r.hydrobasin
Delineates a large number of watersheds using the Memory-Efficient Watershed Delineation (MESHED) OpenMP parallel algorithm by Cho (2025).
r.hydrobasin [-m] direction=name format=string outlets=name [layer=string] [column=name] output=name [nprocs=integer] [--overwrite] [--verbose] [--quiet] [--qq] [--ui]
Example:
r.hydrobasin direction=name format=auto outlets=name output=name
grass.script.run_command("r.hydrobasin", direction, format="auto", outlets, layer="1", column="cat", output, nprocs=0, flags=None, overwrite=None, verbose=None, quiet=None, superquiet=None)
Example:
gs.run_command("r.hydrobasin", direction="name", format="auto", outlets="name", output="name")
grass.tools.Tools.r_hydrobasin(direction, format="auto", outlets, layer="1", column="cat", output, nprocs=0, flags=None, overwrite=None, verbose=None, quiet=None, superquiet=None)
Example:
tools = Tools()
tools.r_hydrobasin(direction="name", format="auto", outlets="name", output="name")
This grass.tools API is experimental in version 8.5 and expected to be stable in version 8.6.
Parameters
direction=name [required]
Name of input direction raster map
format=string [required]
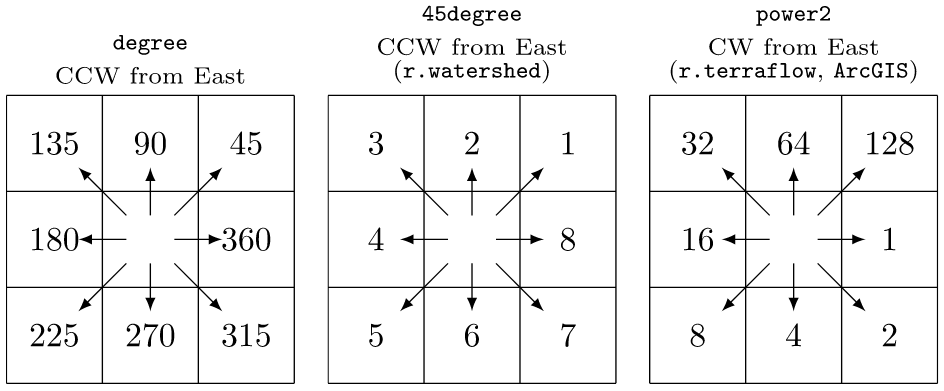
Format of input direction raster map
Allowed values: auto, degree, 45degree, power2
Default: auto
auto: auto-detect direction format
degree: degrees CCW from East
45degree: degrees CCW from East divided by 45 (e.g. r.watershed)
power2: powers of 2 CW from East (e.g., r.terraflow, ArcGIS)
outlets=name [required]
Name of input outlets vector map
Or data source for direct OGR access
layer=string
Layer number or name
Vector features can have category values in different layers. This number determines which layer to use. When used with direct OGR access this is the layer name.
Default: 1
column=name
Name of attribute column for watershed IDs (using a non-default column is slower)
Default: cat
output=name [required]
Name for output watersheds raster map
nprocs=integer
Number of threads for parallel computing
0: use OpenMP default; >0: use nprocs; <0: use MAX-nprocs
Default: 0
-m
Use less memory
--overwrite
Allow output files to overwrite existing files
--help
Print usage summary
--verbose
Verbose module output
--quiet
Quiet module output
--qq
Very quiet module output
--ui
Force launching GUI dialog
direction : str, required
Name of input direction raster map
Used as: input, raster, name
format : str, required
Format of input direction raster map
Allowed values: auto, degree, 45degree, power2
auto: auto-detect direction format
degree: degrees CCW from East
45degree: degrees CCW from East divided by 45 (e.g. r.watershed)
power2: powers of 2 CW from East (e.g., r.terraflow, ArcGIS)
Default: auto
outlets : str, required
Name of input outlets vector map
Or data source for direct OGR access
Used as: input, vector, name
layer : str, optional
Layer number or name
Vector features can have category values in different layers. This number determines which layer to use. When used with direct OGR access this is the layer name.
Used as: input, layer
Default: 1
column : str, optional
Name of attribute column for watershed IDs (using a non-default column is slower)
Used as: input, dbcolumn, name
Default: cat
output : str, required
Name for output watersheds raster map
Used as: output, raster, name
nprocs : int, optional
Number of threads for parallel computing
0: use OpenMP default; >0: use nprocs; <0: use MAX-nprocs
Default: 0
flags : str, optional
Allowed values: m
m
Use less memory
overwrite : bool, optional
Allow output files to overwrite existing files
Default: None
verbose : bool, optional
Verbose module output
Default: None
quiet : bool, optional
Quiet module output
Default: None
superquiet : bool, optional
Very quiet module output
Default: None
direction : str | np.ndarray, required
Name of input direction raster map
Used as: input, raster, name
format : str, required
Format of input direction raster map
Allowed values: auto, degree, 45degree, power2
auto: auto-detect direction format
degree: degrees CCW from East
45degree: degrees CCW from East divided by 45 (e.g. r.watershed)
power2: powers of 2 CW from East (e.g., r.terraflow, ArcGIS)
Default: auto
outlets : str, required
Name of input outlets vector map
Or data source for direct OGR access
Used as: input, vector, name
layer : str, optional
Layer number or name
Vector features can have category values in different layers. This number determines which layer to use. When used with direct OGR access this is the layer name.
Used as: input, layer
Default: 1
column : str, optional
Name of attribute column for watershed IDs (using a non-default column is slower)
Used as: input, dbcolumn, name
Default: cat
output : str | type(np.ndarray) | type(np.array) | type(gs.array.array), required
Name for output watersheds raster map
Used as: output, raster, name
nprocs : int, optional
Number of threads for parallel computing
0: use OpenMP default; >0: use nprocs; <0: use MAX-nprocs
Default: 0
flags : str, optional
Allowed values: m
m
Use less memory
overwrite : bool, optional
Allow output files to overwrite existing files
Default: None
verbose : bool, optional
Verbose module output
Default: None
quiet : bool, optional
Quiet module output
Default: None
superquiet : bool, optional
Very quiet module output
Default: None
Returns:
result : grass.tools.support.ToolResult | np.ndarray | tuple[np.ndarray] | None
If the tool produces text as standard output, a ToolResult object will be returned. Otherwise, None will be returned. If an array type (e.g., np.ndarray) is used for one of the raster outputs, the result will be an array and will have the shape corresponding to the computational region. If an array type is used for more than one raster output, the result will be a tuple of arrays.
Raises:
grass.tools.ToolError: When the tool ended with an error.
DESCRIPTION
r.hydrobasin delineates a large number of watersheds from a flow direction raster map and an outlets vector map using the Memory-Efficient Watershed Delineation (MESHED) OpenMP parallel algorithm by Cho (2025).
NOTES
r.hydrobasin uses a flow direction raster map and an outlets vector map to delineate a large number of watersheds in parallel using OpenMP.
The module recognizes three different formats of flow directions:
r.watershed can be used to create an input flow direction raster map. It can also create watersheds, but it uses an elevation map instead of a flow direction map, which is actually one of its outputs, and does not take outlets as input. r.hydrobasin is more similar to r.water.outlet and r.stream.basins. Both modules take an input flow direction map from r.watershed, but r.water.outlet can delineate a watershed for one outlet point at a time and r.stream.basins is a sequential module for multiple watersheds. Unlike r.stream.basins, r.hydrobasin can use a column for watershed IDs, but using a non-default column is slower than using the default category (cat) column because of database queries.
For comparisons, using an i7-1370P CPU with 64GB memory and a 30-meter flow direction map for the entire Texas (1.8 billion cells), r.hydrobasin took 1 minute 27 seconds to delineate the entire state using 60,993 outlet cells draining away (see below how to extract draining cells) while r.stream.basins 5 minutes 28 seconds, both using the category column. However, r.hydrobasin with a non-category column took 6 minutes 21 seconds because of heavy database queries.
EXAMPLES
These examples use the North Carolina sample dataset.
Calculate flow accumulation using r.watershed and delineate all watersheds from draining cells using r.hydrobasin:
# set computational region
g.region -ap raster=elevation
# calculate drainage directions using r.watershed
r.watershed -s elevation=elevation drainage=drain
# extract draining cells
r.mapcalc ex="dcells=if(\
(isnull(drain[-1,-1])&&abs(drain)==3)||\
(isnull(drain[-1,0])&&abs(drain)==2)||\
(isnull(drain[-1,1])&&abs(drain)==1)||\
(isnull(drain[0,-1])&&abs(drain)==4)||\
(isnull(drain[0,1])&&abs(drain)==8)||\
(isnull(drain[1,-1])&&abs(drain)==5)||\
(isnull(drain[1,0])&&abs(drain)==6)||\
(isnull(drain[1,1])&&abs(drain)==7),1,null())"
r.to.vect input=dcells type=point output=dcells
# delineate all watersheds using r.hydrobasin
r.hydrobasin dir=drain outlets=dcells output=wsheds nprocs=$(nproc)
Perform the same analysis for 10,938 bridges in North Carolina:
# set computational region
g.region -ap raster=elev_state_500m
# calculate drainage directions using r.watershed
r.watershed -s elevation=elev_state_500m drainage=drain_state
# delineate all watersheds using r.hydrobasin
r.hydrobasin dir=drain_state outlets=bridges output=bridge_wsheds nproc=$(nproc)
SEE ALSO
r.flowaccumulation, r.accumulate, r.watershed, r.stream.extract, r.stream.distance
REFERENCES
Huidae Cho, January 2025. Avoid Backtracking and Burn Your Inputs: CONUS-Scale Watershed Delineation Using OpenMP. Environmental Modelling & Software 183, 106244. doi:10.1016/j.envsoft.2024.106244.
AUTHOR
Huidae Cho, New Mexico State University
SOURCE CODE
Available at: r.hydrobasin source code
(history)
Latest change: Sunday Nov 23 09:54:48 2025 in commit 9cf4911