i.histo.match
Calculate histogram matching of several images.
i.histo.match input=name [,name,...] [suffix=string] [output=name] [database=name] [max=integer] [nprocs=integer] [--overwrite] [--verbose] [--quiet] [--qq] [--ui]
Example:
i.histo.match input=name
grass.script.run_command("i.histo.match", input, suffix="match", output=None, database=None, max=255, nprocs=0, overwrite=None, verbose=None, quiet=None, superquiet=None)
Example:
gs.run_command("i.histo.match", input="name")
grass.tools.Tools.i_histo_match(input, suffix="match", output=None, database=None, max=255, nprocs=0, overwrite=None, verbose=None, quiet=None, superquiet=None)
Example:
tools = Tools()
tools.i_histo_match(input="name")
This grass.tools API is experimental in version 8.5 and expected to be stable in version 8.6.
Parameters
input=name [,name,...] [required]
Name of raster maps to be analyzed
suffix=string
Suffix for output maps
Default: match
output=name
Name for mosaic output map
database=name
DEPRECATED, do not use
max=integer
Number of the maximum value for raster maps
Default: 255
nprocs=integer
Number of threads for parallel computing
0: use OpenMP default; >0: use nprocs; <0: use MAX-nprocs
Default: 0
--overwrite
Allow output files to overwrite existing files
--help
Print usage summary
--verbose
Verbose module output
--quiet
Quiet module output
--qq
Very quiet module output
--ui
Force launching GUI dialog
input : str | list[str], required
Name of raster maps to be analyzed
Used as: input, raster, name
suffix : str, optional
Suffix for output maps
Used as: 1
Default: match
output : str, optional
Name for mosaic output map
Used as: output, raster, name
database : str, optional
DEPRECATED, do not use
Used as: input, dbname, name
max : int, optional
Number of the maximum value for raster maps
Used as:
Default: 255
nprocs : int, optional
Number of threads for parallel computing
0: use OpenMP default; >0: use nprocs; <0: use MAX-nprocs
Default: 0
overwrite : bool, optional
Allow output files to overwrite existing files
Default: None
verbose : bool, optional
Verbose module output
Default: None
quiet : bool, optional
Quiet module output
Default: None
superquiet : bool, optional
Very quiet module output
Default: None
input : str | list[str], required
Name of raster maps to be analyzed
Used as: input, raster, name
suffix : str, optional
Suffix for output maps
Used as: 1
Default: match
output : str | type(np.ndarray) | type(np.array) | type(gs.array.array), optional
Name for mosaic output map
Used as: output, raster, name
database : str, optional
DEPRECATED, do not use
Used as: input, dbname, name
max : int, optional
Number of the maximum value for raster maps
Used as:
Default: 255
nprocs : int, optional
Number of threads for parallel computing
0: use OpenMP default; >0: use nprocs; <0: use MAX-nprocs
Default: 0
overwrite : bool, optional
Allow output files to overwrite existing files
Default: None
verbose : bool, optional
Verbose module output
Default: None
quiet : bool, optional
Quiet module output
Default: None
superquiet : bool, optional
Very quiet module output
Default: None
Returns:
result : grass.tools.support.ToolResult | np.ndarray | tuple[np.ndarray] | None
If the tool produces text as standard output, a ToolResult object will be returned. Otherwise, None will be returned. If an array type (e.g., np.ndarray) is used for one of the raster outputs, the result will be an array and will have the shape corresponding to the computational region. If an array type is used for more than one raster output, the result will be a tuple of arrays.
Raises:
grass.tools.ToolError: When the tool ended with an error.
DESCRIPTION
i.histo.match performs histogram matching on the given input images.
NOTES
The histogram matching method is based on the method Cumulative Distribution Function (CDF) of two or more histograms. Each value of original CDF is compared with the target histogram in order to obtain the target CDF value closest to the original value.
EXAMPLE
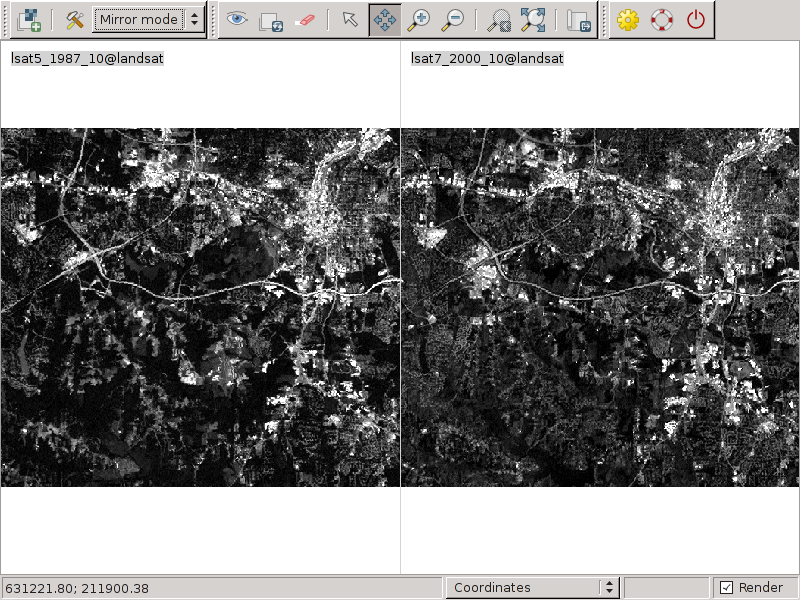
This example is based the North Carolina GRASS sample data set (complete GRASS dataset).
# create the output with histogram matching
i.histo.match input=lsat5_1987_10,lsat7_2000_10
# set grey color to the new maps
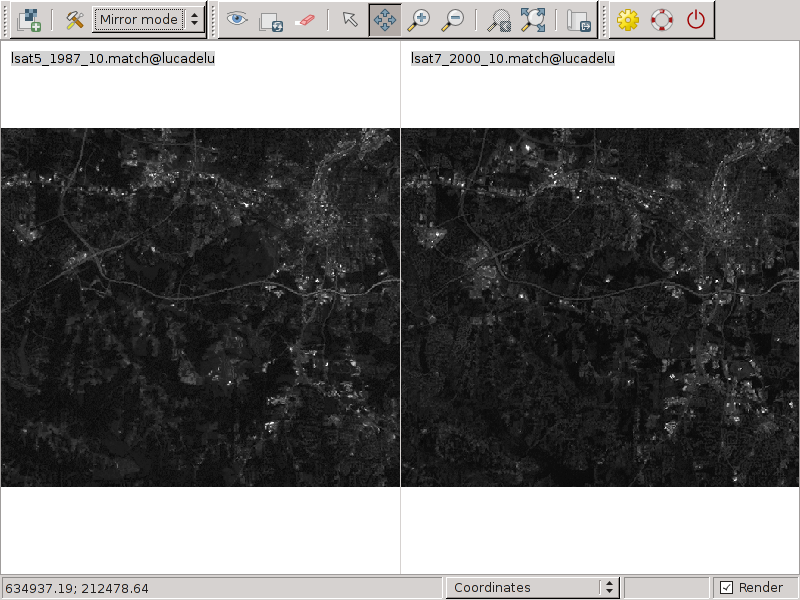
r.colors map=lsat5_1987_10.match color=grey
r.colors map=lsat7_2000_10.match color=grey
# visualize and compare the results
Original data
Matched data
SEE ALSO
AUTHORS
Laura Zampa 2004, student of Dipartimento di Informatica e Telecomunicazioni, Facolta' di Ingegneria, University of Trento and ITC-irst, Trento (Italy); original PERL code
Luca Delucchi, Fondazione E. Mach (Italy); implementation with Python / SQLite
Stefan Blumentrath (Norway); current, parallelized implementation with Numpy
SOURCE CODE
Available at: i.histo.match source code
(history)
Latest change: Friday Feb 21 12:27:42 2025 in commit 8fce680