i.hyper.import
Hyperspectral imagery import.
i.hyper.import [-n] input=name product=string output=name [composites=string [,string,...]] [composites_custom=string] [strength=integer] [--overwrite] [--verbose] [--quiet] [--qq] [--ui]
Example:
i.hyper.import input=name product=prisma output=name
grass.script.run_command("i.hyper.import", input, product="prisma", output, composites=None, composites_custom=None, strength=96, flags=None, overwrite=None, verbose=None, quiet=None, superquiet=None)
Example:
gs.run_command("i.hyper.import", input="name", product="prisma", output="name")
grass.tools.Tools.i_hyper_import(input, product="prisma", output, composites=None, composites_custom=None, strength=96, flags=None, overwrite=None, verbose=None, quiet=None, superquiet=None)
Example:
tools = Tools()
tools.i_hyper_import(input="name", product="prisma", output="name")
This grass.tools API is experimental in version 8.5 and expected to be stable in version 8.6.
Parameters
input=name [required]
Path to the hyperspectral imagery: pick any file if the product is multi-file.
product=string [required]
Define the hyperspectral product you want to import (lowercase).
Allowed values: prisma, enmap, tanager
Default: prisma
output=name [required]
Set the name of the output hyperspectral 3D raster map.
composites=string [,string,...]
Composites to generate during import
Allowed values: rgb, cir, swir_agriculture, swir_geology
composites_custom=string
Wavelenghts for custom composites
strength=integer
Cropping intensity - upper brightness level (0-100)
Default: 96
-n
Import also all-NULL bands
--overwrite
Allow output files to overwrite existing files
--help
Print usage summary
--verbose
Verbose module output
--quiet
Quiet module output
--qq
Very quiet module output
--ui
Force launching GUI dialog
input : str, required
Path to the hyperspectral imagery: pick any file if the product is multi-file.
Used as: input, file, name
product : str, required
Define the hyperspectral product you want to import (lowercase).
Allowed values: prisma, enmap, tanager
Default: prisma
output : str, required
Set the name of the output hyperspectral 3D raster map.
Used as: output, raster_3d, name
composites : str | list[str], optional
Composites to generate during import
Allowed values: rgb, cir, swir_agriculture, swir_geology
composites_custom : str, optional
Wavelenghts for custom composites
strength : int, optional
Cropping intensity - upper brightness level (0-100)
Default: 96
flags : str, optional
Allowed values: n
n
Import also all-NULL bands
overwrite : bool, optional
Allow output files to overwrite existing files
Default: None
verbose : bool, optional
Verbose module output
Default: None
quiet : bool, optional
Quiet module output
Default: None
superquiet : bool, optional
Very quiet module output
Default: None
input : str | io.StringIO, required
Path to the hyperspectral imagery: pick any file if the product is multi-file.
Used as: input, file, name
product : str, required
Define the hyperspectral product you want to import (lowercase).
Allowed values: prisma, enmap, tanager
Default: prisma
output : str, required
Set the name of the output hyperspectral 3D raster map.
Used as: output, raster_3d, name
composites : str | list[str], optional
Composites to generate during import
Allowed values: rgb, cir, swir_agriculture, swir_geology
composites_custom : str, optional
Wavelenghts for custom composites
strength : int, optional
Cropping intensity - upper brightness level (0-100)
Default: 96
flags : str, optional
Allowed values: n
n
Import also all-NULL bands
overwrite : bool, optional
Allow output files to overwrite existing files
Default: None
verbose : bool, optional
Verbose module output
Default: None
quiet : bool, optional
Quiet module output
Default: None
superquiet : bool, optional
Very quiet module output
Default: None
Returns:
result : grass.tools.support.ToolResult | None
If the tool produces text as standard output, a ToolResult object will be returned. Otherwise, None will be returned.
Raises:
grass.tools.ToolError: When the tool ended with an error.
DESCRIPTION
i.hyper.import imports hyperspectral imagery into a 3D raster map
(raster_3d).
The module reads supported hyperspectral products and converts their spectral bands into a single 3D raster map. The vertical (z) dimension of the 3D raster represents the spectral dimension, where each cell (voxel) contains the reflectance value for a specific spatial position (x, y) and spectral band index.
i.hyper.import is part of the i.hyper module family designed for hyperspectral data import, processing, and analysis in GRASS. It is typically used in combination with i.hyper.preproc, i.hyper.explore, i.hyper.composite, and i.hyper.export.
The module currently supports the following hyperspectral products:
- PRISMA -- PRecursore IperSpettrale della Missione Applicativa (ASI)
- EnMAP -- Environmental Mapping and Analysis Program (DLR / GFZ)
- Tanager -- Planet Labs hyperspectral mission
During import, the appropriate product library from i_hyper_lib is
automatically loaded (for example, enmap, prisma, or tanager).
Metadata are parsed, bands are validated, and the resulting 3D raster
map is created with per-band metadata: wavelength, FWHM,
valid, and unit.
The metadata are used by other i.hyper.* modules, so data imported with i.hyper.import or created with the same metadata structure are fully compatible across the toolset.
The resulting raster_3d map can be analysed with standard GRASS 3D
raster tools (r3.mapcalc, r3.stats, r3.univar) or processed
further with the i.hyper suite of modules.
NOTES
Imported 3D raster maps store hyperspectral reflectance or radiance
values (depending on the product). Bands containing only zeros, NULLs,
or invalid values are flagged with valid: 0; others are flagged as
valid: 1.
When the composites option is used, predefined or custom band combinations are exported as 2D raster composites (e.g., RGB, CIR, SWIR). All temporary rasters are automatically removed after import.
During import, i.hyper.import temporarily adjusts the computational region to match the input data, ensuring consistent alignment between imported bands. This region setting is temporary and restored at the end of processing. The module does not perform any on-the-fly spatial or spectral resampling. The imported cube retains the native resolution and extent of the input product, but the region settings are not changed during import.
EXAMPLES
::: code
# EnMAP example
# Create a new GRASS project with EPSG:32633 (UTM Zone 33N)
grass -c EPSG:32633 -e ~/grassdata/hyper_33N
# Initialize and enter the new project (PERMANENT Mapset)
grass ~/grassdata/hyper_33N/PERMANENT
:::
::: code
# PRISMA L2D example
i.hyper.import input=/data/PRISMA.he5 \
product=prisma \
output=prisma \
composites='rgb,cir,swir_agriculture,swir_geology'
# Console output:
Importing product: PRISMA
Loading floating point data with 4 bytes ... (1254x1222x234)
Created 3D raster map with all bands: prisma (234 bands).
Generated composite raster: prisma_rgb
Generated composite raster: prisma_cir
Generated composite raster: prisma_swir_agriculture
Generated composite raster: prisma_swir_geology
(Fri Nov 5 13:12:00 2025) Command finished (1 min 23 sec)
:::
:::::::::: {align="center" style="margin: 10px"}
::: {align="center" style="margin: 10px"}
 {width="600"
height="600" border="0"}\
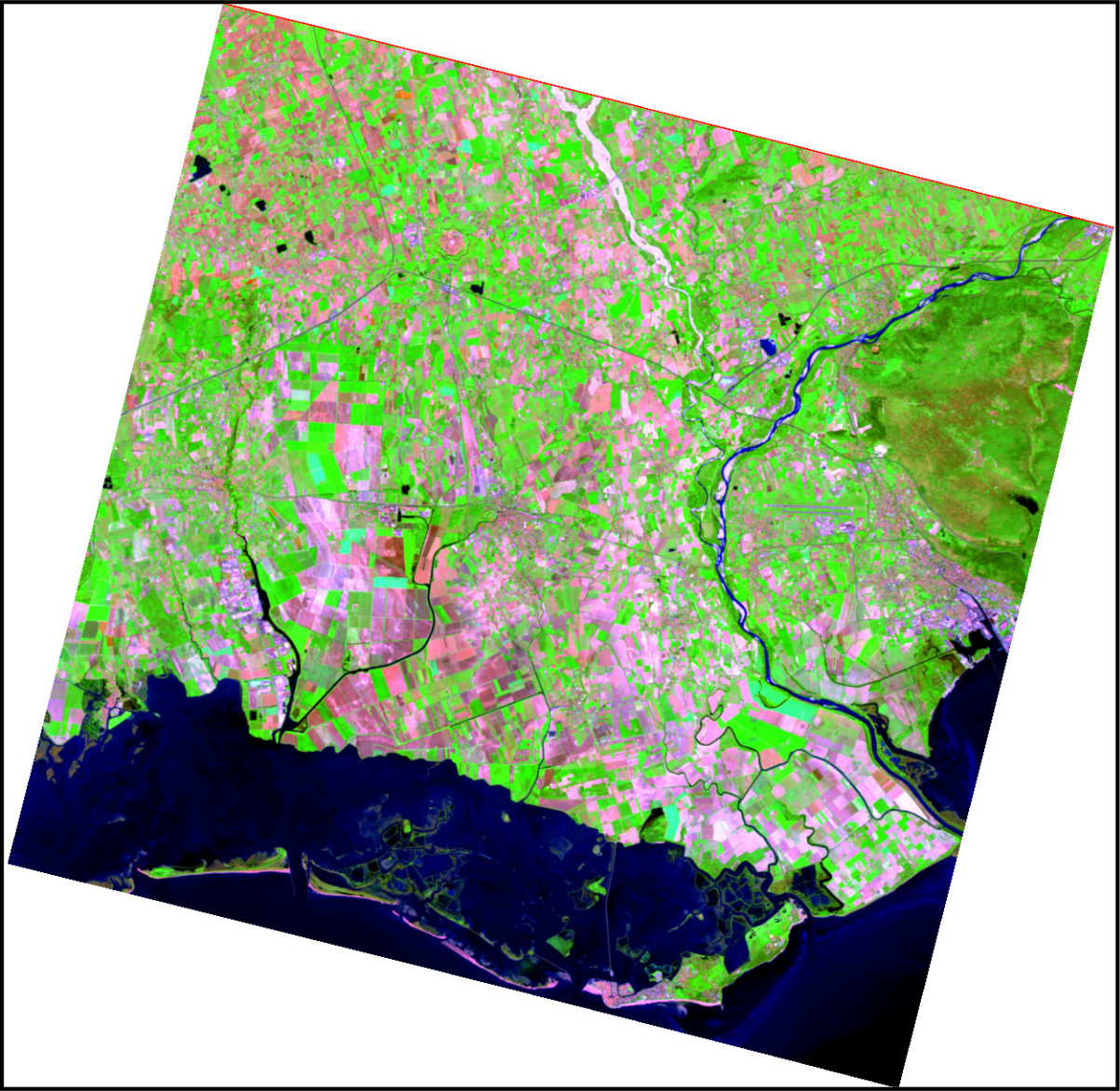
Figure: PRISMA SWIR-geology composite generated with i.hyper.import\
[Data source: PRISMA Product © Italian Space Agency (ASI), used under
ASI License to Use.]{.small}
:::
{width="600"
height="600" border="0"}\
Figure: PRISMA SWIR-geology composite generated with i.hyper.import\
[Data source: PRISMA Product © Italian Space Agency (ASI), used under
ASI License to Use.]{.small}
:::
::: code
# Import an EnMAP L2A product and create RGB and CIR composites
i.hyper.import input=/data/EnMAP_data_folder/ \
product=enmap \
output=enmap \
composites='cir,swir_agriculture'
composites_custom='650,1650,2200'
:::
::::::: {align="center" style="margin: 10px"}
::: {align="center" style="margin: 10px"}
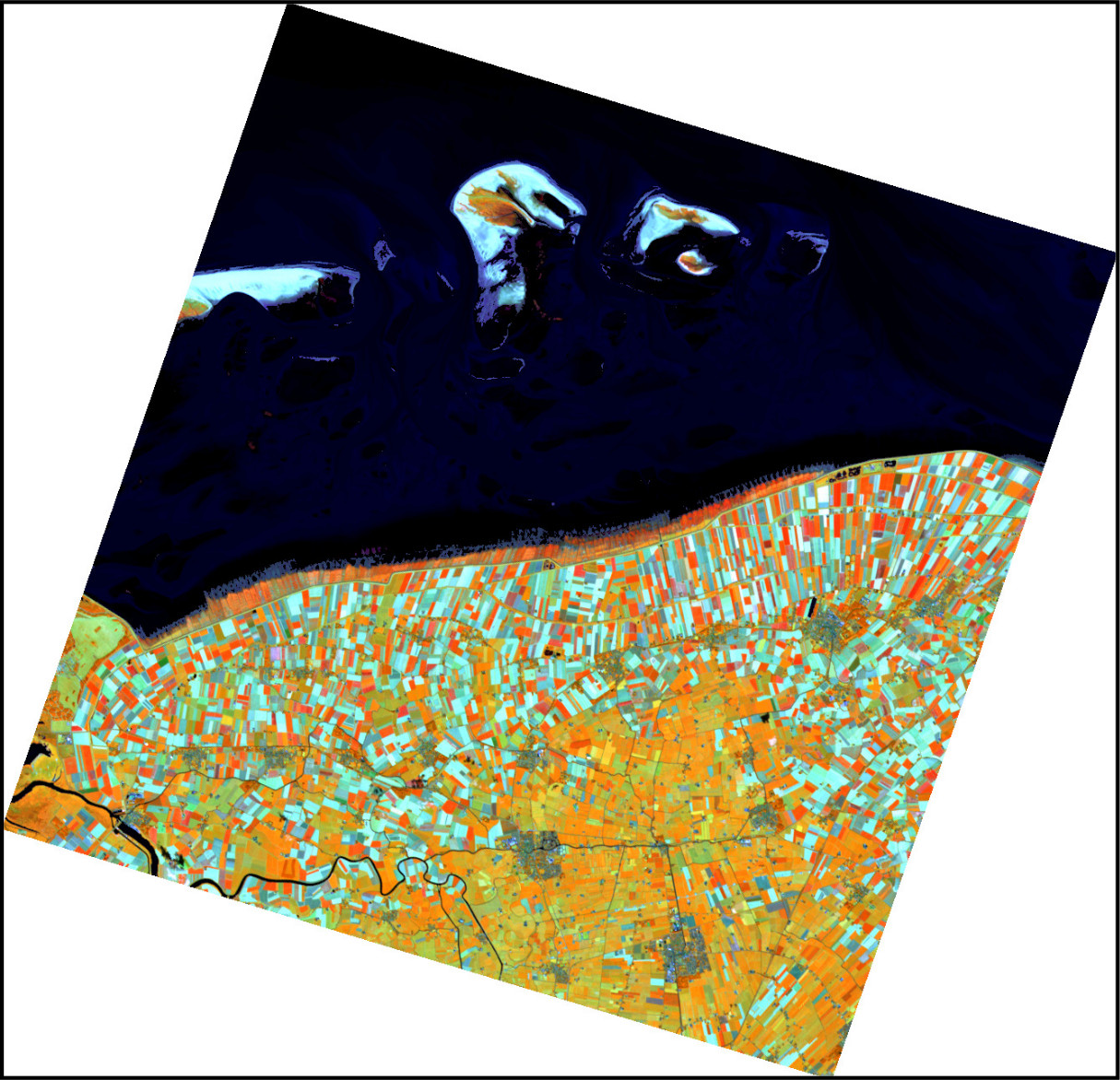 \
Figure: EnMAP SWIR-agriculture composite generated with
i.hyper.import\
[Data source: Copyright © 2012-2025 EnMAP at Earth Observation Center
EOC of DLR.]{.small}
:::
\
Figure: EnMAP SWIR-agriculture composite generated with
i.hyper.import\
[Data source: Copyright © 2012-2025 EnMAP at Earth Observation Center
EOC of DLR.]{.small}
:::
::: code
# Tanager example with a custom-defined composite
# This one has radiance values
i.hyper.import input=/data/Tanager.h5 \
product=tanager \
output=tanager \
composites='rgb' \
:::
:::: {align="center" style="margin: 10px"}
::: {align="center" style="margin: 10px"}
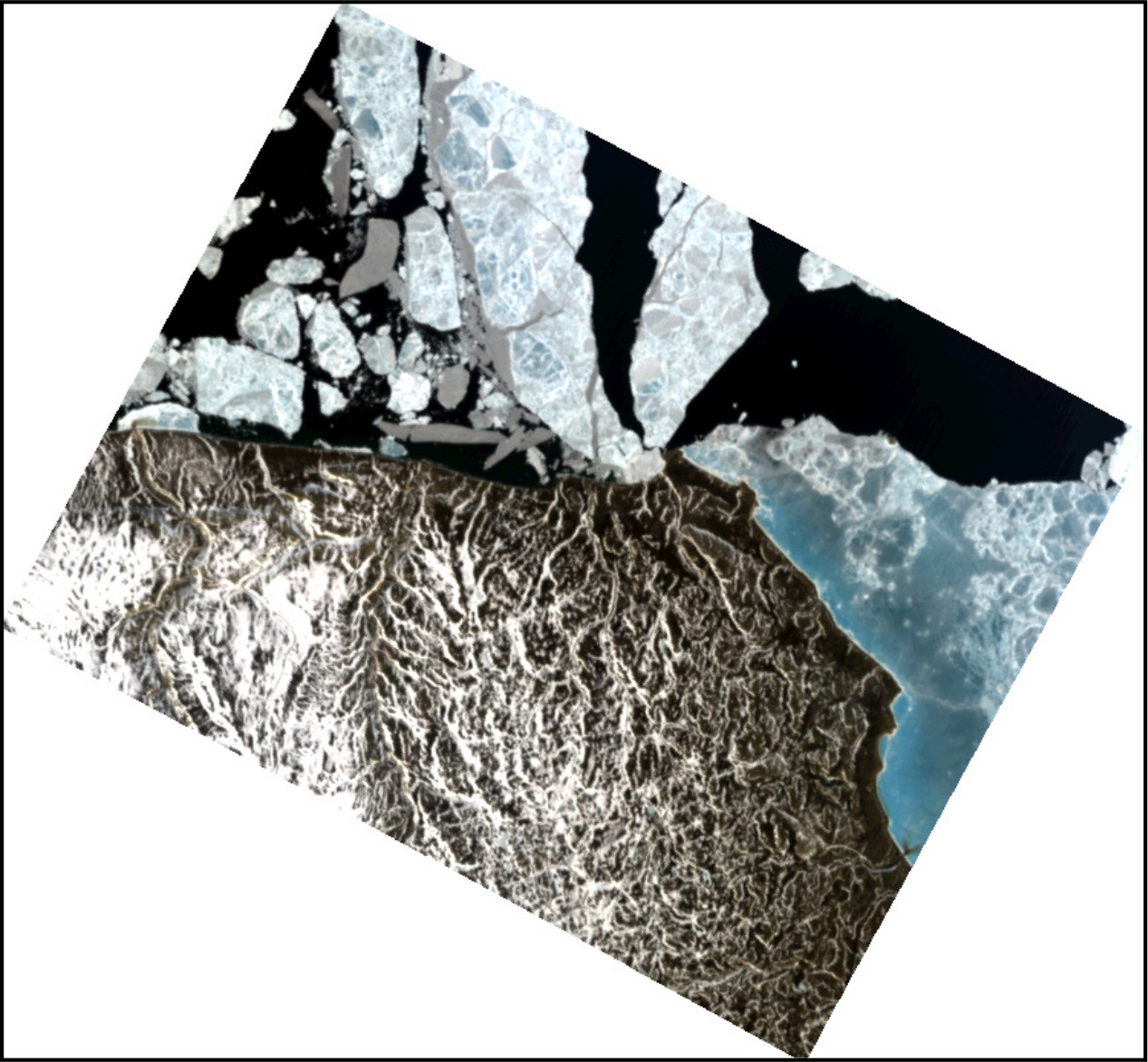 {width="600"
height="600" border="0"}\
Figure: Tanager-1 RGB composite generated with i.hyper.import\
[Data source: Planet Labs - Open Data, CC-BY-4.0.]{.small}
:::
{width="600"
height="600" border="0"}\
Figure: Tanager-1 RGB composite generated with i.hyper.import\
[Data source: Planet Labs - Open Data, CC-BY-4.0.]{.small}
:::
SEE ALSO
EnMAP Example Data Products, Tanager Core Imagery, i.hyper.preproc, i.hyper.explore, i.hyper.composite, i.hyper.export r3.support, r3.stats r3.stats
DEPENDENCIES
- NumPy -- Core numerical operations and array manipulation.
- h5py -- Interface for reading and writing
.h5(HDF5) hyperspectral data products such as PRISMA and Tanager. - pyproj -- Coordinate reference system and geospatial transformation library.
AUTHORS
Alen Mangafić and Tomaž Žagar, Geodetic Institute of Slovenia :::: ::::::: ::::::::::
SOURCE CODE
Available at: i.hyper.import source code
(history)
Latest change: Tuesday Jan 06 21:39:11 2026 in commit 22f101f