r.slope.direction
Calculates slope following a direction raster.
r.slope.direction [-a] elevation=name direction=name dir_type=string steps=string slope_measure=string output=name [,name,...] [--overwrite] [--verbose] [--quiet] [--qq] [--ui]
Example:
r.slope.direction elevation=name direction=name dir_type=auto steps=1 slope_measure=degree output=name
grass.script.run_command("r.slope.direction", elevation, direction, dir_type="auto", steps="1", slope_measure="degree", output, flags=None, overwrite=None, verbose=None, quiet=None, superquiet=None)
Example:
gs.run_command("r.slope.direction", elevation="name", direction="name", dir_type="auto", steps="1", slope_measure="degree", output="name")
grass.tools.Tools.r_slope_direction(elevation, direction, dir_type="auto", steps="1", slope_measure="degree", output, flags=None, overwrite=None, verbose=None, quiet=None, superquiet=None)
Example:
tools = Tools()
tools.r_slope_direction(elevation="name", direction="name", dir_type="auto", steps="1", slope_measure="degree", output="name")
This grass.tools API is experimental in version 8.5 and expected to be stable in version 8.6.
Parameters
elevation=name [required]
Name of input elevation raster map
direction=name [required]
Input Direction raster map
Name of input raster map
dir_type=string [required]
Direction type
Type of diretion encoding in diections input raster map (default: auto)
Allowed values: 45degree, degree, bitmask, bitmask_k, auto
Default: auto
steps=string [required]
Number of steps
Comma separated list of steps in direction for which slope is computed
Default: 1
slope_measure=string [required]
Slope measure
Format for reporting the slope (default: degree)
Allowed values: difference, percent, percent_int, degree, degree_int
Default: degree
output=name [,name,...] [required]
Name for output raster map(s)
-a
Compute slope as absolute values
Compute slope as absolute values (default allows negative slopes)
--overwrite
Allow output files to overwrite existing files
--help
Print usage summary
--verbose
Verbose module output
--quiet
Quiet module output
--qq
Very quiet module output
--ui
Force launching GUI dialog
elevation : str, required
Name of input elevation raster map
Used as: input, raster, name
direction : str, required
Input Direction raster map
Name of input raster map
Used as: input, raster, name
dir_type : str, required
Direction type
Type of diretion encoding in diections input raster map (default: auto)
Allowed values: 45degree, degree, bitmask, bitmask_k, auto
Default: auto
steps : str, required
Number of steps
Comma separated list of steps in direction for which slope is computed
Default: 1
slope_measure : str, required
Slope measure
Format for reporting the slope (default: degree)
Allowed values: difference, percent, percent_int, degree, degree_int
Default: degree
output : str | list[str], required
Name for output raster map(s)
Used as: output, raster, name
flags : str, optional
Allowed values: a
a
Compute slope as absolute values
Compute slope as absolute values (default allows negative slopes)
overwrite : bool, optional
Allow output files to overwrite existing files
Default: None
verbose : bool, optional
Verbose module output
Default: None
quiet : bool, optional
Quiet module output
Default: None
superquiet : bool, optional
Very quiet module output
Default: None
elevation : str | np.ndarray, required
Name of input elevation raster map
Used as: input, raster, name
direction : str | np.ndarray, required
Input Direction raster map
Name of input raster map
Used as: input, raster, name
dir_type : str, required
Direction type
Type of diretion encoding in diections input raster map (default: auto)
Allowed values: 45degree, degree, bitmask, bitmask_k, auto
Default: auto
steps : str, required
Number of steps
Comma separated list of steps in direction for which slope is computed
Default: 1
slope_measure : str, required
Slope measure
Format for reporting the slope (default: degree)
Allowed values: difference, percent, percent_int, degree, degree_int
Default: degree
output : str | list[str], required
Name for output raster map(s)
Used as: output, raster, name
flags : str, optional
Allowed values: a
a
Compute slope as absolute values
Compute slope as absolute values (default allows negative slopes)
overwrite : bool, optional
Allow output files to overwrite existing files
Default: None
verbose : bool, optional
Verbose module output
Default: None
quiet : bool, optional
Quiet module output
Default: None
superquiet : bool, optional
Very quiet module output
Default: None
Returns:
result : grass.tools.support.ToolResult | None
If the tool produces text as standard output, a ToolResult object will be returned. Otherwise, None will be returned.
Raises:
grass.tools.ToolError: When the tool ended with an error.
DESCRIPTION
r.slope.direction computes slope as elevation difference divided by distance along a user given number of steps following a direction map.
Difference in altitude to the neighboring cell in the given direction is measured and divided by the distance (determined by north south and east west resolution of the computational region). With the steps paramter the user can define how many steps along the direction map the algorithm should perform. For each step a temporary raster map is created. Thus, processing time is - in addition to the computational region - mainly determined by the maximum steps value. Multiple neighboorhoods can be given in order to produce slope measures at different spatial scales.
The slope_measure option defines the format in which slope is reported. Possible values are
- degree (the default) - the angle described by the total elevation difference devided by the total distance over the user given number of steps along the direction map
- degree_int - same as degree but multiplied with 100 and rounded to the closest integer to limit data volume
- difference - the total elevation difference independent from the x-y distance along the direction map
- percent - the ratio between the total elevation difference and the total distance over the user given number of steps along the direction map
- percent_int - same as percent but multiplied with 10000 and rounded to the closest integer to limit data volume
The a-flag allows to compute slope as absolute elevation differences.
EXAMPLES
The following examples are based on the North Carolina dataset!
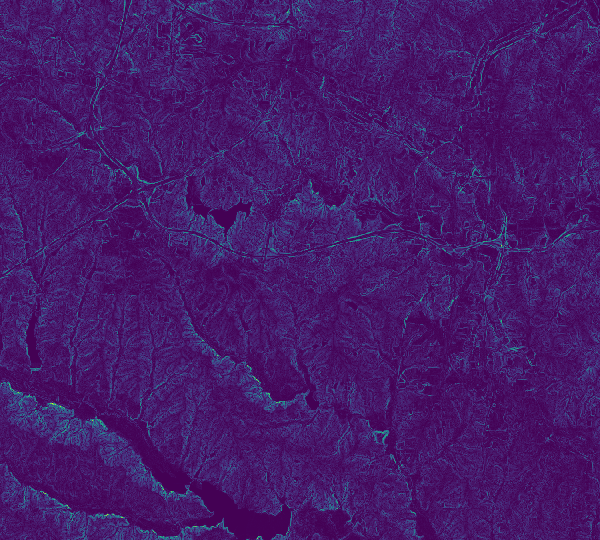
Slope following a flow direction raster at different scales
# Set the computational region
g.region -p raster=elevation
# Convert street network to raster and assign pixels direction value
r.watershed elevation=elevation accumulation=faccum drainage=fdir
r.slope.direction --o --v elevation=elevation direction=fdir \
steps=1,5,13 output=fdir_slope_1,fdir_slope_5,fdir_slope_13 \
method=total_gradient format=percent scale=3 type=CELL
 |
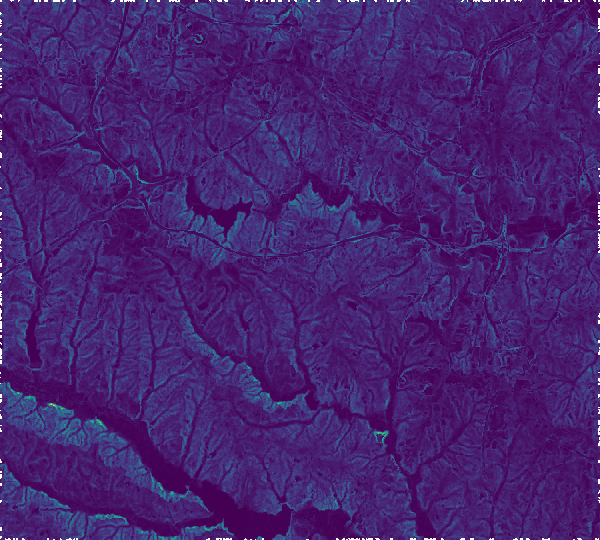 |
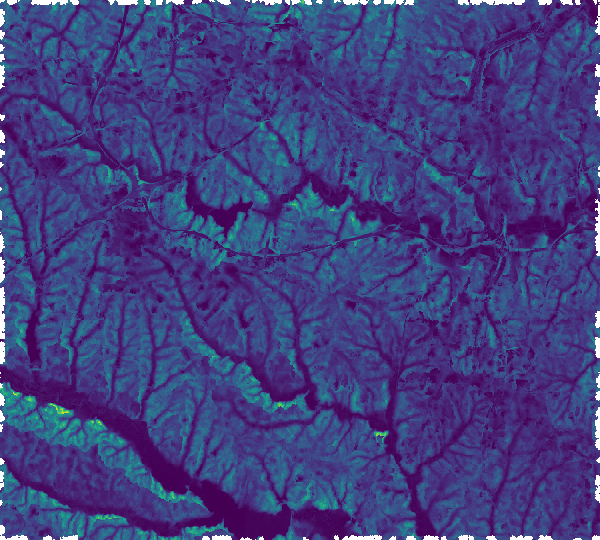 |
| Slope following flow direction for 1 pixel. | Slope following flow direction for 5 pixels. | Slope following flow direction for 13 pixels. |
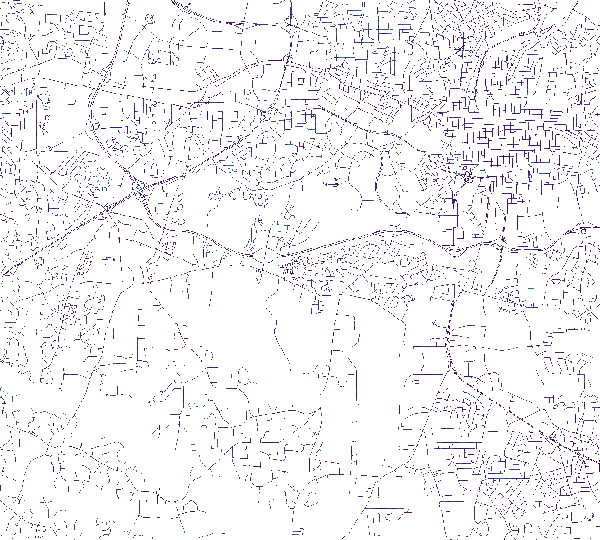
Slope along a street network at different scales
# Set the computational region
g.region -p raster=elevation
# Convert street network to raster and assign pixels direction value
v.to.rast input=streets_wake type=line output=streets_wake use=dir
# Directions output from v.to.rast needs to be adjusted so that:
# - direction information is coded a steps to neighboring cells
# - direction information always points to next pixel on the line
# (only end pixels of a line should point to NULL cells)
# Deinfe variables
in_dir=streets_wake
tmp_dir=streets_wake_45
out_dir=newdir
# Recode direction information
r.mapcalc --o expression="${tmp_dir}=if(int(round(${in_dir}/45.0))==0,8, \
int(round(${in_dir}/45.0)))"
# Make sure that direction points to next non-NULL cell in network
r.mapcalc --o expression="
${out_dir}=if(${in_dir}==8,if(isnull(${in_dir}[0,1]), \
if(isnull(${in_dir}[-1,1]), \
if(isnull(${in_dir}[1,1]), \
if(isnull(${in_dir}[-1,0]), \
if(isnull(${in_dir}[1,0]),8,6),2),7),1),8) \
,if(${in_dir}==7,if(isnull(${in_dir}[1,1]), \
if(isnull(${in_dir}[0,1]), \
if(isnull(${in_dir}[1,0]), \
if(isnull(${in_dir}[-1,1]), \
if(isnull(${in_dir}[1,-1]),7,5),1),6),8),7) \
,if(${in_dir}==6,if(isnull(${in_dir}[1,0]), \
if(isnull(${in_dir}[1,1]), \
if(isnull(${in_dir}[1,-1]), \
if(isnull(${in_dir}[0,1]), \
if(isnull(${in_dir}[0,-1]),6,4),8),5),7),6) \
,if(${in_dir}==5,if(isnull(${in_dir}[1,-1]), \
if(isnull(${in_dir}[1,0]), \
if(isnull(${in_dir}[0,-1]), \
if(isnull(${in_dir}[1,1]), \
if(isnull(${in_dir}[-1,-1]),5,4),7),4),6),5) \
,if(${in_dir}==4,if(isnull(${in_dir}[0,-1]), \
if(isnull(${in_dir}[1,-1]), \
if(isnull(${in_dir}[-1,-1]), \
if(isnull(${in_dir}[1,0]), \
if(isnull(${in_dir}[-1,0]),4,3),6),3),5),4) \
,if(${in_dir}==3,if(isnull(${in_dir}[-1,-1]), \
if(isnull(${in_dir}[0,-1]), \
if(isnull(${in_dir}[-1,0]), \
if(isnull(${in_dir}[1,-1]), \
if(isnull(${in_dir}[-1,-1]),1,3),5),2),4),3) \
,if(${in_dir}==2,if(isnull(${in_dir}[-1,0]), \
if(isnull(${in_dir}[-1,-1]), \
if(isnull(${in_dir}[-1,1]), \
if(isnull(${in_dir}[0,-1]), \
if(isnull(${in_dir}[0,1]),2,8),4),1),3),2) \
,if(${in_dir}==1,if(isnull(${in_dir}[-1,1]), \
if(isnull(${in_dir}[-1,0]), \
if(isnull(${in_dir}[0,1]), \
if(isnull(${in_dir}[-1,-1]), \
if(isnull(${in_dir}[1,1]),1,7),3),8),2),1) \
,null()))))))))"
# Compute slope of the streets for three
# different step-sizes (step)
r.slope.direction -a elevation=elevation \
direction=streets_wake_dir45 steps=1,5,13 \
outputs=streets_wake_slope_1,streets_wake_slope_5,streets_wake_slope_13
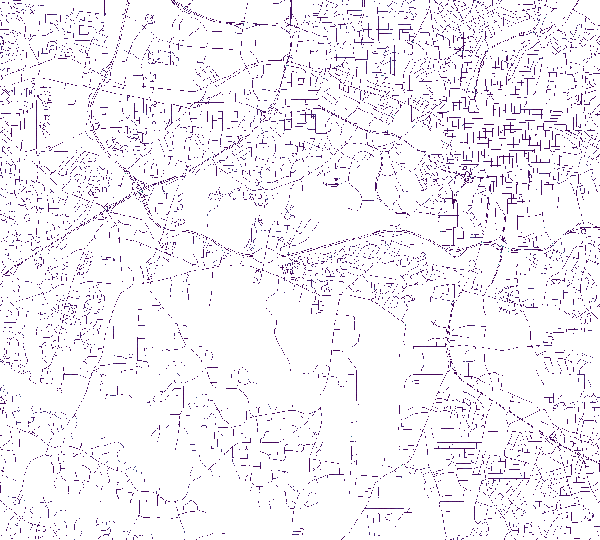 |
 |
 |
| Slope following street direction for 1 pixel. | Slope following street direction for 5 pixels. | Slope following street direction for 13 pixels. |
SEE ALSO
r.mapcalc, r.path, r.slope.aspect, r.stream.slope
AUTHOR
Stefan Blumentrath, Norwegian Institute for Nature Research, Oslo,
Norway
Written for the INVAFISH project (RCN MILJØFORSK grant 243910)
SOURCE CODE
Available at: r.slope.direction source code
(history)
Latest change: Friday Feb 21 12:27:42 2025 in commit 8fce680