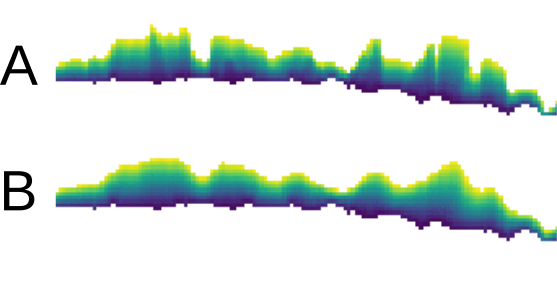
Effect of parallel_smoothing option shown on overlap zone (created by specifying overlap option). Image A shows result with value 3 and B with value 9.
Option blend_mask (experimental) can be used to specify which edges of the input_a DEM should be excluded from the blending. This is useful when DEMs A and B have identical edges (on the coast, for example) and we want to preserve only A (not blend it with B along the coast). The blend_mask raster can be created by digitizing area approximately around the excluded edges, so that the edge of DEM A is inside the areas and the rest are NULLs. This option requires more testing.
SEE ALSO
r.patch, r.mapcalc, r.grow.distanceREFERENCES
Anna Petrasova, Helena Mitasova, Vaclav Petras, Justyna Jeziorska. Fusion of high-resolution DEMs for water flow modeling (2017). Open Geospatial Data, Software and Standards. 2: 6. DOI: 10.1186/s40965-017-0019-2AUTHOR
Anna Petrasova, NCSU GeoForAll LabSOURCE CODE
Available at: r.patch.smooth source code (history)
Latest change: Thursday Feb 20 13:02:26 2025 in commit: 53de8196a10ba5a8a9121898ce87861d227137e3
Main index | Raster index | Topics index | Keywords index | Graphical index | Full index
© 2003-2024 GRASS Development Team, GRASS GIS 8.3.3dev Reference Manual