v.kernel
Generates a raster density map from vector points map.
Density is computed using a moving kernel. Optionally generates a vector density map on a vector network.
v.kernel [-oqnm] input=name [net=name] [output=name] [net_output=name] radius=float [dsize=float] [segmax=float] [distmax=float] [multiplier=float] [node=string] [kernel=string] [--overwrite] [--verbose] [--quiet] [--qq] [--ui]
Example:
v.kernel input=name output=name radius=0.0
grass.script.run_command("v.kernel", input, net=None, output=None, net_output=None, radius, dsize=0., segmax=100., distmax=100., multiplier=1., node="none", kernel="gaussian", flags=None, overwrite=None, verbose=None, quiet=None, superquiet=None)
Example:
gs.run_command("v.kernel", input="name", output="name", radius=0.0)
grass.tools.Tools.v_kernel(input, net=None, output=None, net_output=None, radius, dsize=0., segmax=100., distmax=100., multiplier=1., node="none", kernel="gaussian", flags=None, overwrite=None, verbose=None, quiet=None, superquiet=None)
Example:
tools = Tools()
tools.v_kernel(input="name", output="name", radius=0.0)
This grass.tools API is experimental in version 8.5 and expected to be stable in version 8.6.
Parameters
input=name [required]
Name of input vector map with training points
net=name
Name of input network vector map
output=name
Name for output raster map
net_output=name
Name for output vector density map
Outputs vector map if network map is given
radius=float [required]
Kernel radius in map units
dsize=float
Discretization error in map units
Default: 0.
segmax=float
Maximum length of segment on network
Default: 100.
distmax=float
Maximum distance from point to network
Default: 100.
multiplier=float
Multiply the density result by this number
Default: 1.
node=string
Node method
Allowed values: none, split
Default: none
none: No method applied at nodes with more than 2 arcs
split: Equal split (Okabe 2009) applied at nodes
kernel=string
Kernel function
Allowed values: uniform, triangular, epanechnikov, quartic, triweight, gaussian, cosine
Default: gaussian
-o
Try to calculate an optimal radius with given 'radius' taken as maximum (experimental)
-q
Only calculate optimal radius and exit (no map is written)
-n
In network mode, normalize values by sum of density multiplied by length of each segment. Integral over the output map then gives 1.0 * multiplier
-m
In network mode, multiply the result by number of input points
--overwrite
Allow output files to overwrite existing files
--help
Print usage summary
--verbose
Verbose module output
--quiet
Quiet module output
--qq
Very quiet module output
--ui
Force launching GUI dialog
input : str, required
Name of input vector map with training points
Used as: input, vector, name
net : str, optional
Name of input network vector map
Used as: input, vector, name
output : str, optional
Name for output raster map
Used as: output, raster, name
net_output : str, optional
Name for output vector density map
Outputs vector map if network map is given
Used as: output, vector, name
radius : float, required
Kernel radius in map units
dsize : float, optional
Discretization error in map units
Default: 0.
segmax : float, optional
Maximum length of segment on network
Default: 100.
distmax : float, optional
Maximum distance from point to network
Default: 100.
multiplier : float, optional
Multiply the density result by this number
Default: 1.
node : str, optional
Node method
Allowed values: none, split
none: No method applied at nodes with more than 2 arcs
split: Equal split (Okabe 2009) applied at nodes
Default: none
kernel : str, optional
Kernel function
Allowed values: uniform, triangular, epanechnikov, quartic, triweight, gaussian, cosine
Default: gaussian
flags : str, optional
Allowed values: o, q, n, m
o
Try to calculate an optimal radius with given 'radius' taken as maximum (experimental)
q
Only calculate optimal radius and exit (no map is written)
n
In network mode, normalize values by sum of density multiplied by length of each segment. Integral over the output map then gives 1.0 * multiplier
m
In network mode, multiply the result by number of input points
overwrite : bool, optional
Allow output files to overwrite existing files
Default: None
verbose : bool, optional
Verbose module output
Default: None
quiet : bool, optional
Quiet module output
Default: None
superquiet : bool, optional
Very quiet module output
Default: None
input : str, required
Name of input vector map with training points
Used as: input, vector, name
net : str, optional
Name of input network vector map
Used as: input, vector, name
output : str | type(np.ndarray) | type(np.array) | type(gs.array.array), optional
Name for output raster map
Used as: output, raster, name
net_output : str, optional
Name for output vector density map
Outputs vector map if network map is given
Used as: output, vector, name
radius : float, required
Kernel radius in map units
dsize : float, optional
Discretization error in map units
Default: 0.
segmax : float, optional
Maximum length of segment on network
Default: 100.
distmax : float, optional
Maximum distance from point to network
Default: 100.
multiplier : float, optional
Multiply the density result by this number
Default: 1.
node : str, optional
Node method
Allowed values: none, split
none: No method applied at nodes with more than 2 arcs
split: Equal split (Okabe 2009) applied at nodes
Default: none
kernel : str, optional
Kernel function
Allowed values: uniform, triangular, epanechnikov, quartic, triweight, gaussian, cosine
Default: gaussian
flags : str, optional
Allowed values: o, q, n, m
o
Try to calculate an optimal radius with given 'radius' taken as maximum (experimental)
q
Only calculate optimal radius and exit (no map is written)
n
In network mode, normalize values by sum of density multiplied by length of each segment. Integral over the output map then gives 1.0 * multiplier
m
In network mode, multiply the result by number of input points
overwrite : bool, optional
Allow output files to overwrite existing files
Default: None
verbose : bool, optional
Verbose module output
Default: None
quiet : bool, optional
Quiet module output
Default: None
superquiet : bool, optional
Very quiet module output
Default: None
Returns:
result : grass.tools.support.ToolResult | np.ndarray | tuple[np.ndarray] | None
If the tool produces text as standard output, a ToolResult object will be returned. Otherwise, None will be returned. If an array type (e.g., np.ndarray) is used for one of the raster outputs, the result will be an array and will have the shape corresponding to the computational region. If an array type is used for more than one raster output, the result will be a tuple of arrays.
Raises:
grass.tools.ToolError: When the tool ended with an error.
DESCRIPTION
v.kernel generates a raster density map from vector points data using a moving kernel. Available kernel density functions are uniform, triangular, epanechnikov, quartic, triweight, gaussian, cosine. The default function is gaussian.
The module can also generate a vector density map on a vector network. Conventional kernel functions produce biased estimates by overestimating the densities around network nodes, whereas the equal split method of Okabe et al. (2009) produces unbiased density estimates. The equal split method uses the kernel function selected with the kernel option and can be enabled with node=split.
NOTES
The multiplier option is needed to overcome the limitation that the resulting density in case of a vector map output is stored as category (integer). The density result stored as category may be multiplied by this number.
For the gaussian kernel, standard deviation for the gaussian function is set to 1/4 of the radius.
With the -o flag (experimental) the command tries to calculate an optimal radius. The value of radius is taken as maximum value. The radius is calculated based on the gaussian function, using ALL points, not just those in the current region.
EXAMPLES
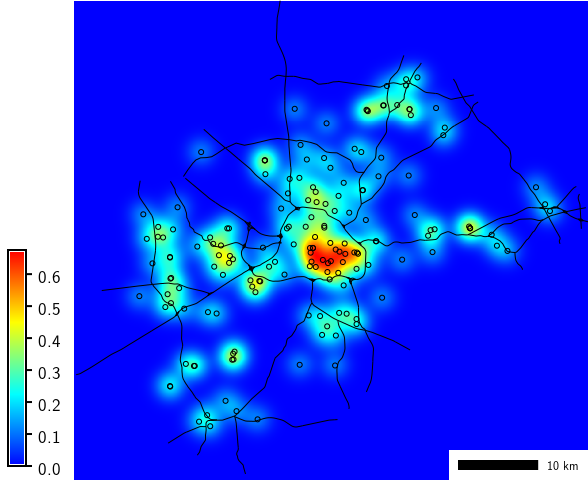
Compute density of points (using vector map of schools from North Carolina sample dataset):
g.region region=wake_30m
v.kernel input=schools_wake output=schools_density radius=5000 multiplier=1000000
r.colors map=schools_density color=bcyr
KNOWN ISSUES
The module only considers the presence of points, but not (yet) any attribute values.
REFERENCES
- Okabe, A., Satoh, T., Sugihara, K. (2009). A kernel density
estimation method for networks, its computational method and a
GIS-based tool. International Journal of Geographical Information
Science, Vol 23(1), pp. 7-32.
DOI: 10.1080/13658810802475491
SEE ALSO
Overview: Interpolation and Resampling in GRASS
AUTHORS
Stefano Menegon, ITC-irst, Trento, Italy
Radim Blazek (additional kernel density functions and network part)
SOURCE CODE
Available at: v.kernel source code
(history)
Latest change: Friday Aug 08 09:39:19 2025 in commit ed72c71