v.rast.move
Move vertices by distance specified in a raster
v.rast.move input=name x_raster=name y_raster=name [nulls=string] output=name [--overwrite] [--verbose] [--quiet] [--qq] [--ui]
Example:
v.rast.move input=name x_raster=name y_raster=name output=name
grass.script.run_command("v.rast.move", input, x_raster, y_raster, nulls="warning", output, overwrite=None, verbose=None, quiet=None, superquiet=None)
Example:
gs.run_command("v.rast.move", input="name", x_raster="name", y_raster="name", output="name")
grass.tools.Tools.v_rast_move(input, x_raster, y_raster, nulls="warning", output, overwrite=None, verbose=None, quiet=None, superquiet=None)
Example:
tools = Tools()
tools.v_rast_move(input="name", x_raster="name", y_raster="name", output="name")
This grass.tools API is experimental in version 8.5 and expected to be stable in version 8.6.
Parameters
input=name [required]
Name of input vector map
Or data source for direct OGR access
x_raster=name [required]
Name of input raster map
y_raster=name [required]
Name of input raster map
nulls=string
Handling of null values
zeros;Null value will be converted to zeros;warning;A null value will cause a warning (one for each raster) and will be converted to zero;error;A null value will cause an error
Allowed values: zeros, warning, error
Default: warning
output=name [required]
Name for output vector map
--overwrite
Allow output files to overwrite existing files
--help
Print usage summary
--verbose
Verbose module output
--quiet
Quiet module output
--qq
Very quiet module output
--ui
Force launching GUI dialog
input : str, required
Name of input vector map
Or data source for direct OGR access
Used as: input, vector, name
x_raster : str, required
Name of input raster map
Used as: input, raster, name
y_raster : str, required
Name of input raster map
Used as: input, raster, name
nulls : str, optional
Handling of null values
zeros;Null value will be converted to zeros;warning;A null value will cause a warning (one for each raster) and will be converted to zero;error;A null value will cause an error
Allowed values: zeros, warning, error
Default: warning
output : str, required
Name for output vector map
Used as: output, vector, name
overwrite : bool, optional
Allow output files to overwrite existing files
Default: None
verbose : bool, optional
Verbose module output
Default: None
quiet : bool, optional
Quiet module output
Default: None
superquiet : bool, optional
Very quiet module output
Default: None
input : str, required
Name of input vector map
Or data source for direct OGR access
Used as: input, vector, name
x_raster : str | np.ndarray, required
Name of input raster map
Used as: input, raster, name
y_raster : str | np.ndarray, required
Name of input raster map
Used as: input, raster, name
nulls : str, optional
Handling of null values
zeros;Null value will be converted to zeros;warning;A null value will cause a warning (one for each raster) and will be converted to zero;error;A null value will cause an error
Allowed values: zeros, warning, error
Default: warning
output : str, required
Name for output vector map
Used as: output, vector, name
overwrite : bool, optional
Allow output files to overwrite existing files
Default: None
verbose : bool, optional
Verbose module output
Default: None
quiet : bool, optional
Quiet module output
Default: None
superquiet : bool, optional
Very quiet module output
Default: None
Returns:
result : grass.tools.support.ToolResult | None
If the tool produces text as standard output, a ToolResult object will be returned. Otherwise, None will be returned.
Raises:
grass.tools.ToolError: When the tool ended with an error.
DESCRIPTION
v.rast.move takes values from raster maps and adds them to X and Y
coordinates of features in a vector map vertex by vertex. Works on lines
only, other features are ignored and not included in the result. Null
values in rasters are turned into zeros by default and a warning is
generated. This behavior can be modified by the nulls option to
either silence the warning with explicit nulls="zeros" or the warning
can be turned into an error with nulls="error". The rasters are loaded
based on the computational region, so the most advantageous use of
resources is to set the computational region to match the vector. To
avoid issues with vector coordinates at the border of the computational
region, it is best to also grow the region one cell on each side. Vector
features outside of the computational region always result in an error
being reported (regardless of the nulls option), but the rasters can
have any extent as along as the computational region is set to match the
vector.
NOTES
Unlike v.perturb which moves points randomly, v.rast.move works on vertices of lines and uses same value for all vertices at a given cell. Unlike v.transform used with raster values in attribute columns, v.rast.move operates on individual vertices in the line, not on the whole line (attributes are associated with features, not their vertices).
EXAMPLES
Shift in X direction
This example uses the North Carolina sample dataset. Set the computational region to match the vector map and use 100-meter resolution.
g.region vector=roadsmajor res=100
Generate rasters for a shift in X direction (one raster is a wave, the other is zero):
g.region vector=roadsmajor res=100
r.mapcalc expression="a = 1000 * sin(row())"
r.mapcalc expression="b = 0"
Use the rasters to move the vector:
v.rast.move input=roadsmajor output=roads_moved x_raster=a y_raster=b
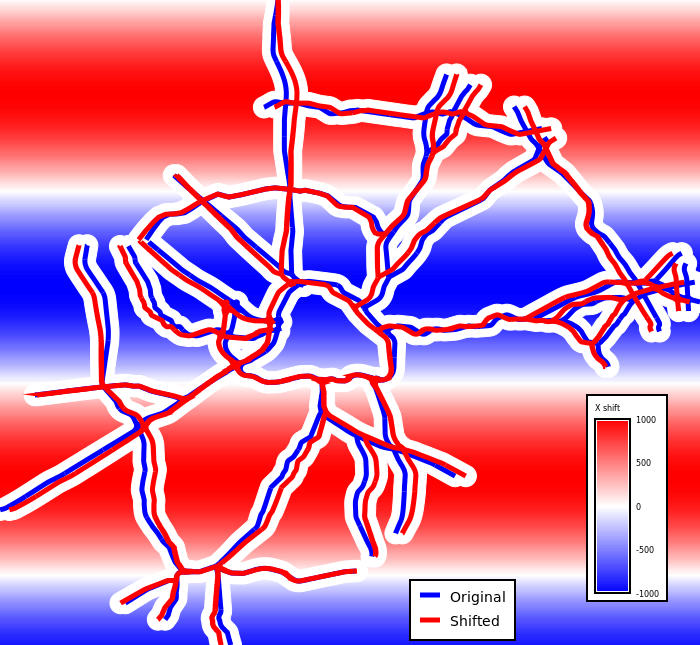
Figure: Original (blue) and shifted (red) road network and the X shift
values in diverging blue-white-red colors (red shift right, blue shift
left, white no shift)
SEE ALSO
- v.transform for changing coordinates for the whole vector map or feature by feature based on the attributes,
- v.perturb for randomly changing point positions by small amounts,
- r.mapcalc for generating or adjusting the raster maps,
- g.region to set the computational region before the computation.
AUTHOR
Vaclav Petras, NCSU Center for Geospatial Analytics, GeoForAll Lab
SOURCE CODE
Available at: v.rast.move source code
(history)
Latest change: Friday Feb 21 10:10:05 2025 in commit 7d78fe3