i.topo.corr
Computes topographic correction of reflectance.
i.topo.corr [-is] [input=name [,name,...]] output=name basemap=name zenith=float [azimuth=float] [method=string] [--overwrite] [--verbose] [--quiet] [--qq] [--ui]
Example:
i.topo.corr output=name basemap=name zenith=0.0
grass.script.run_command("i.topo.corr", input=None, output, basemap, zenith, azimuth=None, method="c-factor", flags=None, overwrite=None, verbose=None, quiet=None, superquiet=None)
Example:
gs.run_command("i.topo.corr", output="name", basemap="name", zenith=0.0)
grass.tools.Tools.i_topo_corr(input=None, output, basemap, zenith, azimuth=None, method="c-factor", flags=None, overwrite=None, verbose=None, quiet=None, superquiet=None)
Example:
tools = Tools()
tools.i_topo_corr(output="name", basemap="name", zenith=0.0)
This grass.tools API is experimental in version 8.5 and expected to be stable in version 8.6.
Parameters
input=name [,name,...]
Name of reflectance raster maps to be corrected topographically
output=name [required]
Name (flag -i) or prefix for output raster maps
basemap=name [required]
Name of input base raster map (elevation or illumination)
zenith=float [required]
Solar zenith in degrees
azimuth=float
Solar azimuth in degrees (only if flag -i)
method=string
Topographic correction method
Allowed values: cosine, minnaert, c-factor, percent
Default: c-factor
-i
Output sun illumination terrain model
-s
Scale output to input and copy color rules
--overwrite
Allow output files to overwrite existing files
--help
Print usage summary
--verbose
Verbose module output
--quiet
Quiet module output
--qq
Very quiet module output
--ui
Force launching GUI dialog
input : str | list[str], optional
Name of reflectance raster maps to be corrected topographically
Used as: input, raster, name
output : str, required
Name (flag -i) or prefix for output raster maps
Used as: output, raster, name
basemap : str, required
Name of input base raster map (elevation or illumination)
Used as: input, raster, name
zenith : float, required
Solar zenith in degrees
azimuth : float, optional
Solar azimuth in degrees (only if flag -i)
method : str, optional
Topographic correction method
Allowed values: cosine, minnaert, c-factor, percent
Default: c-factor
flags : str, optional
Allowed values: i, s
i
Output sun illumination terrain model
s
Scale output to input and copy color rules
overwrite : bool, optional
Allow output files to overwrite existing files
Default: None
verbose : bool, optional
Verbose module output
Default: None
quiet : bool, optional
Quiet module output
Default: None
superquiet : bool, optional
Very quiet module output
Default: None
input : str | list[str], optional
Name of reflectance raster maps to be corrected topographically
Used as: input, raster, name
output : str | type(np.ndarray) | type(np.array) | type(gs.array.array), required
Name (flag -i) or prefix for output raster maps
Used as: output, raster, name
basemap : str | np.ndarray, required
Name of input base raster map (elevation or illumination)
Used as: input, raster, name
zenith : float, required
Solar zenith in degrees
azimuth : float, optional
Solar azimuth in degrees (only if flag -i)
method : str, optional
Topographic correction method
Allowed values: cosine, minnaert, c-factor, percent
Default: c-factor
flags : str, optional
Allowed values: i, s
i
Output sun illumination terrain model
s
Scale output to input and copy color rules
overwrite : bool, optional
Allow output files to overwrite existing files
Default: None
verbose : bool, optional
Verbose module output
Default: None
quiet : bool, optional
Quiet module output
Default: None
superquiet : bool, optional
Very quiet module output
Default: None
Returns:
result : grass.tools.support.ToolResult | np.ndarray | tuple[np.ndarray] | None
If the tool produces text as standard output, a ToolResult object will be returned. Otherwise, None will be returned. If an array type (e.g., np.ndarray) is used for one of the raster outputs, the result will be an array and will have the shape corresponding to the computational region. If an array type is used for more than one raster output, the result will be a tuple of arrays.
Raises:
grass.tools.ToolError: When the tool ended with an error.
DESCRIPTION
i.topo.corr is used to topographically correct reflectance from imagery files, e.g. obtained with i.landsat.toar, using a sun illumination terrain model. This illumination model represents the cosine of the incident angle i, i.e. the angle between the normal to the ground and the sun rays.
Note: If needed, the sun position can be calculated for a given date and time with r.sunmask.
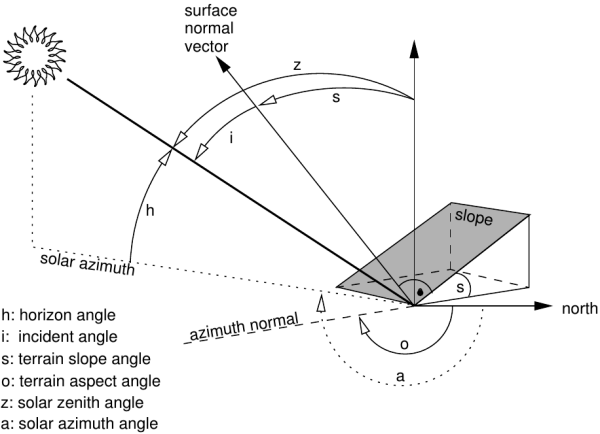
Figure showing terrain and solar angles
Using the -i flag and given an elevation basemap (metric), i.topo.corr creates a simple illumination model using the formula:
- cos_i = cos(s) * cos(z) + sin(s) * sin(z) * cos(a - o)
where,
- i is the incident angle to be calculated,
- s is the terrain slope angle (from r.slope.aspect),
- z is the solar zenith angle (i.e., 90° - solar horizon angle from r.sunmask),
- a the solar azimuth angle (from r.sunmask),
- o the terrain aspect angle (from r.slope.aspect).
For each band file, the corrected reflectance (ref_c) is calculate from the original reflectance (ref_o) using one of the four offered methods (one lambertian and two non-lambertian).
Method: cosine
- ref_c = ref_o * cos_z / cos_i
Method: minnaert
- ref_c = ref_o * (cos_z / cos_i) ^k
where, k is obtained by linear regression of
ln(ref_o) = ln(ref_c) - k ln(cos_i/cos_z)
Method: c-factor
- ref_c = ref_o * (cos_z + c)/ (cos_i + c)
where, c is a/m from ref_o = a + m * cos_i
Method: percent
We can use cos_i to estimate the percent of solar incidence on the surface, then the transformation (cos_i + 1)/2 varied from 0 (surface in the side in opposition to the sun: infinite correction) to 1 (direct exhibition to the sun: no correction) and the corrected reflectance can be calculated as
- ref_c = ref_o * 2 / (cos_i + 1)
NOTES
- The illumination model (cos_i) with flag -i uses the actual region as limits and the resolution of the elevation map.
- The topographic correction use the full reflectance file (null remain null) and its resolution.
- The elevation map to calculate the illumination model should be metric.
EXAMPLES
First, make a illumination model from the elevation map (here, SRTM). Then make perform the topographic correction of e.g. the bands toar.5, toar.4 and toar.3 with output as tcor.toar.5, tcor.toar.4, and tcor.toar.3 using c-factor (= c-correction) method:
# first pass: create illumination model
i.topo.corr -i base=SRTM zenith=33.3631 azimuth=59.8897 output=SRTM.illumination
# second pass: apply illumination model
i.topo.corr base=SRTM.illumination input=toar.5,toar.4,toar.3 output=tcor \
zenith=33.3631 method=c-factor
REFERENCES
- Law K.H. and Nichol J, 2004. Topographic Correction For Differential Illumination Effects On Ikonos Satellite Imagery. International Archives of Photogrammetry Remote Sensing and Spatial Information, pp. 641-646.
- Meyer, P. and Itten, K.I. and Kellenberger, KJ and Sandmeier, S. and Sandmeier, R., 1993. Radiometric corrections of topographically induced effects on Landsat TM data in alpine terrain. Photogrammetric Engineering and Remote Sensing 48(17).
- Riaño, D. and Chuvieco, E. and Salas, J. and Aguado, I., 2003. Assessment of Different Topographic Corrections in Landsat-TM Data for Mapping Vegetation Types. IEEE Transactions On Geoscience And Remote Sensing, Vol. 41, No. 5
- Twele A. and Erasmi S, 2005. Evaluating topographic correction algorithms for improved land cover discrimination in mountainous areas of Central Sulawesi. Göttinger Geographische Abhandlungen, vol. 113.
SEE ALSO
i.landsat.toar, r.mapcalc, r.sun r.sunmask
AUTHOR
E. Jorge Tizado (ej.tizado unileon es)
Dept. Biodiversity and Environmental Management, University of León,
Spain
Figure derived from Neteler & Mitasova, 2008.
SOURCE CODE
Available at: i.topo.corr source code
(history)
Latest change: Monday Aug 04 18:54:37 2025 in commit b7a14bd