Note: This document is for an older version of GRASS GIS that has been discontinued. You should upgrade, and read the current manual page.

NAME
r.local.relief - Creates a local relief model from elevation map.KEYWORDS
raster, elevation, terrain, relief, LRM, visualizationSYNOPSIS
Flags:
- -i
- Save intermediate maps
- -v
- Use bspline interpolation to construct the surface
- Uses v.surf.bspline cubic interpolation instead of r.fillnulls cubic interpolation.
- -n
- Invert colors in the color table
- -g
- Logarithmic scaling of the color table
- -f
- Do not perform histogram equalization on the color table
- --overwrite
- Allow output files to overwrite existing files
- --help
- Print usage summary
- --verbose
- Verbose module output
- --quiet
- Quiet module output
- --ui
- Force launching GUI dialog
Parameters:
- input=string [required]
- Name of the input elevation raster map
- output=string [required]
- Name for output local relief map
- neighborhood_size=integer
- Smoothing neighborhood size
- Neighborhood size used when smoothing the elevation model
- Options: 0-
- Default: 11
- color_table=string
- Color table for the local relief model raster map
- If not provided, grey is used for output and differences is used for the shaded_output
- Options: grey, differences
- shaded_output=name
- Local relief combined with shaded relief
- Local relief model combined with shaded relief of the original elevation
Table of contents
DESCRIPTION
r.local.relief generates a local relief model (LRM) from lidar-derived high-resolution DEMs. Local relief models enhance the visibility of small-scale surface features by removing large-scale landforms from the DEM.
Generating the LRM is accomplished in 7 steps (Hesse 2010:69):
- Creation of the DEM from the LIDAR data. Buildings, trees and other objects on the earth's surface should be removed.
- Apply a low pass filter to the DEM. The low pass filter approximates the large-scale landforms. The neighborhood size of the low pass filter determines the scale of features that will be visible in the LRM. A default neighborhood size of 11 is used.
- Subtract the low-pass filter result from the DEM to get the local relief.
- Extract the zero contour lines from the difference map.
- Extract the input DEM's elevation values along the zero contour lines.
- Create a purged DEM by interpolating the null values between the rasterized contours generated in the previous step. This layer represents the large-scale landforms that will be removed to expose the local relief in the final step.
- Subtract the purged DEM from the original DEM to get the local relief model.
The interpolation step is performed by the r.fillnulls module by default (using cubic interpolation). If this is not working on your data, you can use -v flag to use v.surf.bspline cubic interpolation instead (this might be slower on some types of data).
OUTPUT
The final local relief model is named according to the output parameter. When the -i flag is specified, r.local.relief creates additional output files representing the intermediate steps in the LRM generation process. The names and number of the intermediate files vary depending on whether r.fillnulls (default) or v.surf.bspline (specified by using the -v flag) is used for interpolation. The intermediate maps are composed of the user-specified output parameter and suffixes describing the intermediate map.
Without using the -v flag (r.fillnulls interpolation), intermediate maps have the following suffixes:
- _smooth_elevation: The result of running the low pass filter on the DEM.
- _subtracted_smooth_elevation: The result of subtracting the low pass filter map from the DEM.
- _raster_contours_with_values: The rasterized zero contours with the values from elevation map.
- _purged_elevation: The raster interpolated from the _raster_contours_with_values map based that represents the large-scale landforms.
With using the -v flag (v.surf.bspline interpolation), intermediate maps have the following suffixes:
- _smooth_elevation: The result of running the low pass filter on the DEM.
- _subtracted_smooth_elevation: The result of subtracting the low pass filter map from the DEM.
- _vector_contours: The zero contours extracted from the DEM.
- _contour_points: The points extractacted along the zero contour lines with the input DEM elevation values.
- _purged_elevation: The raster interpolated from the _contour_points map that represents the large-scale landforms.
The module sets equalized gray scale color table for local relief model map and for the elevation difference (subtracted elevations). The color tables of other raster maps are set to the same color table as the input elevation map has.
EXAMPLE
Basic example using the default neighborhood size of 11:r.local.relief input=elevation output=lrm11
r.local.relief input=elevation output=lrm25 neighborhood_size=25
r.local.relief -i input=elevation output=lrm11
r.local.relief -i -v input=elevation output=lrm11
# set the computational region to area of interest g.region n=228010 s=223380 w=637980 e=644920 res=10 # compute local relief model r.local.relief input=elevation output=elevation_lrm # show the maps, e.g. using monitors d.mon wx0 d.rast elevation d.rast elevation_lrm # try alternative red (negative values) and blue (positive values) color table # color table shows only the high values which hides small streets # for non-unix operating systems use file or interactive input in GUI # instead of rules=- and EOF syntax r.colors map=elevation_lrm@PERMANENT rules=- <<EOF 100% 0:0:255 0 255:255:255 0% 255:0:0 nv 255:255:255 default 255:255:255 EOF

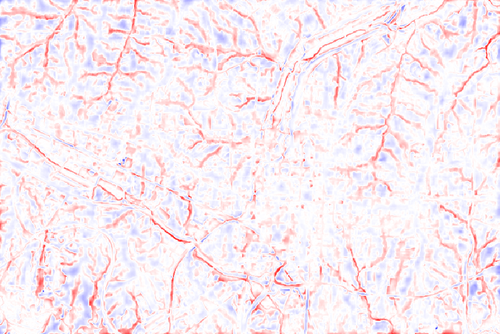
Figure: Local relief model of downtown Raleigh area created from elevation raster map in NC sample location with the default (gray scale) color table and custom red (negative values) and blue (positive values) color table
SEE ALSO
r.relief, r.shaded.pca, r.skyviewREFERENCES
- Hesse, Ralf (2010). LiDAR-derived Local Relief Models - a new tool for archaeological prospection. Archaeological Prospection 17:67-72.
- Bennett, Rebecca (2011). Archaeological Remote Sensing: Visualization and Analysis of grass-dominated environments using laser scanning and digital spectra data. Unpublished PhD Thesis. Electronic Document, http://eprints.bournemouth.ac.uk/20459/1/Bennett%2C_Rebecca_PhD_Thesis_2011.pdf, Accessed 25 February 2013. (provided bash script with v.surf.bspline-based implementation)
AUTHORS
Vaclav Petras, NCSU OSGeoREL,
Eric Goddard
SOURCE CODE
Available at: r.local.relief source code (history)
Latest change: Monday Jun 28 07:54:09 2021 in commit: 1cfc0af029a35a5d6c7dae5ca7204d0eb85dbc55
Main index | Raster index | Topics index | Keywords index | Graphical index | Full index
© 2003-2023 GRASS Development Team, GRASS GIS 7.8.9dev Reference Manual