g.gui.rdigit
Interactive editing and digitizing of raster maps.
g.gui.rdigit [create=name] [base=name] [type=string] [edit=name] [--overwrite] [--verbose] [--quiet] [--qq] [--ui]
Example:
g.gui.rdigit create=name
grass.script.run_command("g.gui.rdigit", create=None, base=None, type="CELL", edit=None, overwrite=None, verbose=None, quiet=None, superquiet=None)
Example:
gs.run_command("g.gui.rdigit", create="name")
grass.tools.Tools.g_gui_rdigit(create=None, base=None, type="CELL", edit=None, overwrite=None, verbose=None, quiet=None, superquiet=None)
Example:
tools = Tools()
tools.g_gui_rdigit(create="name")
This grass.tools API is experimental in version 8.5 and expected to be stable in version 8.6.
Parameters
create=name
Name of new raster map to create
Name for output raster map
base=name
Name of base raster map
type=string
Type of raster map to be created
Storage type for resultant raster map
Allowed values: CELL, FCELL, DCELL
Default: CELL
CELL: Integer
FCELL: Single precision floating point
DCELL: Double precision floating point
edit=name
Name of existing raster map to edit
Name of input raster map
--overwrite
Allow output files to overwrite existing files
--help
Print usage summary
--verbose
Verbose module output
--quiet
Quiet module output
--qq
Very quiet module output
--ui
Force launching GUI dialog
create : str, optional
Name of new raster map to create
Name for output raster map
Used as: output, raster, name
base : str, optional
Name of base raster map
Used as: input, raster, name
type : str, optional
Type of raster map to be created
Storage type for resultant raster map
Allowed values: CELL, FCELL, DCELL
CELL: Integer
FCELL: Single precision floating point
DCELL: Double precision floating point
Default: CELL
edit : str, optional
Name of existing raster map to edit
Name of input raster map
Used as: input, raster, name
overwrite : bool, optional
Allow output files to overwrite existing files
Default: None
verbose : bool, optional
Verbose module output
Default: None
quiet : bool, optional
Quiet module output
Default: None
superquiet : bool, optional
Very quiet module output
Default: None
create : str | type(np.ndarray) | type(np.array) | type(gs.array.array), optional
Name of new raster map to create
Name for output raster map
Used as: output, raster, name
base : str | np.ndarray, optional
Name of base raster map
Used as: input, raster, name
type : str, optional
Type of raster map to be created
Storage type for resultant raster map
Allowed values: CELL, FCELL, DCELL
CELL: Integer
FCELL: Single precision floating point
DCELL: Double precision floating point
Default: CELL
edit : str | np.ndarray, optional
Name of existing raster map to edit
Name of input raster map
Used as: input, raster, name
overwrite : bool, optional
Allow output files to overwrite existing files
Default: None
verbose : bool, optional
Verbose module output
Default: None
quiet : bool, optional
Quiet module output
Default: None
superquiet : bool, optional
Very quiet module output
Default: None
Returns:
result : grass.tools.support.ToolResult | np.ndarray | tuple[np.ndarray] | None
If the tool produces text as standard output, a ToolResult object will be returned. Otherwise, None will be returned. If an array type (e.g., np.ndarray) is used for one of the raster outputs, the result will be an array and will have the shape corresponding to the computational region. If an array type is used for more than one raster output, the result will be a tuple of arrays.
Raises:
grass.tools.ToolError: When the tool ended with an error.
DESCRIPTION
Raster Digitizer is a simple tool to quickly draw lines, areas, and circles and save these features in a raster map. It is accessible from the Map Display toolbar (from the combo box on the right).
Raster Digitizer currently allows you to:
- draw polygons, lines and points
- set category value of the feature you are drawing
- set feature width (width of currently digitized line or diameter of a digitized point in map units)
- create a new raster from scratch or from an already existing raster
- undo edits and save edits before leaving the digitizer
The typical workflow includes these steps:
- Set computational region as needed.
- Switch to Raster Digitizer and select a map to create. Select either a new raster or create a new raster from existing raster, also select raster type (CELL, FCELL, DCELL)
- Specify category value and width before drawing a feature
- Specify digitizing tool (area, line, point)
- Start digitizing and when you want to finish area or line, use right click
- Change color of temporary overlay depending on your needs
- Set different category and repeat
- At any point you can use Undo or Save
- If existing raster is used for the new raster, digitized areas will respect the color table, but you can always set different color table.
NOTES
Raster Digitizer respects computational region including the currently set resolution.
EXAMPLES
In the following figures we start with elev_lid792_1m raster map in North carolina sample dataset and digitize two buildings, one rectangular and one with circular footprint. Both buildings have the roof level at 130 m. We set the width when digitizing the point to 50 meters which results in the building having 50 m in diameter. When we are done with digitizing, we save the result and explore cast shadows of the buildings with r.sun module:
g.region raster=elev_lid792_1m
# now create elev_edited raster by digitizing and save
r.slope.aspect elevation=elev_edited slope=slope aspect=aspect
r.sun elevation=elev_edited aspect=aspect slope=slope beam_rad=beam day=172 time=6
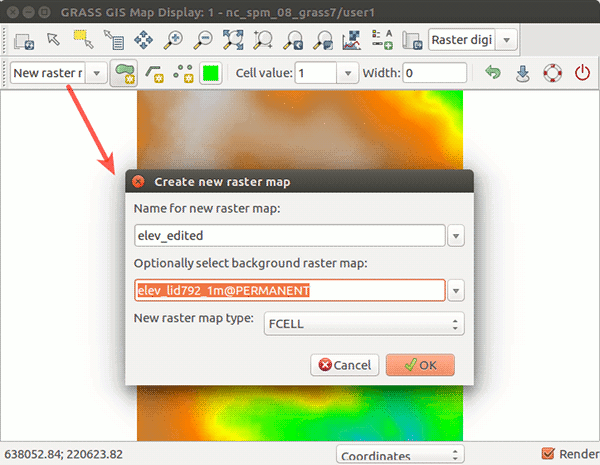
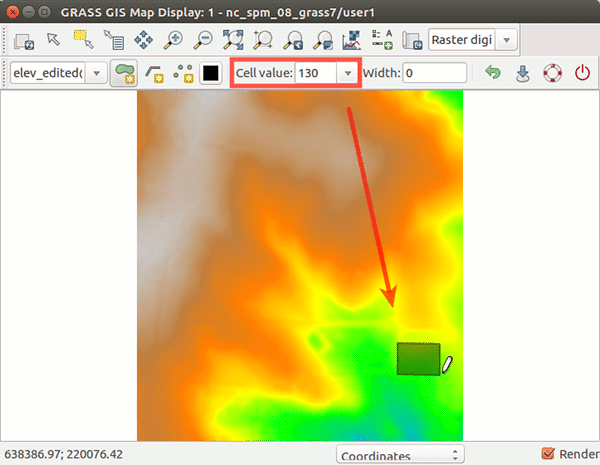
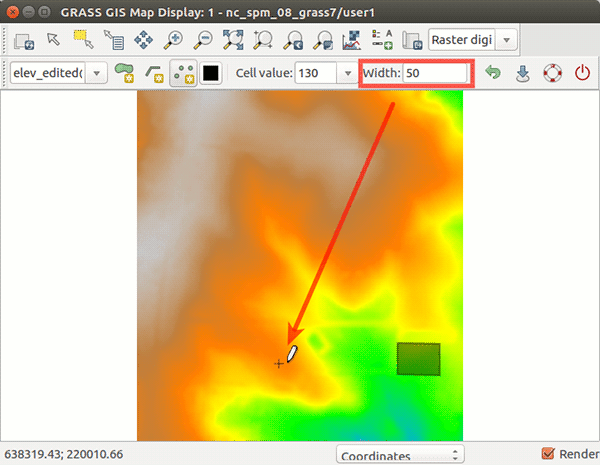
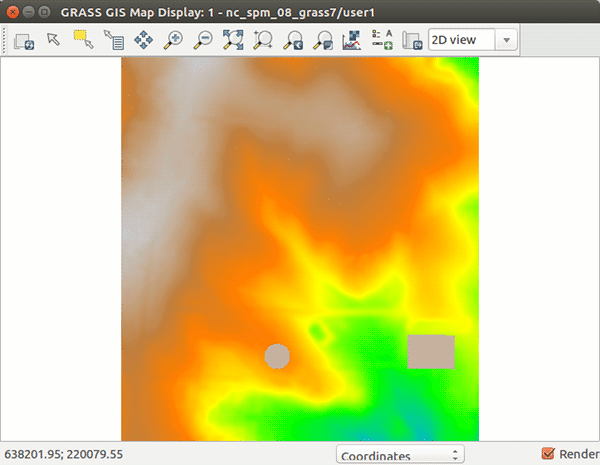
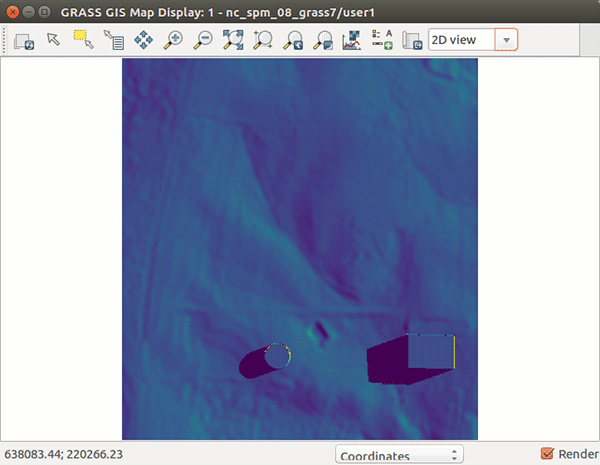
Figure: Steps to digitize new buildings on elev_lid792_1m raster map.
SEE ALSO
wxGUI, wxGUI components, r.in.poly (backend of digitizer), g.gui.vdigit
AUTHORS
Anna Petrasova, NCSU GeoForALL Laboratory
Tomas Zigo (standalone module)
SOURCE CODE
Available at: g.gui.rdigit source code
(history)
Latest change: Wednesday Jan 28 08:16:26 2026 in commit 0a9db34