r3.cross.rast
Creates cross section 2D raster map from 3D raster map based on 2D elevation map
r3.cross.rast [-m] input=string elevation=string output=string [--overwrite] [--verbose] [--quiet] [--qq] [--ui]
Example:
r3.cross.rast input=string elevation=string output=string
grass.script.run_command("r3.cross.rast", input, elevation, output, flags=None, overwrite=None, verbose=None, quiet=None, superquiet=None)
Example:
gs.run_command("r3.cross.rast", input="string", elevation="string", output="string")
grass.tools.Tools.r3_cross_rast(input, elevation, output, flags=None, overwrite=None, verbose=None, quiet=None, superquiet=None)
Example:
tools = Tools()
tools.r3_cross_rast(input="string", elevation="string", output="string")
This grass.tools API is experimental in version 8.5 and expected to be stable in version 8.6.
Parameters
input=string [required]
Input 3D raster map for cross section
elevation=string [required]
2D elevation map used to create the cross section map
output=string [required]
Resulting cross section 2D raster map
-m
Use 3D raster mask (if exists) with input map
--overwrite
Allow output files to overwrite existing files
--help
Print usage summary
--verbose
Verbose module output
--quiet
Quiet module output
--qq
Very quiet module output
--ui
Force launching GUI dialog
input : str, required
Input 3D raster map for cross section
Used as: input, 3d-raster
elevation : str, required
2D elevation map used to create the cross section map
Used as: input, raster
output : str, required
Resulting cross section 2D raster map
Used as: output, raster
flags : str, optional
Allowed values: m
m
Use 3D raster mask (if exists) with input map
overwrite : bool, optional
Allow output files to overwrite existing files
Default: None
verbose : bool, optional
Verbose module output
Default: None
quiet : bool, optional
Quiet module output
Default: None
superquiet : bool, optional
Very quiet module output
Default: None
input : str, required
Input 3D raster map for cross section
Used as: input, 3d-raster
elevation : str | np.ndarray, required
2D elevation map used to create the cross section map
Used as: input, raster
output : str | type(np.ndarray) | type(np.array) | type(gs.array.array), required
Resulting cross section 2D raster map
Used as: output, raster
flags : str, optional
Allowed values: m
m
Use 3D raster mask (if exists) with input map
overwrite : bool, optional
Allow output files to overwrite existing files
Default: None
verbose : bool, optional
Verbose module output
Default: None
quiet : bool, optional
Quiet module output
Default: None
superquiet : bool, optional
Very quiet module output
Default: None
Returns:
result : grass.tools.support.ToolResult | np.ndarray | tuple[np.ndarray] | None
If the tool produces text as standard output, a ToolResult object will be returned. Otherwise, None will be returned. If an array type (e.g., np.ndarray) is used for one of the raster outputs, the result will be an array and will have the shape corresponding to the computational region. If an array type is used for more than one raster output, the result will be a tuple of arrays.
Raises:
grass.tools.ToolError: When the tool ended with an error.
DESCRIPTION
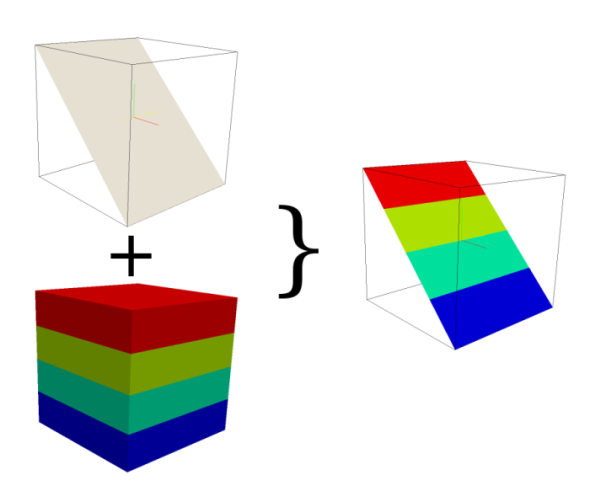
r3.cross.rast creates a cross section 2D map from one 3D raster volume map based on a 2D elevation map. It checks if the value of the elevation map is located in the z-coordinate space of the 3D map. If so, the 3D voxel value for this position is transferred to the related cross section output map cell, otherwise the NULL value is set.
If the 2D and 3D region settings are different, the 2D resolution will be adjust to the 3D resolution.
NOTES
To create a cut plane elevation map use r.mapcalc. Some examples:
- To create a cut plane elevation map in x direction type
r.mapcalc "cutplane = col()*x",
x be the value for the elevation. If the range of col() is 1 ... 10, the elevation map has the range 1 ... 10 if x == 1 and if x == 10 the range 10 ... 100 - To create a cut plane elevation map in y direction type
r.mapcalc "cutplane = row()*x",
x be the value for the elevation. If the range of col() is 1 ... 10, the elevation map has the range 1 ... 10 if x == 1 and if x == 10 the range 10 ... 100 - The user can also make a cut in y and x direction with r.mapcalc by
using
r.mapcalc "cutplane = (row()+col())*x"
EXAMPLES
Simple Spearfish example
g.region -d
g.region res=150 res3=150 t=1000 b=0 tbres=100
# synthetic data, could be geological structures:
r3.mapcalc "map3d = sin(row())+sin(col())+sin(depth()*depth())"
#create a cutplane map
r.mapcalc "cutplane = col()*10"
#create the cross section map
r3.cross.rast input=map3d elevation=cutplane output=crosssection
SEE ALSO
g.region, r.mapcalc, r3.mapcalc, r3.to.rast
AUTHOR
Sören Gebbert
SOURCE CODE
Available at: r3.cross.rast source code
(history)
Latest change: Saturday Jul 26 17:35:15 2025 in commit ab6f350