r.surf.random
Produces a raster surface map of uniform random deviates with defined range.
r.surf.random [-i] output=name [min=float] [max=float] [seed=integer] [--overwrite] [--verbose] [--quiet] [--qq] [--ui]
Example:
r.surf.random output=name
grass.script.run_command("r.surf.random", output, min=0, max=100, seed=None, flags=None, overwrite=None, verbose=None, quiet=None, superquiet=None)
Example:
gs.run_command("r.surf.random", output="name")
grass.tools.Tools.r_surf_random(output, min=0, max=100, seed=None, flags=None, overwrite=None, verbose=None, quiet=None, superquiet=None)
Example:
tools = Tools()
tools.r_surf_random(output="name")
This grass.tools API is experimental in version 8.5 and expected to be stable in version 8.6.
Parameters
output=name [required]
Name for output raster map
min=float
Minimum random value
Default: 0
max=float
Maximum random value
Default: 100
seed=integer
Seed value for the random number generator
Using the same seed ensures identical results, while a randomly generated seed produces different outcomes in each run.
-i
Create an integer raster map
--overwrite
Allow output files to overwrite existing files
--help
Print usage summary
--verbose
Verbose module output
--quiet
Quiet module output
--qq
Very quiet module output
--ui
Force launching GUI dialog
output : str, required
Name for output raster map
Used as: output, raster, name
min : float, optional
Minimum random value
Default: 0
max : float, optional
Maximum random value
Default: 100
seed : int, optional
Seed value for the random number generator
Using the same seed ensures identical results, while a randomly generated seed produces different outcomes in each run.
flags : str, optional
Allowed values: i
i
Create an integer raster map
overwrite : bool, optional
Allow output files to overwrite existing files
Default: None
verbose : bool, optional
Verbose module output
Default: None
quiet : bool, optional
Quiet module output
Default: None
superquiet : bool, optional
Very quiet module output
Default: None
output : str | type(np.ndarray) | type(np.array) | type(gs.array.array), required
Name for output raster map
Used as: output, raster, name
min : float, optional
Minimum random value
Default: 0
max : float, optional
Maximum random value
Default: 100
seed : int, optional
Seed value for the random number generator
Using the same seed ensures identical results, while a randomly generated seed produces different outcomes in each run.
flags : str, optional
Allowed values: i
i
Create an integer raster map
overwrite : bool, optional
Allow output files to overwrite existing files
Default: None
verbose : bool, optional
Verbose module output
Default: None
quiet : bool, optional
Quiet module output
Default: None
superquiet : bool, optional
Very quiet module output
Default: None
Returns:
result : grass.tools.support.ToolResult | np.ndarray | tuple[np.ndarray] | None
If the tool produces text as standard output, a ToolResult object will be returned. Otherwise, None will be returned. If an array type (e.g., np.ndarray) is used for one of the raster outputs, the result will be an array and will have the shape corresponding to the computational region. If an array type is used for more than one raster output, the result will be a tuple of arrays.
Raises:
grass.tools.ToolError: When the tool ended with an error.
DESCRIPTION
r.surf.random produces a raster map layer of uniform random deviates whose range can be expressed by the user. It is essentially the same as r.surf.gauss, but uses a linear random number generator instead. It uses the random number generator drand48() or rand(), depending on the user's platform.
EXAMPLE
g.region -p n=228500 s=215000 w=630000 e=645000 res=10
r.surf.random out=random min=0 max=100
# check result
r.univar random
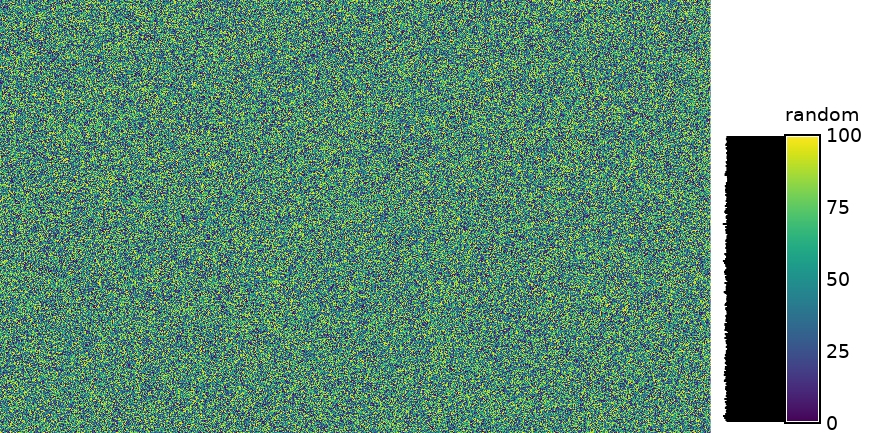
Figure: Random surface example (min: 10; max: 100)
With the histogram tool the cell values versus count can be shown.
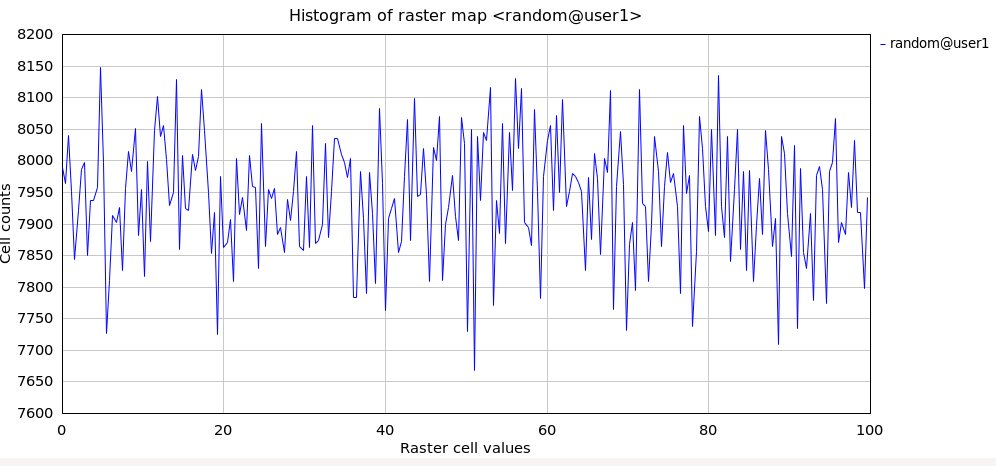
Figure: Histogram of random surface example (min: 10; max: 100)
SEE ALSO
r.random.surface, r.surf.contour, r.surf.fractal, r.surf.gauss, r.surf.idw, v.surf.rst
AUTHOR
Jo Wood
Midlands Regional Research Laboratory (ASSIST)
University of Leicester
October 1991
SOURCE CODE
Available at: r.surf.random source code
(history)
Latest change: Thursday May 08 20:58:05 2025 in commit 4144ba8